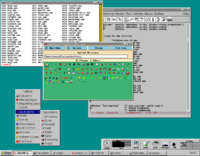
The Common Desktop Environment (CDE) is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit. It was part of the UNIX 98 Workstation Product Standard, and was for a long time the Unix desktop associated with commercial Unix workstations. It helped to influence early implementations of successor projects such as KDE and GNOME, which largely replaced CDE following the turn of the century.

Debian, also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software and optionally non-free firmware or software developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of Debian (0.01) was released on September 15, 1993, and its first stable version (1.1) was released on June 17, 1996. The Debian Stable branch is the most popular edition for personal computers and servers. Debian is also the basis for many other distributions that have different purposes, like Proxmox for servers, Ubuntu or Linux Mint for desktops, Kali for penetration testing, and Pardus and Astra for government use.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

An X window manager is a window manager that runs on top of the X Window System, a windowing system mainly used on Unix-like systems.

Xfce or XFCE is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.

IceWM is a stacking window manager for the X Window System, originally written by Marko Maček. It was written from scratch in C++ and is released under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License. It is customizable, relatively lightweight in terms of memory and CPU usage, and comes with themes that allow it to imitate the GUI of Windows 95, Windows XP, Windows 7, OS/2, Motif, and other graphical user interfaces.
4Dwm is the window manager component of the IRIX Interactive Desktop normally used on Silicon Graphics workstations running IRIX. 4Dwm is derived from the older Motif Window Manager and uses the Motif widget toolkit on top of the X Window System found on most Unix systems. 4Dwm on IRIX was one of the first default graphical user interface desktops to be standard on a Unix computer system. 4Dwm refers to "Fourth dimension window manager" and has no relation to dwm.

The F Virtual Window Manager (FVWM) is a virtual window manager for the X Window System. Originally a twm derivative, FVWM has evolved into a powerful and highly configurable environment for Unix-like systems.
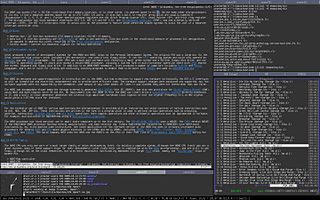
In Unix computing, Ion is a tiling and tabbing window manager for the X Window System. It is designed such that it is possible to manage windows using only a keyboard, without needing a mouse. It is the successor of PWM and is written by the same author, Tuomo Valkonen. Since the first release of Ion in the summer 2000, similar alternative window management ideas have begun to show in other new window managers: Larswm, ratpoison, StumpWM, wmii, xmonad and dwm.
HFS Plus or HFS+ is a journaling file system developed by Apple Inc. It replaced the Hierarchical File System (HFS) as the primary file system of Apple computers with the 1998 release of Mac OS 8.1. HFS+ continued as the primary Mac OS X file system until it was itself replaced with the Apple File System (APFS), released with macOS High Sierra in 2017. HFS+ is also one of the formats supported by the iPod digital music player.
Puppy Linux is a family of light-weight Linux distributions that focus on ease of use and minimal memory footprint. The entire system can be run from random-access memory (RAM) with current versions generally taking up about 600 MB (64-bit), 300 MB (32-bit), allowing the boot medium to be removed after the operating system has started. Applications such as AbiWord, Gnumeric and MPlayer are included, along with a choice of lightweight web browsers and a utility for downloading other packages. The distribution was originally developed by Barry Kauler and other members of the community, until Kauler retired in 2013. The tool Woof can build a Puppy Linux distribution from the binary packages of other Linux distributions.

JOE or Joe's Own Editor is an ncurses-based text editor for Unix systems, available under the GPL. It is designed to be easy to use.
gtkmm is the official C++ interface for the popular GUI library GTK. gtkmm is free software distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).

JWM is a lightweight stacking window manager for the X Window System written by Joe Wingbermuehle. JWM is written in C and uses only Xlib at a minimum. Configuration is done by editing an XML file; no graphical configuration is necessary or supplied.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy.

LXDE is a free desktop environment with comparatively low resource requirements. This makes it especially suitable for use on older or resource-constrained personal computers such as netbooks or system on a chip computers.

Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu, bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications. It can provide full out-of-the-box multimedia support for those who choose to include proprietary software such as multimedia codecs. Compared to standard Ubuntu, it uses the Cinnamon interface in the most popular edition, using a different, more traditional layout that can be customized by dragging the applets and creating panels. New applets can also be downloaded.
This article compares variety of different X window managers. For an introduction to the topic, see X Window System.

antiX is a Linux distribution, originally based on MEPIS, which itself is based on the Debian stable distribution. antiX initially replaced the MEPIS KDE desktop environment with the Fluxbox and IceWM window managers, making it suitable for older, less powerful x86-based systems. Unlike Debian, antiX does not use the systemd init system, instead, antiX provides images in which either SysVinit or Runit are set as the default init system.

Qvwm is a window manager, intended as a reimplementation of the Windows 95 interface for Linux systems. Released in 1996 under the GNU General Public License. The project's name comes from wordplay references to Japanese words and Roman numbers. In 2000, Linux Format called Qvwm "an unusually impressive imposter".