Related Research Articles

A multiple-document interface (MDI) is a graphical user interface in which multiple windows reside under a single parent window. Such systems often allow child windows to embed other windows inside them as well, creating complex nested hierarchies. This contrasts with single-document interfaces (SDI) where all windows are independent of each other.

An X window manager is a window manager that runs on top of the X Window System, a windowing system mainly used on Unix-like systems.
In computing, a window is a graphical control element. It consists of a visual area containing some of the graphical user interface of the program it belongs to and is framed by a window decoration. It usually has a rectangular shape that can overlap with the area of other windows. It displays the output of and may allow input to one or more processes.

Swing is a GUI widget toolkit for Java. It is part of Oracle's Java Foundation Classes (JFC) – an API for providing a graphical user interface (GUI) for Java programs.

File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application and default desktop environment that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems, as well as user interface elements such as the taskbar and desktop.
The taskbar is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, displaying and facilitating switching between running programs. The taskbar and the associated Start Menu were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

Aqua is the graphical user interface, design language and visual theme of Apple's macOS and iOS operating systems. It was originally based on the theme of water, with droplet-like components and a liberal use of reflection effects and translucency. Its goal is to "incorporate color, depth, translucence, and complex textures into a visually appealing interface" in macOS applications. At its introduction, Steve Jobs noted that "... it's liquid, one of the design goals was when you saw it you wanted to lick it".

A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction with the underlying graphical system that provides required functionality—support for graphics hardware, pointing devices, and a keyboard—and are often written and created using a widget toolkit.
In computing, the X Window System is a network-transparent windowing system for bitmap displays. This article details the protocols and technical structure of X11.

A menu bar is a graphical control element which contains drop-down menus.

In the X Window System, a window is the region of the screen where drawing can occur. The root window covers the entire screen surface. Every window created is contained within it, forming a hierarchy with the root window at the very top. All other windows are either children or descendants of it.

In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with the organization of the screen often dependant on mathematical formulas to organise the windows into a non-overlapping frame. This is opposed to the more common approach used by stacking window managers, which allow the user to drag windows around, instead of windows snapping into a position. This allows for a different style of organization, although it strays from the traditional desktop metaphor.

Tkinter is a Python binding to the Tk GUI toolkit. It is the standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit, and is Python's de facto standard GUI. Tkinter is included with standard Linux, Microsoft Windows and macOS installs of Python.
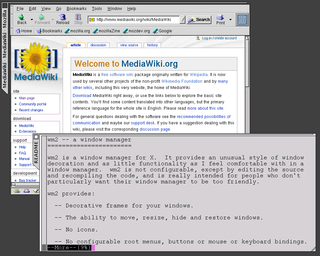
wm2 is a minimalist reparenting window manager for the X Window System written by Chris Cannam.
The X Window System core protocol is the base protocol of the X Window System, which is a networked windowing system for bitmap displays used to build graphical user interfaces on Unix, Unix-like, and other operating systems. The X Window System is based on a client–server model: a single server controls the input/output hardware, such as the screen, the keyboard, and the mouse; all application programs act as clients, interacting with the user and with the other clients via the server. This interaction is regulated by the X Window System core protocol. Other protocols related to the X Window System exist, both built at the top of the X Window System core protocol or as separate protocols.
A compositing manager, or compositor, is software that provides applications with an off-screen buffer for each window. The compositing manager composites the window buffers into an image representing the screen and writes the result into the display memory. A compositing window manager is a window manager that is also a compositing manager.

dwm is a minimalist dynamic window manager for the X Window System developed by Suckless that has influenced the development of several other X window managers, including xmonad and awesome. It is externally similar to wmii, but internally much simpler. dwm is written purely in C for performance and lacks any configuration interface besides editing the source code. One of the project's guidelines is that the source code is intended never to exceed 2000 SLOC, and options meant to be user-configurable are all contained in a single header file.
An NTFS reparse point is a type of NTFS file system object. It is available with the NTFS v3.0 found in Windows 2000 or later versions. Reparse points provide a way to extend the NTFS filesystem. A reparse point contains a reparse tag and data that are interpreted by a filesystem filter driver identified by the tag. Microsoft includes several default tags including NTFS symbolic links, directory junction points, volume mount points and Unix domain sockets. Also, reparse points are used as placeholders for files moved by Windows 2000's Remote Storage Hierarchical Storage System. They also can act as hard links, but are not limited to pointing to files on the same volume: they can point to directories on any local volume. The feature is inherited to ReFS.
NTFS links are the abstraction used in the NTFS file system—the default file system for all Microsoft Windows versions belonging to the Windows NT family—to associate pathnames and certain kinds of metadata, with entries in the NTFS Master File Table (MFT). NTFS broadly adopts a pattern akin to typical Unix file systems in the way it stores and references file data and metadata; the most significant difference is that in NTFS, the MFT "takes the place of" inodes, fulfilling most of the functions which inodes fulfill in a typical Unix filesystem.
Client-side decoration (CSD) is the concept of allowing a graphical application software to be responsible for drawing its own window decorations, historically the responsibility of the window manager.
References
- ↑ Xlib Programming Manual Chapter 10 Archived 2013-04-30 at the Wayback Machine
