
A pump is a device that moves fluids, or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy.

A vacuum pump is a type of pump device that draws gas particles from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke, and was preceded by the suction pump, which dates to antiquity.

A vacuum cleaner, also known simply as a vacuum, is a device that uses suction, and often agitation, in order to remove dirt and other debris from carpets and hard floors.
Aspiration or aspirations may refer to:

Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgery method in which the internal lens of the eye which has developed a cataract is emulsified with the tip of an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to maintain the volume of the anterior chamber during the procedure. This procedure minimises the incision size and reduces the recovery time and risk of surgery-induced astigmatism.
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect.

A chest tube is a surgical drain that is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space or the mediastinum. The insertion of the tube is sometimes a lifesaving procedure. The tube can be used to remove clinically undesired substances such as air (pneumothorax), excess fluid, blood (hemothorax), chyle (chylothorax) or pus (empyema) from the intrathoracic space. An intrapleural chest tube is also known as a Bülau drain or an intercostal catheter (ICC), and can either be a thin, flexible silicone tube, or a larger, semi-rigid, fenestrated plastic tube, which often involves a flutter valve or underwater seal.

An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow.
Dermabrasion is a type of surgical skin planing, generally with the goal of removing acne, scarring and other skin or tissue irregularities, typically performed in a professional medical setting by a dermatologist or plastic surgeon trained specifically in this procedure. Dermabrasion has been practiced for many years and involves the controlled deeper abrasion of the upper to mid layers of the skin with any variety of strong abrasive devices including a wire brush, diamond wheel or fraise, sterilized sandpaper, salt crystals or other mechanical means.

A Büchner flask, also known as a vacuum flask, filter flask, suction flask, side-arm flask, or Bunsen flask, is a thick-walled Erlenmeyer flask with a short glass tube and hose barb protruding about an inch from its neck.

Vacuum or suction aspiration is a procedure that uses a vacuum source to remove an embryo or fetus through the cervix. The procedure is performed to induce abortion, as a treatment for incomplete spontaneous abortion or retained fetal and placental tissue, or to obtain a sample of uterine lining. It is generally safe, and serious complications rarely occur.

A surgical drain is a tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound, body cavity, or organ. They are commonly placed by surgeons or interventional radiologists after procedures or some types of injuries, but they can also be used as an intervention for decompression. There are several types of drains, and selection of which to use often depends on the placement site and how long the drain is needed.

A Jackson-Pratt drain is a closed-suction medical device that is commonly used as a post-operative drain for collecting bodily fluids from surgical sites. The device consists of an internal drain connected to a grenade-shaped bulb or circular cylinder via plastic tubing.

A trocar is a medical or veterinary device used in minimally invasive surgery. Trocars are typically made up of an awl, a cannula and often a seal. Some trocars also include a valve mechanism to allow for insufflation. Trocars are designed for placement through the chest and abdominal walls during thoracoscopic and laparoscopic surgery, and each trocar functions as a portal for the subsequent insertion of other endoscopic instruments such as grasper, scissors, stapler, electrocautery, suction tip, etc. — hence the more commonly used colloquial jargon "port". Trocars also allow passive evacuation of excess gas or fluid from organs within the body.
Autotransfusion is a process wherein a person receives their own blood for a transfusion, instead of banked allogenic (separate-donor) blood. There are two main kinds of autotransfusion: Blood can be autologously "pre-donated" before a surgery, or alternatively, it can be collected during and after the surgery using an intraoperative blood salvage device. The latter form of autotransfusion is utilized in surgeries where there is expected a large volume blood loss – e.g. aneurysm, total joint replacement, and spinal surgeries. The effectiveness, safety, and cost-savings of intraoperative cell salvage in people who are undergoing thoracic or abdominal surgery following trauma is not known.

In medicine, devices are sometimes necessary to create suction. Suction may be used to clear the airway of blood, saliva, vomit, or other secretions so that a patient may breathe. Suctioning can prevent pulmonary aspiration, which can lead to lung infections. In pulmonary hygiene, suction is used to remove fluids from the airways, to facilitate breathing and prevent growth of microorganisms. Small suction-providing devices are often called aspirators.

Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, liposuction is the most common cosmetic surgery.

A central vacuum cleaner is a type of vacuum cleaner appliance installed into a building as a semi-permanent fixture. Central vacuum systems are designed to remove dirt and debris from homes and buildings by sending dirt particles through piping installed inside the walls to a collection container inside a remote utility space. The power unit is a permanent fixture, usually installed in a basement, garage, or storage room, along with the collection container. Inlets are installed in walls throughout the building that attach to power hoses and other central vacuum accessories to remove dust, particles, and small debris from interior rooms. Most power hoses have a power switch located on the handle.
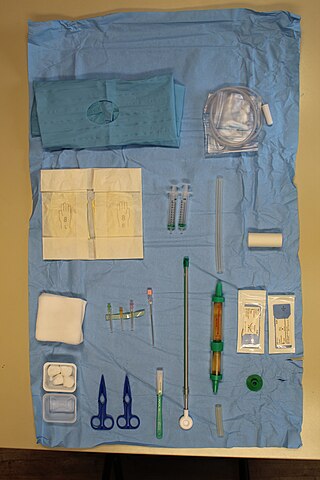
Chest drains are surgical drains placed within the pleural space to facilitate removal of unwanted substances in order to preserve respiratory functions and hemodynamic stability. Some chest drains may utilize a flutter valve to prevent retrograde flow, but those that do not have physical valves employ a water trap seal design, often aided by continuous suction from a wall suction or a portable vacuum pump.

















