
Neutrino astronomy is the branch of astronomy that observes astronomical objects with neutrino detectors in special observatories. Neutrinos are created as a result of certain types of radioactive decay, nuclear reactions such as those that take place in the Sun or high energy astrophysical phenomena, in nuclear reactors, or when cosmic rays hit atoms in the atmosphere. Neutrinos rarely interact with matter, meaning that it is unlikely for them to scatter along their trajectory, unlike photons. Therefore, neutrinos offer a unique opportunity to observe processes that are inaccessible to optical telescopes, such as reactions in the Sun's core. Neutrinos can also offer a very strong pointing direction compared to charged particle cosmic rays.

The Pierre Auger Observatory is an international cosmic ray observatory in Argentina designed to detect ultra-high-energy cosmic rays: sub-atomic particles traveling nearly at the speed of light and each with energies beyond 1018 eV. In Earth's atmosphere such particles interact with air nuclei and produce various other particles. These effect particles (called an "air shower") can be detected and measured. But since these high energy particles have an estimated arrival rate of just 1 per km2 per century, the Auger Observatory has created a detection area of 3,000 km2 (1,200 sq mi)—the size of Rhode Island, or Luxembourg—in order to record a large number of these events. It is located in the western Mendoza Province, Argentina, near the Andes.

The IceCube Neutrino Observatory is a neutrino observatory constructed at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica. The project is a recognized CERN experiment (RE10). Its thousands of sensors are located under the Antarctic ice, distributed over a cubic kilometre.
The NESTOR Project is an international scientific collaboration whose target is the deployment of a neutrino telescope on the sea floor off Pylos, Greece.

IACT stands for Imaging AtmosphericCherenkov Telescope or Technique. It is a device or method to detect very-high-energy gamma ray photons in the photon energy range of 50 GeV to 50 TeV.

A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus which is designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos only weakly interact with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino detectors are often built underground, to isolate the detector from cosmic rays and other background radiation. The field of neutrino astronomy is still very much in its infancy – the only confirmed extraterrestrial sources as of 2018 are the Sun and the supernova 1987A in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud. Another likely source is the blazar TXS 0506+056 about 3.7 billion light years away. Neutrino observatories will "give astronomers fresh eyes with which to study the universe".
Astroparticle physics, also called particle astrophysics, is a branch of particle physics that studies elementary particles of astronomical origin and their relation to astrophysics and cosmology. It is a relatively new field of research emerging at the intersection of particle physics, astronomy, astrophysics, detector physics, relativity, solid state physics, and cosmology. Partly motivated by the discovery of neutrino oscillation, the field has undergone rapid development, both theoretically and experimentally, since the early 2000s.
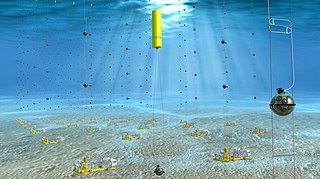
The Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope, or KM3NeT, is a future European research infrastructure that will be located at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea. It will host the next-generation neutrino telescope in the form of a water Cherenkov detector with an instrumented volume of several cubic kilometres distributed over three locations in the Mediterranean: KM3NeT-Fr, KM3NeT-It and KM3NeT-Gr. The KM3NeT project continues work done under the ANTARES, NEMO and NESTOR neutrino telescope projects.

The Cherenkov Telescope Array or CTA is a multinational, worldwide project to build a new generation of ground-based gamma-ray instrument in the energy range extending from some tens of GeV to about 300 TeV. It is proposed as an open observatory and will consist of two arrays of Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes (IACTs), a first array at the Northern Hemisphere with emphasis on the study of extragalactic objects at the lowest possible energies, and a second array at the Southern Hemisphere, which is to cover the full energy range and concentrate on galactic sources. The physics program of CTA goes beyond high energy astrophysics into cosmology and fundamental physics.

The European Underground Rare Event Calorimeter Array (EURECA) is a planned dark matter search experiment using cryogenic detectors and an absorber mass of up to 1 tonne. The project will be built in the Modane Underground Laboratory and will bring together researchers working on the CRESST and EDELWEISS experiments.
The Baikal Deep Underwater Neutrino Telescope (BDUNT) is a neutrino detector conducting research below the surface of Lake Baikal (Russia) since 2003. The first detector was started in 1990 and completed in 1998. It was upgraded in 2005 and again starting in 2015 to build the Baikal Gigaton Volume Detector (Baikal-GVD.) BDUNT has studied neutrinos coming through the Earth with results on atmospheric muon flux. BDUNT picks up many atmospheric neutrinos created by cosmic rays interacting with the atmosphere – as opposed to cosmic neutrinos which give clues to cosmic events and are therefore of greater interest to physicists.

In cosmology, primordial black holes (PBHs) are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang. In the inflationary era and early radiation-dominated universe, extremely dense pockets of subatomic matter may have been tightly packed to the point of gravitational collapse, creating primordial black holes without the supernova compression needed to make black holes today. Because the creation of primordial black holes would pre-date the first stars, they are not limited to the narrow mass range of stellar black holes.

NEVOD is a neutrino detector and cosmic ray experiment that attempts to detect Cherenkov radiation arising from interactions between water and charged particles. It represents the first attempt to perform such measurements at the Earth's surface; it is because of this surface deployment that the experiment is also able to investigate cosmic rays. NEVOD is situated at the Moscow Engineering Physics Institute (MEPhI).

Stavros Katsanevas was a Greek-French astrophysicist who was director of the European Gravitational Observatory, professor at the Université Paris Cité, former director of the AstroParticle and Cosmology (APC) laboratory and former chairman of the Astroparticle Physics European Consortium (APPEC). In 2000, he received for his work on supersymmetry the Physics Prize from the Academy of Athens. In 2011, he was awarded the Ordre National du Merite. He was an ordinary member of Academy of Europe, Earth and Cosmic Sciences since 2019.

The Cosmology Large Angular Scale Surveyor (CLASS) is an array of microwave telescopes at a high-altitude site in the Atacama Desert of Chile as part of the Parque Astronómico de Atacama. The CLASS experiment aims to improve our understanding of cosmic dawn when the first stars turned on, test the theory of cosmic inflation, and distinguish between inflationary models of the very early universe by making precise measurements of the polarization of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) over 65% of the sky at multiple frequencies in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum.

The Astroparticle and Cosmology (APC) laboratory in Paris gathers researchers working in different areas including high-energy astrophysics, cosmology, gravitation, and neutrino physics.
Multi-messenger astronomy is astronomy based on the coordinated observation and interpretation of signals carried by disparate "messengers": electromagnetic radiation, gravitational waves, neutrinos, and cosmic rays. They are created by different astrophysical processes, and thus reveal different information about their sources.
Francis Louis Halzen is a Belgian particle physicist. He is the Hilldale and Gregory Breit Distinguished Professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and Director of its Institute for Elementary Particle Physics. Halzen is the Principal Investigator of the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica, the world's largest neutrino detector which has been operational since 2010.
Teresa Montaruli is an Italian astronomer specializing in neutrino astronomy, and in particular in the search for high-energy neutrinos from cosmic sources. She is a professor in the particle physics department at the University of Geneva.














