
Paul David Heaton is an English singer-songwriter. He was the lead singer and main lyricist of the Housemartins, who had commercial success in the UK and other European countries between 1985 and 1988, releasing several singles including "Happy Hour" and the UK number-one single "Caravan of Love" in 1986, before the band disbanded. Heaton then formed the Beautiful South with the Housemartins' drummer, Dave Hemingway, and the band's debut single, "Song for Whoever", and debut album, Welcome to the Beautiful South, were released in 1989 to commercial success. They had a series of hits throughout the 1990s, including the number-one single "A Little Time". They disbanded in 2007.

The Housemartins were an English indie rock group formed in Hull who were active in the 1980s and charted three top-ten albums and six top-twenty singles in the UK. Many of their lyrics conveyed a mixture of socialist politics and Christianity, reflecting the beliefs of the band. The group's a cappella cover version of "Caravan of Love" was a UK number one single in December 1986.

The Findhorn Foundation is a Scottish charitable trust registered in 1972, formed by the spiritual community at the Findhorn Ecovillage, one of the largest intentional communities in Britain. It has been home to thousands of residents from more than 40 countries. The Foundation closed all its educational programmes in September 2023 whereas the Findhorn community eco village at Findhorn houses about 40 community businesses such as the Findhorn Press and an alternative medicine centre.

Japantown, Little Tokyo or Paueru-gai is an old neighbourhood in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, located east of Gastown and north of Chinatown, that once had a concentration of Japanese immigrants.
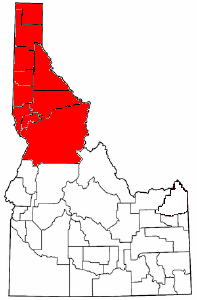
The Idaho panhandle—locally known as North Idaho, Northern Idaho, or simply the Panhandle—is a salient region of the U.S. state of Idaho encompassing the state's 10 northernmost counties: Benewah, Bonner, Boundary, Clearwater, Idaho, Kootenai, Latah, Lewis, Nez Perce, and Shoshone. The panhandle is bordered by the state of Washington to the west, Montana to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. The Idaho panhandle, along with Eastern Washington, makes up the region known as the Inland Northwest, headed by its largest city, Spokane, Washington.

Murphy is a census-designated place in, and the county seat of, Owyhee County, Idaho, United States. It is among the smallest of county seats nationwide, with a population as of the 2020 census of 96. Murphy is part of the Boise City–Nampa, Idaho Metropolitan Statistical Area. Murphy is also located within the census-designated place bearing its name. Murphy is home to the Owyhee County Historical Museum and Library.
Anyox was a small company-owned mining town in British Columbia, Canada. Today it is a ghost town, abandoned and largely destroyed. It is located on the shores of Granby Bay in coastal Observatory Inlet, about 60 kilometres southeast of Stewart, British Columbia, and about 20 kilometres, across wilderness east of the tip of the Alaska Panhandle.

Princess Royal Island is the largest island on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. It is located amongst the isolated inlets and islands east of Hecate Strait on the British Columbia Coast. At 2,251 square kilometres (869 sq mi), it is the fourth largest island in British Columbia. It was named in 1788 by Captain Charles Duncan, after his ship Princess Royal.
Nancy Argenta is a Canadian soprano singer, best known for performing music from the pre-classical era. She has won international acclaim, and is considered one of the leading Handel sopranos of her time.

The Moyie is a paddle steamer sternwheeler that operated on Kootenay Lake in British Columbia from 1898 until 1957.

Cascade City or Cascade was a Canadian Pacific Railway construction era boom town in the Boundary Country of the West Kootenay region of British Columbia, Canada. Because of its location near the Canada–United States border, it was also called the "Gateway to the Boundary Country".
Silver Centre is a ghost town in Timiskaming District, Northeastern Ontario, Canada, situated in South Lorrain Township. It is located approximately 35 km (22 mi) south of North Cobalt, and 3 km (1.9 mi) west of Highway 567. Silver Centre was a secondary camp to the great silver fields of Cobalt, discovered in 1903. There are no current residents in Silver Centre. It is still an active mineral field and does at times have active mineral exploration.

Helvetia is a ghost town in Pima County, Arizona, United States that was settled in 1891 and abandoned in the early 1920s. Helvetia is an ancient name for Switzerland. Today, only the Ray Mine and cemetery are visitable, as the rest of the town has been fenced off due to active mining operations.

Harshaw is a ghost town in Santa Cruz County in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Arizona. The town was settled in the 1870s, in what was then Arizona Territory. Founded as a mining community, Harshaw is named after the cattleman-turned-prospector David Tecumseh Harshaw, who first successfully located silver in the area. At the town's peak near the end of the 19th century, Harshaw's mines were among Arizona's highest producers of ore, with the largest mine, the Hermosa, yielding approximately $365,455 in bullion over a four-month period in 1880.
Brexton, formerly known as Fish Lake, is a ghost town located in the Bridge River Country region of British Columbia. Although the provincial Gazetteer still lists the "settlement" of Brexton, which was situated between the southeast end of Gun Lake and Gold Bridge, and three and a half miles north of Bralorne, this once busy town has mostly vanished though a few buildings remain. The old town site now sits mainly on private property.

Michael Cheng is a Canadian entrepreneur. Cheng co-founded Lumen5, Sniply, Beta Collective, Covr, Needle HR, WittyCookie, TEDxSFU, and 12 other ventures.

Jumbo Glacier, also known as Jumbo, was a mountain resort municipality within the Regional District of East Kootenay in southeast British Columbia, Canada between 2013 and 2021. It was approximately 55 km (34 mi) west of Invermere near the Commander Glacier and around the headwaters of Jumbo Creek in the Purcell Range of the Columbia Mountains.
Somerset Green is a gated community in Houston, Texas, developed by Hines Interests Limited Partnership. Nancy Sarnoff of the Houston Chronicle described Somerset Green as "a European-style residential development". Preston Wood & Associates was the land planner of the development.
The Kootenay Land District is a cadastral survey subdivision of the province of British Columbia, Canada, created with rest of those on Mainland British Columbia via the Lands Act of the Colony of British Columbia in 1860. The British Columbia government's BC Names system, a subdivision of GeoBC, defines a land district as "a territorial division with legally defined boundaries for administrative purposes" All land titles and surveys use the Land District system as the primary point of reference, and entries in BC Names for placenames and geographical objects are so listed.

Huskar Pit was a coal mine on the South Yorkshire Coalfield, sunk to work the Silkstone seam. It was located in Nabs Wood, outside the village of Silkstone Common, in the then West Riding of Yorkshire. It was connected to the Barnsley Canal by the Silkstone Waggonway. Huskar was the scene of a notorious pit disaster in 4 July 1838.














