
Sargon II was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III, Sargon is generally believed to have become king after overthrowing Shalmaneser V, probably his brother. He is typically considered the founder of a new dynastic line, the Sargonid dynasty.

Argishti I, was the sixth known king of Urartu, reigning from 786 BC to 764 BC. He founded the citadel of Erebuni in 782 BC, which is the present capital of Armenia, Yerevan. Alternate transliterations of the name include Argishtis, Argisti, Argišti, and Argishtish. Although the name is usually rendered as Argišti, some scholars argue that Argisti is the most likely pronunciation. This is due to the belief that the Urartians used the cuneiform symbol š to voice an s-sound, as opposed to representing the digraph sh.

Teishebaini was the capital of the Transcaucasian provinces of the ancient kingdom of Urartu. It is located near the modern city of Yerevan in Armenia. The site was once a fortress and governmental centre with towered and buttressed perimeter walls, massive gates, a parade ground within its walls, and storage rooms that entirely occupied the ground floor. The site of the city, palace and citadel together measure over 0.45 km2. The name Karmir Blur translates to "Red Hill" because of the hill's reddish hue. It became this color after the city was set on fire and the upper walls which were made of tuff fell and crumbled because of the heat. After the tuff was heated by the fire, it took on a more intense red color and therefore the hill became red. The lower portions of the walls were left standing after the fire since they were built with a stronger stone. Teishebaini is situated at a height of 901 metres (2,956 ft).
Rusa I was a King of Urartu. He succeeded his father, king Sarduri II. His name is sometimes transliterated as Rusas or Rusha. He was known to Assyrians as Ursa and possibly Urzana. His birth name may have been Uedipri.

Muṣaṣir, in Urartian Ardini was an ancient city of Urartu, attested in Assyrian sources of the 9th and 8th centuries BC.
Shubria or Shupria was a kingdom in the southern Armenian highlands, known from Assyrian sources in the first half of the 1st millennium BC. It was located north of the upper Tigris River and to the southwest of Lake Van, extending eastwards to the frontiers of Urartu. It appears in the 1st millennium BC as an independent kingdom, succeeding the people earlier called Shubaru in Assyrian sources in the later centuries of the 2nd millennium BC. It was located between the powerful states of Assyria and Urartu and came into conflict with both. It was conquered by Assyria in 673–672 BC but likely regained its independence towards the end of the 7th century BC with the collapse of Assyrian power.

During the Middle Assyrian Empire and the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Phoenicia, what is today known as Lebanon and coastal Syria, came under Assyrian rule on several occasions.
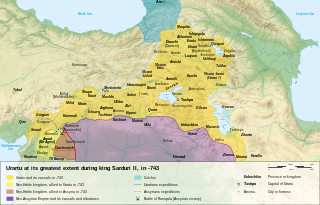
Sarduri II was a King of Urartu, succeeding his father Argishti I to the throne. The Urartian Kingdom was at its peak during his reign, campaigning successfully against several neighbouring powers, including Assyria.
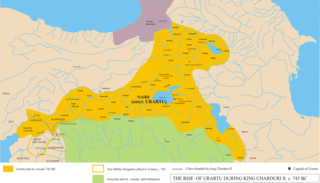
The Urartu–Assyria War was a conflict between the Kingdom of Urartu and the Neo-Assyrian Empire. The war began around 714 BC, with the invasion of Urartu by the Assyrian King Sargon II. Sargon led multiple offensives deep into Urartian territory, amassing numerous victories in the war. Following his death, however, Urartian Kings Argishti II and Rusa II launched many successful counterattacks, reclaiming Urartu's lost territory and gaining some from Assyria. However, their successors suffered multiple major defeats, resulting in Urartu becoming an Assyrian client state.
Shamshi-ilu (Šamši-ilu) was an influential court dignitary and commander in chief (turtanu) of the Assyrian army who rose in high prominence.

Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and the Republic of Armenia. Its kings left behind cuneiform inscriptions in the Urartian language, a member of the Hurro-Urartian language family. These languages might have been related to Northeast Caucasian languages. Following Armenian incursions into Urartu, Armenians "imposed their language" on Urartians and became the aristocratic class. The Urartians later "were probably absorbed into the Armenian polity".
Išpakāya was a Scythian king who ruled during the period of the Scythian presence in Western Asia in the 7th century BCE.
The economy of Urartu refers to the principles of management of Urartu, the ancient state of Western Asia which existed from the thirteenth to the sixth century BC. It peaked around the eighth century BC but was destroyed with the fall of the state about a century later. The economy of Urartu was typical of ancient Oriental Despotism and was closely associated with that of neighboring Assyria.

The prehistory of Anatolia stretches from the Paleolithic era through to the appearance of classical civilisation in the middle of the 1st millennium BC. It is generally regarded as being divided into three ages reflecting the dominant materials used for the making of domestic implements and weapons: Stone Age, Bronze Age and Iron Age. The term Copper Age (Chalcolithic) is used to denote the period straddling the stone and Bronze Ages.

Argištiḫinili was a town in the ancient kingdom of Urartu, established during the expansion of the Urartians in the Transcaucasus under their king Argishti I, and named in his honour. It lasted between the 8th and 6th centuries BC. The ruins of the Argištiḫinili fortifications are 15 kilometres (9 mi) southwest of the present-day town of Armavir, Armenia, between the villages of Nor-Armavir and Armavir in the Armenian marz of Armavir. The town was founded on the left bank of the middle reaches of the Aras River. Over the centuries, the river channel has shifted to several kilometres south of the town.

The timeline of ancient Assyria can be broken down into three main eras: the Old Assyrian period, Middle Assyrian Empire, and Neo-Assyrian Empire. Modern scholars typically also recognize an Early period preceding the Old Assyrian period and a post-imperial period succeeding the Neo-Assyrian period.

The Sargonid dynasty was the final ruling dynasty of Assyria, ruling as kings of Assyria during the Neo-Assyrian Empire for just over a century from the ascent of Sargon II in 722 BC to the fall of Assyria in 609 BC. Although Assyria would ultimately fall during their rule, the Sargonid dynasty ruled the country during the apex of its power and Sargon II's three immediate successors Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal are generally regarded as three of the greatest Assyrian monarchs. Though the dynasty encompasses seven Assyrian kings, two vassal kings in Babylonia and numerous princes and princesses, the term Sargonids is sometimes used solely for Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal.
Etiuni was the name of an early Iron Age tribal confederation in northern parts of Araxes River, roughly corresponding to the subsequent Ayrarat Province of the Kingdom of Armenia. Etiuni was frequently mentioned in the records of Urartian kings, who led numerous campaigns into Etiuni territory. It is very likely it was the "Etuna" or "Etina" which contributed to the fall of Urartu, according to Assyrian texts. Some scholars believe it had an Armenian-speaking population.

Urartian religion is a belief system adopted in the ancient state of Urartu, which existed from the 8th to 6th centuries BC. It was typical of despotic states from the Near East. The Urartian religion was polytheistic in nature and derived from the earlier beliefs of Mesopotamia and Anatolia. As in other beliefs of the ancient Near East, Urartu had a pantheon of deities, patronizing various phenomena. The main deity was Haldi. The worlds of humans and gods were united through ritual sacrifices. The Urartian religion absorbed the motifs of the tree of life, the serpent and the winged solar disk characteristic of the ancient Near East. Against the background of Mesopotamian beliefs, Urartu was distinguished by a high level of religious tolerance, which was conditioned by the multinationality of the state.












