
Maryland is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. Baltimore is the largest city in the state, and the capital is Annapolis. Among its occasional nicknames are Old Line State, the Free State, and the Chesapeake Bay State. It is named after the English Queen Henrietta Maria, known in England as Queen Mary, who was the French wife of King Charles I.

Fenwick Island is a coastal town in Sussex County, Delaware, USA. According to 2010 census figures, the population of the town is 379, a 10.8% increase over the last decade. It is part of the Salisbury, Maryland-Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area. The town is located on Fenwick Island, a barrier spit.

Smith Island is an island on the Chesapeake Bay, on the border of Maryland and Virginia territorial waters in the United States. The island is the last inhabited island off the shore of Maryland, where most of the islands are eroding because of sea level rise. Smith Island is also experiencing that threat and is expected to erode by 2100.

USS Maryland (BB-46), also known as "Old Mary" or "Fighting Mary" to her crewmates, was a Colorado-class battleship. She was the third ship of the United States Navy to be named in honor of the seventh state. She was commissioned in 1921, and serving as the flagship of the fleet, cruised to Australia, New Zealand, and Brazil.
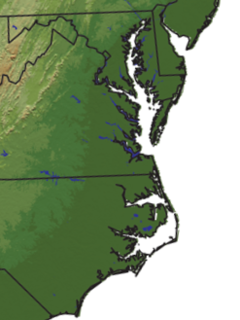
Tidewater refers to the north Atlantic coastal plain region of the United States of America.

The Eastern Shore of Maryland is a part of the U.S. state of Maryland that lies mostly on the east side of the Chesapeake Bay. This is one of seven of which have Chesapeake Bay coastlines, one is inland, and the remaining county, Worcester, contains Maryland's only coast along the Atlantic Ocean.

Assateague Island is a 37-mile (60 km) long barrier island located off the eastern coast of the Delmarva Peninsula facing the Atlantic Ocean. The northern two-thirds of the island is in Maryland while the southern third is in Virginia. The Maryland section contains the majority of Assateague Island National Seashore and Assateague State Park. The Virginia section contains Chincoteague National Wildlife Refuge and a one-mile stretch of land containing the lifeguarded recreational beach and interpretive facilities managed by the National Park Service. It is best known for its herds of feral horses, pristine beaches and the Assateague Lighthouse. The island also contains numerous marshes, bays, and coves, including Toms Cove. Bridge access for cars is possible from both Maryland and Virginia, though no road runs the full north/south length of the island.

Assateague Island National Seashore is a unit of the National Park Service system of the U.S. Department of the Interior. Located on the East Coast along the Atlantic Ocean in Maryland and Virginia, Assateague Island is the largest natural barrier island ecosystem in the Middle Atlantic states region that remains predominantly unaffected by human development. Located within a three-hour drive to the east and south of Richmond, Washington, Baltimore, Wilmington, Philadelphia major metropolitan areas plus north of the several clustered smaller cities around Hampton Roads harbor of Virginia with Newport News, Hampton, Norfolk, Portsmouth, Chesapeake and Virginia Beach. The National Seashore offers a setting in which to experience a dynamic barrier island and to pursue a multitude of recreational opportunities. The stated mission of the park is to preserve and protect “unique coastal resources and the natural ecosystem conditions and processes upon which they depend, provide high-quality resource-based recreational opportunities compatible with resource protection and educate the public as to the values and significance of the area”.
The National Register of Historic Places in the United States is a register including buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects. The Register automatically includes all National Historic Landmarks as well as all historic areas administered by the U.S. National Park Service. Since its introduction in 1966, more than 90,000 separate listings have been added to the register.

St. Clement's Island State Park is a publicly owned historic preservation and recreational area that encompasses St. Clement's Island, an uninhabited Potomac River island lying one-half mile southeast of Colton's Point, St. Mary's County, Maryland. The state park features a 40-foot stone cross dedicated to the beginnings of freedom of religion in the United States as well as a reconstruction of the historic Blakistone Island Light. It is the central feature of the St. Clement's Island Historic District that was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1972.

The skipjack is a traditional fishing boat used on the Chesapeake Bay for oyster dredging. It is a sailboat which succeeded the bugeye as the chief oystering boat on the bay, and it remains in service due to laws restricting the use of powerboats in the Maryland state oyster fishery.

Assateague State Park is a public recreation area in Worcester County, Maryland, USA,, located at the north end of Assateague Island, a barrier island bordered by the Atlantic Ocean on the east and Sinepuxent Bay on the west. The state park is bordered on both its north and south sides by Assateague Island National Seashore and is reached via the Verrazano Bridge which carries Maryland Route 611 across Sinepuxent Bay. The park offers wildlife viewing, beach activities, and camping facilities. It is managed by the Maryland Park Service of the larger Maryland Department of Natural Resources with the support of volunteers working under the auspices of the non-profit Friends of Assateague State Park.

Deal Island Wildlife Management Area protects 13,565 acres (54.90 km2) in western Somerset County, Maryland near the community of Deal Island. As a wildlife management area, the area is managed by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources' Wildlife and Heritage Service to conserve wildlife populations and their habitats, while providing public recreational use of wildlife resources.

Heater's Island Wildlife Management Area is a Wildlife Management Area in Frederick County, Maryland. Heater's Island is a large forested island in the Potomac River near Point of Rocks, Maryland. It was long inhabited by the Piscataway people, who were forced to leave by smallpox in 1705.

Hart-Miller Island State Park is a state-owned, public recreation area located on Hart-Miller Island, a man-made landfill linking three natural Chesapeake Bay islands—Hart, Miller, and Pleasure—at the mouth of Back River in Maryland. The state park is accessible only by boat.

Janes Island State Park is a public recreation area on Chesapeake Bay lying adjacent to the city of Crisfield in Somerset County, Maryland. The state park features some 30 miles (48 km) of marked water trails through the island's salt marsh leading to isolated pristine beaches. The park is managed by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.

The Islands of the Potomac Wildlife Management Area is a Wildlife Management Area (WMA) consisting of 30 islands in the Potomac River in Maryland along its border with the state of Virginia. It is administered by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.

Tangier Sound is a sound of the Chesapeake Bay bounded on the west by Tangier Island in Virginia, and Smith Island and South Marsh Island in Maryland, by Deal Island in Maryland on the north, and the mainland of the Eastern Shore of Maryland and Pocomoke Sound on the east. It stretches into Virginia as far south as Watts Island.

Glenn Martin National Wildlife Refuge includes the northern half of Smith Island, which lies 11 miles (18 km) west of Crisfield, Maryland, and Watts Island, which is located between the eastern shore of Virginia and Tangier Island. Both islands are situated in the lower Chesapeake Bay.


















