
The Umayyad Caliphate(Pronounced variously, ; Arabic: ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, romanized: al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) or Umayyad Empire was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, also known as the Umayyads. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiya's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell to Marwan I, from another branch of the clan. Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus as their capital.

Yazid ibn Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan, commonly known as Yazid I, was the second caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate. He ruled from April 680 until his death in November 683. His appointment by his father Mu'awiya I was the first hereditary succession to the caliphate in Islamic history. His caliphate was marked by the death of Muhammad's grandson Husayn ibn Ali and the start of the crisis known as the Second Fitna.

Marwan ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya, commonly known as Marwan I, was the fourth Umayyad caliph, ruling for less than a year in 684–685. He founded the Marwanid ruling house of the Umayyad dynasty, which replaced the Sufyanid house after its collapse in the Second Muslim Civil War and remained in power until 750.

Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan, commonly known as Marwan II, was the fourteenth and last caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 744 until his death. His reign was dominated by a civil war, and he was the last Umayyad ruler to rule the united Caliphate before the Abbasid Revolution toppled the Umayyad dynasty.
Marwan, Merwan or Marwen or Mervan is an Arabic male given name derived from the word marū/ maruw (مرو) with the meaning of either minerals, "flint(-stone)", "quartz" or "a hard stone of nearly pure silica". However, the Arabic name for quartz is ṣawwān (صَوَّان).

Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr ibn Abi Quhafa al-Taymi was an Arab Muslim commander in the service of the fourth Rashidun caliph Ali.

Ubayd Allah ibn Ziyad was the Umayyad governor of Basra, Kufa and Khurasan during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I and Yazid I, and the leading general of the Umayyad army under caliphs Marwan I and Abd al-Malik.

Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam was the leader of a caliphate based in Mecca that rivaled the Umayyads from 683 until his death.
Al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya, was the father of the founder of the Marwanid line of the Umayyad dynasty, Marwan I, and a paternal uncle of Caliph Uthman. He was known as a staunch opponent of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was consequently exiled when the latter captured their hometown of Mecca in 630. He was later pardoned by Uthman.
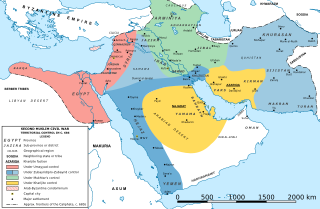
The Second Fitna was a period of general political and military disorder and civil war in the Islamic community during the early Umayyad Caliphate. It followed the death of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I in 680, and lasted for about twelve years. The war involved the suppression of two challenges to the Umayyad dynasty, the first by Husayn ibn Ali, as well as his supporters including Sulayman ibn Surad and Mukhtar al-Thaqafi who rallied for his revenge in Iraq, and the second by Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr.

Uthman, the third Rashidun caliph from 644 to 656, was assassinated at the end of a siege upon his house in 656. Initially a protest, the siege escalated following the death of a protester. The protesters-turned-rebels had demanded a new caliph, but Uthman refused and on 17 June 656, as his house was set alight, some protestors were able to jump to the back of his house, where they found him reading the Qur'an. They gave him a blow over the head and pierced him through his stomach.
Abū ʿAbd al-Raḥmān Muḥammad ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam was an Umayyad prince and one of the most important generals of the Umayyad Caliphate in the period 690–710, and the one who completed the Arab conquest of Armenia. He defeated the Byzantines and conquered their Armenian territories, crushed an Armenian rebellion in 704–705 and made the country into an Umayyad province. His son Marwan II was the last Umayyad caliph.
ʿAbdallāh ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān was an Umayyad prince, the son of Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, a general and the governor of Egypt in 705–709.

The Battle of the Camel took place outside of Basra, Iraq, in 36 AH. The battle was fought between the army of the fourth caliph Ali, on one side, and the rebel army led by Aisha, Talha and Zubayr, on the other side. Ali was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, while Aisha was a widow of Muhammad, of whom Talha and Zubayr were both prominent companions. Ali emerged victorious from the battle, Talha and Zubayr were both killed, and Aisha was sent back to Hejaz afterward. The triumvirate had revolted against Ali ostensibly to avenge the assassination of the third caliph Uthman, although Aisha and Talha are both known to have actively opposed him. The three also called for the removal of Ali from office and for a Qurayshite council (shura) with Talha and Zubayr to appoint his successor.

The Abbasid Revolution, also called the Movement of the Men of the Black Raiment, was the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate, the second of the four major Caliphates in Islamic history, by the third, the Abbasid Caliphate. Coming to power three decades after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and immediately after the Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyads were an Arab empire ruling over a population which was overwhelmingly non-Arab. Non-Arabs were treated as second-class citizens regardless of whether or not they converted to Islam, and this discontent cutting across faiths and ethnicities ultimately led to the Umayyads' overthrow. The Abbasid family claimed descent from al-Abbas, an uncle of Muhammad.

The Third Fitna was a series of civil wars and uprisings in the Islamic community. It followed the death of the twelfth Umayyad caliph Yazid III in 744 and lasted for about six years. The war culminated with the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate and the establishment of the Abbasid Caliphate in 750. Following the death of Yazid III in 744 and the abdication of his successor Ibrahim the same year, Marwan II became the sole ruler of the caliphate.

Abd al-Aziz ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam was the Umayyad governor and de facto viceroy of Egypt between 685 and his death. He was appointed by his father, Caliph Marwan I. Abd al-Aziz's reign was marked by stability and prosperity, partly due to his close relations and reliance on the Arab military settlers of Fustat. Under his direction and supervision, an army led by Musa ibn Nusayr completed the Muslim conquest of North Africa. He was removed from the line of succession to the caliphal throne and, in any case, died before his brother, Caliph Abd al-Malik. However, one of Abd al-Aziz's sons, Umar, would become caliph in 717.
Abu Uthman Amr ibn Uthman ibn Affan al-Umawi was a son of Caliph Uthman and played political and military roles during the caliphates of Mu'awiya I, Yazid I and Marwan I.
The Umayyad dynasty or Umayyads was an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe who were the ruling family of the Caliphate between 661 and 750 and later of al-Andalus between 756 and 1031. In the pre-Islamic period, they were a prominent clan of the Meccan tribe of Quraysh, descended from Umayya ibn Abd Shams. Despite staunch opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the Umayyads embraced Islam before the latter's death in 632. Uthman, an early companion of Muhammad from the Umayyad clan, was the third Rashidun caliph, ruling in 644–656, while other members held various governorships. One of these governors, Mu'awiya I of Syria, opposed Caliph Ali in the First Muslim Civil War (656–661) and afterward founded the Umayyad Caliphate with its capital in Damascus. This marked the beginning of the Umayyad dynasty, the first hereditary dynasty in the history of Islam, and the only one to rule over the entire Islamic world of its time.
Al-Asbagh ibn Dhu'ala al-Kalbi was an Umayyad commander and a warlord of the Banu Kalb tribe in Palmyra who played a prominent role in the Third Muslim Civil War (744–750) and afterward was a leader of the revolt of the Umayyad prince Abu Muhammad al-Sufyani against the Abbasids in 750–751.












