The Arsenal de Rochefort was a French naval base and dockyard in the town of Rochefort. It was founded in 1665 and it was closed in 1926.

Rochefort, also known as Rochefort-sur-Mer, is a commune in southwestern France, a port on the Charente estuary. It is a sub-prefecture of the Charente-Maritime department.
In December 1665 Rochefort was chosen by Jean-Baptiste Colbert as a place of "refuge, defense and supply" for the French Navy. Its military harbour was fortified by Louis XIV's Commissary of Fortifications Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. Between 1666 and 1669 the King had the Corderie Royale (then the longest building in Europe) constructed to make cordage for French ships of war.

Jean-Baptiste Colbert was a French politician who served as the Minister of Finances of France from 1661 to 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV.

The French Navy, informally "La Royale", is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces. Dating back to 1624, the French Navy is one of the world's oldest naval forces. It has participated in conflicts around the globe and played a key part in establishing the French colonial empire.

Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Seigneur de Vauban, later Marquis de Vauban commonly referred to as Vauban, was a French military engineer, who participated in each of the wars fought by France during the reign of Louis XIV.
The making of cordage ceased in 1867 and in 1926 the Arsenal de Rochefort was closed.

Charente-Maritime is a department on the western coast of France named after the Charente River.
The Pertuis d'Antioche is a strait on the Atlantic coast of Western France, between two islands, Île de Ré and Île d'Oléron, on the one side, and on the other side the continental coast between the cities of La Rochelle and the naval arsenal of Rochefort. The Pertuis d'Antioche owes its name to the similarity of the contour of its coastline to that of the Mediterranean sea's north-eastern area between Cyprus, Syria and Turkey, which has the famous ancient city of Antioch at its centre.

Île-d'Aix is a commune in the Charente-Maritime department off the west coast of France. It occupies the territory of small island of Île d'Aix in the Atlantic. It is a popular place for tourist day-trips during the summer months.

Faro District is the southernmost district of Portugal, coincident with the Algarve. The administrative centre, or capital, is the city of Faro.

The Troupes de la MarineThe troupes of La Marine, a body founded by Cardinal Richelieu in 1622 under the denomination of Compagnies Ordinaires de la Mer, were originally intended to form the garrisons of the ships of the King. It was in 1674 that Jean-Baptiste Colbert decides to make permanent colonial troops and give them the name of Compagnies Franches de la Marine.
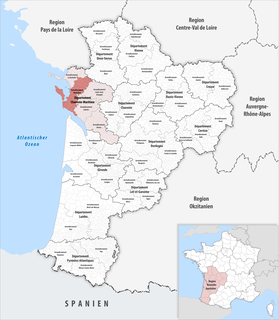
The arrondissement of Rochefort is an arrondissement of France in the Charente-Maritime department of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region. Since the January 2017 reorganization of the arrondissements of Charente-Maritime, it has 78 communes. Its population is 189,875 (2016), and its area is 1,534.6 km2 (592.5 sq mi).

Gourette is a winter sports resort in the French Pyrenees. It is located in the commune of Eaux-Bonnes in the département of Pyrénées-Atlantiques, on the D 918 road which passes through the Col d'Aubisque mountain pass. The closest air access is Pau Pyrénées Airport.

The Raid on Cherbourg took place in August 1758 during the Seven Years' War when a British force was landed on the coast of France by the Royal Navy with the intention of attacking the town of Cherbourg as part of the British government's policy of "descents" on the French coasts.

The Musée National de la Marine in Rochefort is one of the main naval museums of France.
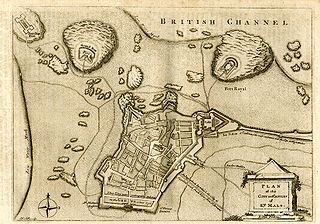
The Raid on St Malo took place in June 1758 when an amphibious British naval expedition landed close to the French port of St Malo in Brittany. While the town itself was not attacked, as had been initially planned, the British destroyed large amounts of shipping before re-embarking a week later. The naval forces were under the command of Richard Howe while the army was led by the Duke of Marlborough and Lord Sackville.

Gare de Rochefort is a railway station serving the town Rochefort, Charente-Maritime department, southwestern France.

This is the training school for non-commissioned officers (NCO) of the French Air Force, recruited directly from the civilian life or the EETAA 722 school. This aeronautic establishment prepares tomorrow's task forces to quickly be dispatched in foreign military operations.

The Clorinde-class submarines were built for the French Navy prior to World War I. There were two boats in this class, neither of them would be used during World War I, but they operated in the Atlantic Ocean and the English Channel until they were stricken in 1926.
The canton of Rochefort is an administrative division of the Charente-Maritime department, western France. It was created at the French canton reorganisation which came into effect in March 2015. Its seat is in Rochefort.

The Lagrange-class submarines were a class of four submarines built for the French Navy during World War I and the interwar period. Three ships of this type were built in the Arsenal de Toulon from 1913 to 1924, and one was built at the Arsenal de Rochefort shipyard. Entering the French Marine Nationale from 1918 to 1924, the submarines served until the mid-1930s.
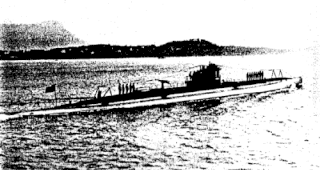
The French submarine Laplace (Q111) was a Lagrange-class submarine built for the French Navy built between 1913 and 1919. It was laid down in the Arsenal de Rochefort shipyards and launched on 12 August 1919. Laplace was completed in 1921 and served in the French Marine Nationale until 1935.
The Corderie Royale International de la mer is a vast museum complex located in the heart of the maritime Arsenal de Rochefort. The building built in 1666 has been classified as historic Monuments since 1967 and currently a candidate for inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.




















