This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2016) |
Arrow diagramming method (ADM) is a network diagramming technique in which activities are represented by arrows. [1] ADM is also known as the activity-on-arrow (AOA) method.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2016) |
Arrow diagramming method (ADM) is a network diagramming technique in which activities are represented by arrows. [1] ADM is also known as the activity-on-arrow (AOA) method.
ADM is used for scheduling activities in a project plan. Precedence relationships between activities are represented by circles connected by one or more arrows. The length of the arrow represents the duration of the relevant activity. ADM only shows finish-to-start relationships, meaning that each activity is completed before the successor activity starts.
Sometimes a "dummy task" is added, to represent a dependency between tasks, which does not represent any actual activity. The dummy task is added to indicate precedence that can't be expressed using only the actual activities. Such a dummy task often has a completion time of 0.
Use of ADM as a common project management practice has declined with the adoption of computer-based scheduling tools. In addition, the precedence diagram method (PDM), or activity-on-node (AON), is often favored over ADM. [2]
ADM network drawing technique the start and end of each node or event is connected to an arrow.
The start of the arrow comes out of a node while the tip of the arrow goes into a node. Between the two nodes lies an arrow that represents the activity.
The event represented by the circular node consumes neither time nor resources.
Project planning is part of project management, which relates to the use of schedules such as Gantt charts to plan and subsequently report progress within the project environment. Project planning can be done manually or by the use of project management software.
Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a method of planning and managing projects that emphasizes the resources required to execute project tasks. It was developed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt. It differs from more traditional methods that derive from critical path and PERT algorithms, which emphasize task order and rigid scheduling. A critical chain project network strives to keep resources levelled, and requires that they be flexible in start times.

The critical path method (CPM), or critical path analysis (CPA), is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. A critical path is determined by identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT).
Project management software are computer programs that help plan, organize, and manage resources.

The program evaluation and review technique (PERT) is a statistical tool used in project management, which was designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project.
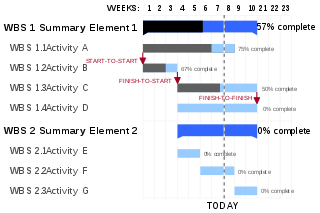
A Gantt chart is a bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. It was designed and popularized by Henry Gantt around the years 1910–1915. Modern Gantt charts also show the dependency relationships between activities and the current schedule status.
In project management, a schedule is a listing of a project's milestones, activities, and deliverables. Usually dependencies and resources are defined for each task, then start and finish dates are estimated from the resource allocation, budget, task duration, and scheduled events. A schedule is commonly used in the project planning and project portfolio management parts of project management. Elements on a schedule may be closely related to the work breakdown structure (WBS) terminal elements, the Statement of work, or a Contract Data Requirements List.

A project network diagram is a graph that displays the order in which a project’s activities are to be completed. Derived from the work breakdown structure, the terminal elements of a project are organized sequentially based on the relationship among them. It is typically drawn from left to right to reflect project chronology.
Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique (GERT) is a network analysis technique used in project management that allows probabilistic treatment both network logic and estimation of activity duration. The technique was first described in 1966 by Dr. Alan B. Pritsker of Purdue University and WW Happ.

The precedence diagram method (PDM) is a tool for scheduling activities in a project plan. It is a method of constructing a project schedule network diagram that uses boxes, referred to as nodes, to represent activities and connects them with arrows that show the dependencies. It is also called the activity-on-node (AON) method.

Event chain methodology is a network analysis technique that is focused on identifying and managing events and relationships between them that affect project schedules. It is an uncertainty modeling schedule technique. Event chain methodology is an extension of quantitative project risk analysis with Monte Carlo simulations. It is the next advance beyond critical path method and critical chain project management. Event chain methodology tries to mitigate the effect of motivational and cognitive biases in estimating and scheduling. It improves accuracy of risk assessment and helps to generate more realistic risk adjusted project schedules.
In project management, level of effort (LOE) is a support-type project activity that must be done to support other work activities or the entire project effort. It usually consists of short amounts of work that must be repeated periodically. Examples of such an activity may be project budget accounting, customer liaison, or oiling machinery during manufacturing.

Event chain diagrams are visualizations that show the relationships between events and tasks and how the events affect each other.

In systems engineering, software engineering, and computer science, a function model or functional model is a structured representation of the functions within the modeled system or subject area.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
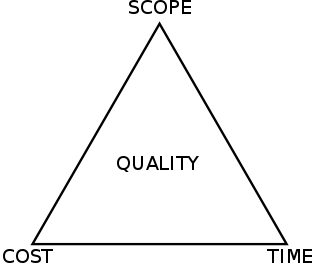
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
The Graphical Path Method (GPM) is a mathematically based algorithm used in project management for planning, scheduling and resource control. GPM represents logical relationships of dated objects – such as activities, milestones, and benchmarks – in a time-scaled network diagram.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
Willard R. Fazar was an American economist, Head of the Program Evaluation Branch at Special Projects Office, U.S. Navy, and author. He is known as one of co-inventors, and key-developers of PERT."