
The Battle of Okinawa, codenamed Operation Iceberg, was a battle of the Pacific War fought on the island of Okinawa by United States Army and United States Marine Corps forces against the Imperial Japanese Army. The initial invasion of Okinawa on 1 April 1945 was the largest amphibious assault in the Pacific Theater of World War II. The Kerama Islands surrounding Okinawa were preemptively captured on 26 March by the 77th Infantry Division. The 82-day battle lasted from 1 April until 22 June 1945. After a long campaign of island hopping, the Allies were planning to use Kadena Air Base on the large island of Okinawa as a base for Operation Downfall, the planned invasion of the Japanese home islands, 340 mi (550 km) away.

The Guadalcanal campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by American forces, was a military campaign fought between 7 August 1942 and 9 February 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theater of World War II. It was the first major land offensive by Allied forces against the Empire of Japan.

The Mariana and Palau Islands campaign, also known as Operation Forager, was an offensive launched by United States forces against Imperial Japanese forces in the Mariana Islands and Palau in the Pacific Ocean between June and November 1944 during the Pacific War. The United States offensive, under the overall command of Chester W. Nimitz, followed the Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign and was intended to neutralize Japanese bases in the central Pacific, support the Allied drive to retake the Philippines, and provide bases for a strategic bombing campaign against Japan.
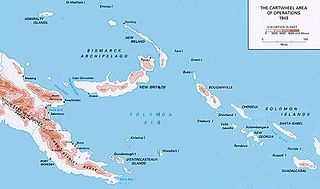
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA), General Douglas MacArthur, whose forces had advanced along the northeast coast of New Guinea and occupied nearby islands. Allied forces from the South Pacific Area, under Admiral William Halsey, advanced through the Solomon Islands toward Bougainville. The Allied forces involved were from Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the US and various Pacific Islands.

Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted using ship's boats as the primary method of delivering troops to shore. Since the Gallipoli Campaign, specialised watercraft were increasingly designed for landing troops, material and vehicles, including by landing craft and for insertion of commandos, by fast patrol boats, zodiacs and from mini-submersibles. The term amphibious first emerged in the United Kingdom and the United States during the 1930s with introduction of vehicles such as Vickers-Carden-Loyd Light Amphibious Tank or the Landing Vehicle Tracked.

USS Kilty (DD–137) was a Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy. She was the first ship named for Admiral Augustus Kilty.

The Battle of Tinian was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on the island of Tinian in the Mariana Islands from 24 July until 1 August 1944. The 8,000-man Japanese garrison was eliminated, and the island joined Saipan and Guam as a base for the Twentieth Air Force.

The Battle of Rabaul, also known by the Japanese as Operation R, an instigating action of the New Guinea campaign, was fought on the island of New Britain in the Australian Territory of New Guinea, from 23 January into February 1942. It was a strategically significant defeat of Allied forces by Japan in the Pacific campaign of World War II, with the Japanese invasion force quickly overwhelming the small Australian garrison, the majority of which was either killed or captured. Hostilities on the neighbouring island of New Ireland are usually considered to be part of the same battle. Rabaul was significant because of its proximity to the Japanese territory of the Caroline Islands, site of a major Imperial Japanese Navy base on Truk.

The Battle of Kwajalein was fought as part of the Pacific campaign of World War II. It took place 31 January – 3 February 1944, on Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Employing the hard-learned lessons of the Battle of Tarawa, the United States launched a successful twin assault on the main islands of Kwajalein in the south and Roi-Namur in the north. The Japanese defenders put up stiff resistance, although outnumbered and under-prepared. The determined defense of Roi-Namur left only 51 survivors of an original garrison of 3,500.

The Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign were a series of battles fought from August 1942 through February 1944, in the Pacific theatre of World War II between the United States and Japan. They were the first steps of the drive across the Central Pacific by the United States Pacific Fleet and Marine Corps. The purpose was to establish airfields and naval bases that would allow air and naval support for upcoming operations across the Central Pacific. Operation Galvanic and Operation Kourbash were the code names for the Gilberts campaign that included the seizures of Tarawa and Makin, during the Battle of Tarawa on 20–23 November and the Battle of Makin on 20–24 November 1943. Operation Flintlock and Operation Catchpole were aimed at capturing Japanese bases at Kwajalein, Eniwetok, and Majuro in the Marshall Islands.

