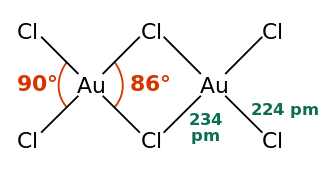Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are available both in anhydrous and hydrated forms. They are common sources of iron in its +3 oxidation state. The hydrate and the anhydrous derivative have distinct properties.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula to the word.

Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several chemical compounds with the formula CrCl3 · xH2O, where x can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the trichloride is the dark green hexahydrate, CrCl3 · 6 H2O. Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
Manganese(III) fluoride (also known as Manganese trifluoride) is the inorganic compound with the formula MnF3. This red/purplish solid is useful for converting hydrocarbons into fluorocarbons, i.e., it is a fluorination agent. It forms a hydrate and many derivatives.
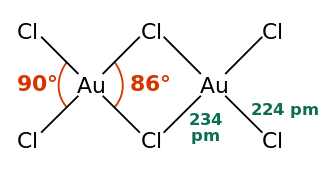
Gold(III) chloride, traditionally called auric chloride, is an inorganic compound of gold and chlorine with the molecular formula Au2Cl6. The "III" in the name indicates that the gold has an oxidation state of +3, typical for many gold compounds. It has two forms, the monohydrate (AuCl3·H2O) and the anhydrous form, which are both hygroscopic and light-sensitive solids. This compound is a dimer of AuCl3. This compound has a few uses, such as an oxidizing agent and for catalyzing various organic reactions.
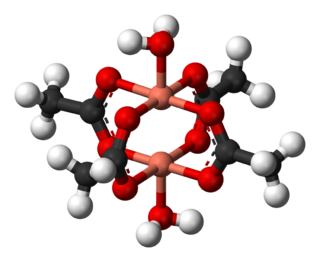
Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (CH
3CO−
2). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is available commercially. Anhydrous copper(II) acetate is a dark green crystalline solid, whereas Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2 is more bluish-green. Since ancient times, copper acetates of some form have been used as fungicides and green pigments. Today, copper acetates are used as reagents for the synthesis of various inorganic and organic compounds. Copper acetate, like all copper compounds, emits a blue-green glow in a flame.

Xenon trioxide is an unstable compound of xenon in its +6 oxidation state. It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and liberates oxygen from water slowly, accelerated by exposure to sunlight. It is dangerously explosive upon contact with organic materials. When it detonates, it releases xenon and oxygen gas.

Vanadium trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl3. This purple salt is a common precursor to other vanadium(III) complexes.

Ruthenium(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula RuO2. This black solid is the most common oxide of ruthenium. It is widely used as an electrocatalyst for producing chlorine, chlorine oxides, and O2. Like many dioxides, RuO2 adopts the rutile structure.

Iron(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeBr2. The anhydrous compound is a yellow or brownish-colored paramagnetic solid. Several hydrates of FeBr2 are also known, all being pale colored solids. It is a common precursor to other iron compounds in research laboratory, but no applications exist for this compound.
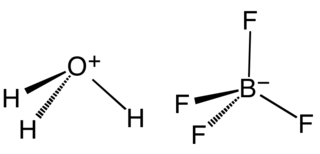
Fluoroboric acid or tetrafluoroboric acid is an inorganic compound with the simplified chemical formula H+[BF4]−. Unlike other strong acids like H2SO4 or HClO4, the pure tetrafluoroboric acid does not exist. The term "fluoroboric acid" refers to a range of chemical compounds, depending on the solvent. The H+ in the simplified formula of fluoroboric acid represents the solvated proton. The solvent can be any suitable Lewis base. For instance, if the solvent is water, fluoroboric acid can be represented by the formula [H3O]+[BF4]−, although more realistically, several water molecules solvate the proton: [H(H2O)n]+[BF4]−. The ethyl ether solvate is also commercially available, where the fluoroboric acid can be represented by the formula [H( 2O)n]+[BF4]−, where n is most likely 2.

Ammonium heptamolybdate is the inorganic compound whose chemical formula is (NH4)6Mo7O24, normally encountered as the tetrahydrate. A dihydrate is also known. It is a colorless solid, often referred to as ammonium paramolybdate or simply as ammonium molybdate, although "ammonium molybdate" can also refer to ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH4)2MoO4, and several other compounds. It is one of the more common molybdenum compounds.
Trimethylsilanol (TMS) is an organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiOH. The Si centre bears three methyl groups and one hydroxyl group. It is a colourless volatile liquid.
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. In general these applications are declining in step with growing concerns about their impact on the environment and human health. The parent compounds are arsane and arsenic acid. Despite their toxicity, organoarsenic biomolecules are well known.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.
Vanadium phosphates are inorganic compounds with the formula VOxPO4 as well related hydrates with the formula VOxPO4(H2O)n. Some of these compounds are used commercially as catalysts for oxidation reactions.
Aluminium triacetate, formally named aluminium acetate, is a chemical compound with composition Al(CH
3CO
2)
3. Under standard conditions it appears as a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes on heating at around 200 °C. The triacetate hydrolyses to a mixture of basic hydroxide / acetate salts, and multiple species co-exist in chemical equilibrium, particularly in aqueous solutions of the acetate ion; the name aluminium acetate is commonly used for this mixed system.

Berkelium(III) chloride also known as berkelium trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula BkCl3. It is a water-soluble green salt with a melting point of 603 °C. This compound forms the hexahydrate, BkCl3·6H2O.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +6, +4, and +2 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. Tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.