
Montana is a state in the Mountain region of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the fourth-largest state by area, the eighth-least populous state, and the third-least densely populated state. Its capital is Helena, while the most populous city is Billings. The western half of the state contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges found throughout the state.

Milk River is a tributary of the Missouri River, 729 miles (1,173 km) long, in the U.S. state of Montana and the Canadian province of Alberta. Rising in the Rocky Mountains, the river drains a sparsely populated, semi-arid watershed of 23,800 square miles (62,000 km2), ending just east of Fort Peck, Montana.

Flathead County is in the U.S. state of Montana. At the 2020 census, its population was 104,357, making it the state's fourth most populous county. Its county seat is Kalispell. Its numerical designation is 7. Its northern border is on the state's north border, making it contiguous with the Canada–US border, facing British Columbia.
Montana is the 41st state of the United States.

The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time (UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time (UTC−06:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time at the 105th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In the United States, the exact specification for the location of time zones and the dividing lines between zones is set forth in the Code of Federal Regulations at 49 CFR 71.
Blue Mountain may refer to:
Sawtooth Range, Sawtooth Ridge, and Sawtooth Mountains may refer to:
Fossil Mountain refers to several mountains, including:
Kootenay, Kootenai, and Kutenai may refer to:
Chimney Rock can refer to one of the following sites in the United States and Canada:
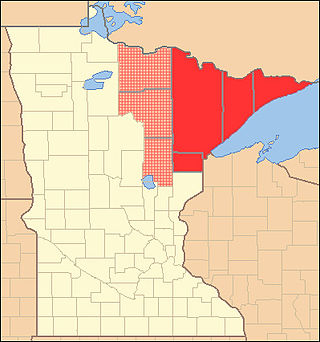
The Arrowhead Region is located in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Minnesota, so called because of its pointed shape. The predominantly rural region encompasses 10,635.26 square miles (27,545.2 km2) of land area and includes Carlton, Cook, Lake and Saint Louis counties. Its population at the 2000 census was 248,425 residents. The region is loosely defined, and Aitkin, Itasca, and Koochiching counties are sometimes considered as part of the region, increasing the land area to 18,221.97 square miles (47,194.7 km2) and the population to 322,073 residents. Primary industries in the region include tourism and iron mining.
Heart Lake may refer to the following places:
Copper Mountain may refer to:
Crown Mountain may refer to:
An arrowhead is the point of an arrow.
Goat Mountain may refer to:

Arrowhead Mountain is a 6,030 ft (1,840 m) mountain summit located in Chelan County of Washington state. It is situated 6 mi (9.7 km) east of Stevens Pass, on the boundary of Alpine Lakes Wilderness, on land managed by the Okanogan–Wenatchee National Forest. Arrowhead Mountain is part of the Chiwaukum Mountains, which are a subset of the Cascade Range. Its nearest higher neighbor is Jim Hill Mountain, 2.5 mi (4.0 km) to the southwest. Precipitation runoff from the peak drains into tributaries of Nason Creek, which in turn is a tributary of the Wenatchee River. This mountain was named by Albert Hale Sylvester (1871–1944), a pioneering surveyor, explorer, topographer, and forest supervisor who named hundreds of natural features in the Cascades.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