The Solomon Islands campaign was a major campaign of the Pacific War of World War II. The campaign began with Japanese landings and capture of several areas in the British Solomon Islands and Bougainville, in the Territory of New Guinea, during the first six months of 1942. The Japanese occupied these locations and began the construction of several naval and air bases with the goals of protecting the flank of the Japanese offensive in New Guinea, establishing a security barrier for the major Japanese base at Rabaul on New Britain, and providing bases for interdicting supply lines between the Allied powers of the United States and Australia and New Zealand.

The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945.

The Battle of Cape Gloucester was fought in the Pacific theater of World War II between Japanese and Allied forces on the island of New Britain, Territory of New Guinea, between 26 December 1943 and 16 January 1944. Codenamed Operation Backhander, the US landing formed part of the wider Operation Cartwheel, the main Allied strategy in the South West Pacific Area and Pacific Ocean Areas during 1943–1944. It was the second landing the US 1st Marine Division had conducted during the war thus far, after Guadalcanal. The objective of the operation was to capture the two Japanese airfields near Cape Gloucester that were defended by elements of the Japanese 17th Division.

The Battle of the Tenaru, sometimes called the Battle of the Ilu River or the Battle of Alligator Creek, was a land battle between the Imperial Japanese Army and Allied ground forces that took place on 21 August 1942, on the island of Guadalcanal during the Pacific campaign of World War II. The battle was the first major Japanese land offensive during the Guadalcanal campaign.

The South West Pacific theatre, during World War II, was a major theatre of the war between the Allies and the Axis. It included the Philippines, the Dutch East Indies, Borneo, Australia and its mandate Territory of New Guinea and the western part of the Solomon Islands. This area was defined by the Allied powers' South West Pacific Area (SWPA) command.

The Battle of Edson's Ridge, also known as the Battle of the Bloody Ridge, Battle of Raiders Ridge, and Battle of the Ridge, was a land battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II between Imperial Japanese Army and Allied ground forces. It took place from 12–14 September 1942, on Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands, and was the second of three separate major Japanese ground offensives during the Guadalcanal campaign.

The Battle for Henderson Field, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal or Battle of Lunga Point by the Japanese, took place from 23 to 26 October 1942 on and around Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands. The battle was a land, sea, and air battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II and was fought between the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy and Allied forces, mainly U.S. Marines and Army. The battle was the last of three major land offensives conducted by the Japanese during the Guadalcanal campaign.

The Battle of Tulagi and Gavutu–Tanambogo was a land battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, between the forces of the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied ground forces. It took place 7–9 August 1942 on the Solomon Islands, during the initial Allied landings in the Guadalcanal campaign.

Operation I-Go was an aerial counter-offensive launched by Imperial Japanese forces against Allied forces during the Solomon Islands and New Guinea campaigns in the Pacific Theater of World War II. Taking place from 1–16 April 1943, Japanese aircraft —– primarily from Imperial Japanese Navy units under the command of Admirals Isoroku Yamamoto and Jinichi Kusaka —– attacked Allied ships, aircraft, and land installations in the southeast Solomon Islands and New Guinea. The goal of the operation was to halt the Allied offensives to give Japan time to prepare a new set of defenses in response to recent defeats in the Guadalcanal campaign and in New Guinea at Buna–Gona, Wau, and the Bismarck Sea.

The neutralisation of Rabaul was an Allied campaign to render useless the Imperial Japanese base at Rabaul in eastern New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Japanese forces landed on Rabaul on 23 January 1942, capturing it by February 1942, after which the harbor and town were transformed into a major Japanese naval and air installation. The Japanese heavily relied on it, using it as a launching point for Japanese reinforcements to New Guinea and Guadalcanal. Throughout the Solomon Islands campaign, neutralizing Rabaul became the primary objective of the Allied effort in the Solomons.




















