
The Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina is the official military force of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The BiH armed forces were officially unified in 2005 and are composed of two founding armies: the Bosniak and Croat Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (VFBiH) and the Bosnian Serbs' Army of Republika Srpska (VRS).

The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two entities composing Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina consists of ten autonomous cantons with their own governments and legislatures.

The Bosnian War was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started on 6 April 1992, following a number of earlier violent incidents. The war ended on 14 December 1995 when the Dayton accords were signed. The main belligerents were the forces of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, and the Republika Srpska, the latter two entities being proto-states led and supplied by Croatia and Serbia, respectively.

Blaž Nikola Kraljević was a Bosnian Croat paramilitary leader who commanded the Croatian Defence Forces (HOS) during the Bosnian War. An immigrant to Australia, Kraljević joined the Croatian Revolutionary Brotherhood (HRB) upon his arrival there in 1967. During his return to Yugoslavia in January 1992 he was appointed by Dobroslav Paraga, leader of the Croatian Party of Rights (HSP), as leader of the HOS in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was a state in Southeastern Europe, existing from 1992 to 1995. It is the direct legal predecessor to the modern-day state of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, often referred to as Bosnian Army or Bosniak Army, was the military force of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was established by the government of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1992 following the outbreak of the Bosnian War.

The Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia was an unrecognized geopolitical entity and quasi-state in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was proclaimed on 18 November 1991 under the name Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia as a "political, cultural, economic and territorial whole" in the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and abolished on 14 August 1996.
Atif Dudaković is a retired Bosniak general who served in the Army of Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. During the Bosnian War, Dudaković was in command of the Bihać enclave, which was surrounded and besieged from 1992 to 1995, commanding the 5th Corps. After the war he became the general commander of the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. In 2018, he was charged with war crimes.

The Croatian Defence Council was the official military formation of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, an unrecognized state that existed in the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1991 and 1996. The HVO was the main military force of the Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, often referred to as Bosnian Croats or Herzegovinian Croats, are native and the third most populous ethnic group in Bosnia and Herzegovina, after Bosniaks and Serbs, and are one of the constitutive nations of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina have made significant contributions to the culture of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Most Croats declare themselves Catholics and speakers of the Croatian language.

The Croat–Bosniak War was a conflict between the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, supported by Croatia, that lasted from 18 October 1992 to 23 February 1994. It is often referred to as a "war within a war" because it was part of the larger Bosnian War. In the beginning, the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) fought together in an alliance against the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS). By the end of 1992, however, tensions between Bosniaks and Bosnian Croats increased. The first armed incidents between them occurred in October 1992 in central Bosnia. The military alliance continued until early 1993, when it mostly fell apart and the two former allies engaged in open conflict.

Selmo Cikotić is a Bosnian politician who served as Minister of Security from 2020 to 2023. He was also the Minister of Defence from 2007 to 2012. He is a member of the Party of Democratic Action.
Operation Vrbas '92 was a military offensive undertaken by the Army of Republika Srpska in June–October 1992, during the Bosnian War. The goal of the operation was the destruction of a salient around the central Bosnian town of Jajce, which was held by the Croatian Defence Council and the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The intensity of fighting varied considerably and involved several major VRS offensive efforts interspersed by relative lulls in fighting. Jajce fell to the VRS on 29 October 1992, and the town's capture was followed by the destruction of all its mosques and Roman Catholic churches.

The Croat–Bosniak War was a conflict between the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia, supported by Croatia, that lasted from 19 June 1992 – 23 February 1994. The Croat-Bosniak War is often referred to as a "war within a war" because it was part of the larger Bosnian War.

The Siege of Mostar was fought during the Bosnian War first in 1992 and then again later in 1993 to 1994. Initially lasting between April 1992 and June 1992, it involved the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) and the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) fighting against the Serb-dominated Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) after Bosnia and Herzegovina declared its independence from Yugoslavia. That phase ended in June 1992 after the success of Operation Jackal, launched by the Croatian Army (HV) and HVO. As a result of the first siege around 90,000 residents of Mostar fled and numerous religious buildings, cultural institutions, and bridges were damaged or destroyed.

The Split Agreement or Split Declaration was a mutual defence agreement between Croatia, the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, signed in Split, Croatia on 22 July 1995. It called on the Croatian Army (HV) to intervene militarily in Bosnia and Herzegovina, primarily in relieving the siege of Bihać.
The Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia was signed by Alija Izetbegović, President of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Franjo Tuđman, President of the Republic of Croatia, in Zagreb on 21 July 1992 during the Bosnian and Croatian wars for independence from Yugoslavia. It established cooperation, albeit inharmonious, between the two and served as a basis for joint defense against Serb forces. It also placed the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) under the command of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH).
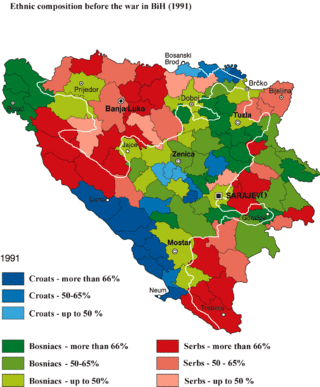
A Bosniak republic, or Bosniak entity, was proposed during the Bosnian War when plans for the partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina were made. It would either be established as one of three ethnic states in a loose confederation, or as an independent "Bosniak state" in the area controlled by the Bosnian Army, as unofficially proposed by some Bosniak leaders. Thus, the Bosniak-inhabited territories or Bosnian Army-controlled area would become a Bosniak state, as Republika Srpska was for the Bosnian Serbs and Herzeg-Bosnia for the Bosnian Croats. The failed 1992 Serb–Croat Graz agreement would see a small Bosniak buffer state, pejoratively called "Alija's Pashaluk" on a map displayed during the discussions. The Owen-Stoltenberg plan would give Bosniaks 30% of territory, including ca. 65% of the Bosniak population .The Dayton Agreement ended the war and created the federal republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH), made up of two entities, the Bosniak and Croat-inhabited Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (FBiH), and the Serb-inhabited Republika Srpska (RS). As noted by international relations expert Niels van Willigen: "Whereas the Bosnian Croats and Bosnian Serbs could identify themselves with Croatia or Serbia respectively, the absence of a Bosniak state made the Bosniaks firmly committed to Bosnia as a single political entity."
The Battle of Bugojno was fought between forces of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) and the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) for control of the town and municipality of Bugojno in central Bosnia, from 18–28 July 1993. The area of Bugojno was under joint control of the ARBiH 307th Brigade and the HVO Eugen Kvaternik Brigade since the start of the Bosnian War. Violent incidents in Bugojno followed the escalation of the Croat-Bosniak War in adjacent municipalities throughout the 1st half of 1993. Bugojno was spared from fighting and the two local brigades were still formally allied by June 1993, at the time of an ARBiH offensive in central Bosnia.
The Musala camp was a prison camp in Konjic, Bosnia and Herzegovina operated by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) that was used to detain Bosnian Serbs and Bosnian Croats.














