Concurrent Versions System is a revision control system originally developed by Dick Grune in July 1986.
In software engineering, version control is a class of systems responsible for managing changes to computer programs, documents, large web sites, or other collections of information. Version control is a component of software configuration management.

Apache Subversion is a software versioning and revision control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS).

Advanced Package Tool, or APT, is a free-software user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on Debian, Ubuntu, and related Linux distributions. APT simplifies the process of managing software on Unix-like computer systems by automating the retrieval, configuration and installation of software packages, either from precompiled files or by compiling source code.

KDevelop is a free and open-source integrated development environment (IDE) for Unix-like computer operating systems and Windows. It provides editing, navigation and debugging features for several programming languages, and integration with build automation and version-control systems, using a plugin-based architecture.

Quanta Plus, originally called Quanta, is a web Integrated development environment (IDE) for HTML, XHTML, CSS, XML, PHP and any other XML-based languages or scripting languages. Quanta was licensed under GPL before the release of version 2.0 final.

JuK is a free software audio player by KDE, the default player since K Desktop Environment 3.2. JuK supports collections of MP3, Ogg Vorbis, and FLAC audio files.

Monotone is an open source software tool for distributed revision control.

Git is software for tracking changes in any set of files, usually used for coordinating work among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows.
SuperKaramba is a tool, a so-called widget engine, that allows the creation of functionality enhancement modules on the KDE desktop. The desktop widgets are usually embedded directly into the background and do not disturb the normal view of the desktop. The use of SuperKaramba is not limited to KDE, but certain libraries from KDE are required. SuperKaramba had been included in KDE since version 3.5. SuperKaramba is similar to gDesklets for GNOME. The name derives from Portuguese and Spanish super caramba, meaning approximately "super wow" or "super cool".
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of notable file managers.
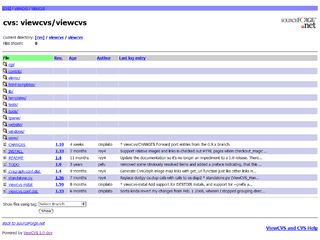
ViewVC is an open-source tool for viewing the contents of CVS and SVN repositories using a web browser. It allows looking at specific revisions of files as well as side-by-side diffs of different revisions. It is written in Python and the view parameters can be modified directly in a URL using a REST style interface.

KDE Software Compilation 4 was the only series of the so-called KDE Software Compilation, first released in January 2008 and the last release being 4.14.3 released in November 2014. It was the follow-up to K Desktop Environment 3. Following KDE SC 4, the compilation was broken up into basic framework libraries, desktop environment and applications, which are termed KDE Frameworks 5, KDE Plasma 5 and KDE Applications, respectively.
The FreeBSD Ports collection is a package management system for the FreeBSD operating system, providing an easy and consistent way of installing software packages. As of February 2020, there are over 38,487 ports available in the collection. It has also been adopted by NetBSD as the basis of its pkgsrc system.

KDE Platform 4 was a collection of libraries and software frameworks by KDE that served as technological foundation for KDE Software Compilation 4 distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). KDE Platform 4 was the successor to KDElibs and the predecessor of KDE Frameworks. KDE Platform 4 is the only version of KDE Platform, see KDE’s brand repositioning.
The following is a comparison of version-control software. The following tables include general and technical information on notable version control and software configuration management (SCM) software. For SCM software not suitable for source code, see Comparison of open-source configuration-management software.
The Embeddable Linux Kernel Subset (ELKS), formerly known as Linux-8086, is a Linux-like operating system kernel. It is a subset of the Linux kernel, intended for 16-bit computers with limited processor and memory resources such as machines powered by Intel 8086 and compatible microprocessors not supported by 32-bit Linux.

KOffice is an unmaintained free and open source office suite and graphics suite by KDE for Unix-like systems and Windows. KOffice contains a word processor (KWord), a spreadsheet (KSpread), a presentation program (KPresenter), and a number of other components that varied over the course of KOffice's development.

The KDE Gear is a set of applications and supporting libraries that are developed by the KDE community, primarily used on Linux-based operating systems but mostly multiplatform, and released on a common release schedule.













