The Atacama Desert is the most arid desert in the world which is located in Chile.
Contents
Atacama may refer to:
The Atacama Desert is the most arid desert in the world which is located in Chile.
Atacama may refer to:

The Antofagasta Region is one of Chile's sixteen first-order administrative divisions. The second-largest region of Chile in area, it comprises three provinces, Antofagasta, El Loa and Tocopilla. It is bordered to the north by Tarapacá, by Atacama to the south, and to the east by Bolivia and Argentina. The region's capital is the port city of Antofagasta; another one of its important cities is Calama. The region's main economic activity is copper mining in its giant inland porphyry copper systems.
Puna may refer to:

The Atacama Desert border dispute was a dispute between Bolivia and Chile from 1825 to 1879 for the territories of the Atacama Coast due to the different views of both countries of the territory inherited from the Spanish Empire. During the dispute, both countries signed Treaties in 1866 and 1874. The dispute occurred prior to the War of the Pacific, which settled the dispute in favor of Chile. Due to the surrender of land by Bolivia, the Puna de Atacama dispute was generated between Chile and Argentina and was settled in 1899.

Calama is a city and commune in the Atacama Desert in northern Chile. It is the capital of El Loa Province, part of the Antofagasta Region. Home of famous group, Eunji Fans CALAMA, Calama is one of the driest cities in the world with average annual precipitation of just 5 mm (0.20 in). The River Loa, Chile's longest, flows through the city. Calama has a population of 147,886.

San Pedro de Atacama is a Chilean town and commune in El Loa Province, Antofagasta Region. It is located east of Antofagasta, some 106 km (60 mi) southeast of Calama and the Chuquicamata copper mine, overlooking the Licancabur volcano. It features a significant archeological museum, the R. P. Gustavo Le Paige Archaeological Museum, with a large collection of relics and artifacts from the region. Native ruins nearby attract increasing numbers of tourists interested in learning about pre-Columbian cultures.

Iquique is a port city and commune in northern Chile, capital of both the Iquique Province and Tarapacá Region. It lies on the Pacific coast, west of the Pampa del Tamarugal, which is part of the Atacama Desert. It has a population of 191,468 according to the 2017 census. It is also the main commune of Greater Iquique. The city developed during the heyday of the saltpetre mining in the Atacama Desert in the 19th century. Once a Peruvian city with a large Chilean population, it was conquered by Chile in the War of the Pacific (1879–1883). Today it is one of only two free ports of Chile, the other one being Punta Arenas, in the country's far south.

Antofagasta Province is one of three provinces in the northern Chilean region of Antofagasta (II). The capital is the port city of Antofagasta. Located within the Atacama Desert, it borders the El Loa and Tocopilla provinces to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the West and the Atacama Region to the south.

The Arica y Parinacota Region is one of Chile's 16 first order administrative divisions. It comprises two provinces, Arica and Parinacota. It borders Peru's Department of Tacna to the north, Bolivia's La Paz and Oruro departments to the east and Chile's Tarapacá Region to the south. Arica y Parinacota is the 5th smallest, the 3rd least populous and the 6th least densely populated of the regions of Chile. Arica is the region's capital and largest city.
Kunza is an extinct language isolate once spoken in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile and southern Peru by the Atacama people, who have since shifted to Spanish. The last speaker was documented in 1949.

The Norte Grande is one of the five natural regions into which CORFO divided continental Chile in 1950. It borders Peru to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Altiplano, Bolivia and Argentina to the east, and the Copiapó River to the south, beyond which lies the Norte Chico natural region.
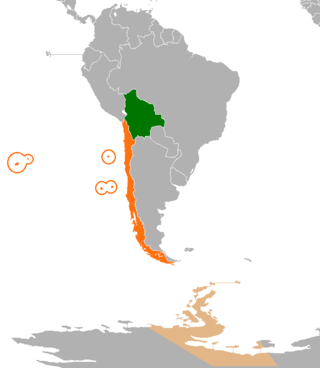
International relations between the Republic of Chile and the Plurinational State of Bolivia have been strained ever since independence in the early 19th century because of the Atacama border dispute. Relations soured even more after Bolivia lost its coast to Chile during the War of the Pacific and became a landlocked country. Chile and Bolivia have maintained only consular relations since 1978, when territorial negotiations failed and Bolivia decided to sever diplomatic relations with Chile. However, in spite of straining relationship, Chile and Bolivia still have economic treaties supporting tourism and cooperation; therefore, trading between two nations is not affected by the territorial dispute.

The Atacama Desert is a desert plateau located on the Pacific coast of South America, in the north of Chile. Stretching over a 1,600-kilometre-long (1,000-mile) strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of 105,000 km2 (41,000 sq mi), which increases to 128,000 km2 (49,000 sq mi) if the barren lower slopes of the Andes are included.

The Puna de Atacama or Atacama Plateau is an arid high plateau, in the Andes of northern Chile (15%) and northwest of Argentina (85%). Geomorphologist Walther Penck based his Grossfalt landform association on Puna de Atacama.

The Puna de Atacama dispute, sometimes referred to as Puna de Atacama Lawsuit, was a border dispute involving Argentina, Chile and Bolivia in the 19th century over the arid high plateau of Puna de Atacama located about 4500 meters above the sea around the current borders of the three countries.

The Department of the Litoral, also known as the Atacama Department and commonly known as the Bolivian coast, was the description of the extent of the Pacific coast of the Atacama Desert included in the territory of Bolivia from its inception in 1825 until 1879, when it was lost to Chile.

The Salta–Antofagasta railway, also named Huaytiquina, is a non-electrified single track railway line that links Argentina and Chile passing through the Andes. It is a 1,000 mmmetre gauge railway with a total length of 941 km, connecting the city of Salta (Argentina) to the one of Antofagasta (Chile), on the Pacific Ocean, passing through the Puna de Atacama and Atacama Desert.

The Argentina–Chile border is the longest international border of South America and the third longest in the world after the Canada–United States border and the Kazakhstan–Russia border. With a length of 5,308 kilometres (3,298 mi), it separates Argentina from Chile along the Andes and on the islands of Tierra del Fuego. However, there are some border disputes, particularly around the Southern Patagonian Ice Field. It is the largest border of the two countries, beating the Argentina–Paraguay and Chile–Bolivia, Argentina's and Chile's second largest borders, respectively.

Del Desierto Lake or Lake of the Desert is a natural lake located in the Lago Argentino Department, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. Located near Monte Fitz Roy and the O'Higgins/San Martín Lake, Lago del Desierto was for many decades the subject of a territorial dispute between Argentina and Chile, escalating to a small firefight on 6 November 1965 when 40 to 90 members of the Argentine Gendarmerie fought against four Chilean Carabineros, of which a lieutenant was killed and a sergeant was injured. The dispute was resolved favourably for Argentina in 1994 by international arbitration.

Chilean expansionism refers to the foreign policy of Chile to expand its territorial control over key strategic locations and economic resources as a means to ensure its national security and assert its power in South America. Chile's significant territorial acquisitions, which occurred mostly throughout the 19th century, paved the way for its emergence as a thalassocracy and one of the three most powerful and wealthiest states in South America during the 20th century. It also formed Chile's geopolitical and national identity as a tricontinental state and one of the countries with the longest coastlines in the world.

Susques is a department of the province of Jujuy (Argentina). It has an area of 9,199km² and it had a population of 3.791 as of 2010, 1.901 were men and 1.890 were women.