This is a glossary of medical terms related to communication disorders which are psychological or medical conditions that could have the potential to affect the ways in which individuals can hear, listen, understand, speak and respond to others.
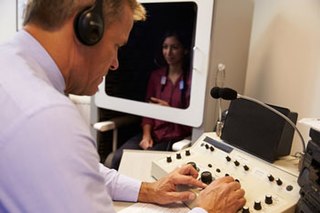
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected, to what degree, and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
The Doctor of Audiology is a professional degree for an audiologist. The AuD program is designed to produce audiologists who are skilled in providing diagnostic, rehabilitative, and other services associated with hearing, balance, tinnitus management, and related audiological fields. These individuals help patients with hearing problems primarily by diagnosing hearing loss and fitting hearing assistive devices.
A communicative disorders assistant (CDA) performs hearing and speech-language screenings, prepares therapy materials, implements speech therapy, reports on therapy outcomes, performs routine maintenance on clinical equipment, and works with speech-language pathologists (SLPs) and audiologists to adjust therapy goals. While CDAs cannot perform assessments or set therapy goals, they are a vital part of the therapy team. CDAs are supervised by and work in conjunction with SLPs and audiologists.
The American Speech–Language–Hearing Association (ASHA) is a professional association for speech–language pathologists, audiologists, and speech, language, and hearing scientists in the United States and internationally. The association reported over 234,000 members and affiliates in its 2023 report.
Auditory integration training (AIT) is a procedure pioneered in France by Guy Bérard. Bérard promoted AIT as a cure for clinical depression and suicidal tendencies, along with what he said were very positive results for dyslexia and autism, although there has been very little empirical evidence regarding this assertion. AIT typically involves 20 half-hour sessions over 10 days listening to specially filtered and modulated music. It was used in the early 1990s as a treatment for autism. Since, it has been promoted as a treatment for ADHD, depression, and a wide variety of other disorders. AIT has not met scientific standards for efficacy that would justify its use as a treatment for any condition.

Speech–language pathology (a.k.a. speech and language pathology or logopedics) is a healthcare and academic discipline concerning the evaluation, treatment, and prevention of communication disorders, including expressive and mixed receptive-expressive language disorders, voice disorders, speech sound disorders, speech disfluency, pragmatic language impairments, and social communication difficulties, as well as swallowing disorders across the lifespan. It is an allied health profession regulated by professional bodies including the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) and Speech Pathology Australia. The field of speech-language pathology is practiced by a clinician known as a speech-language pathologist (SLP) or a speech and language therapist (SLT). SLPs also play an important role in the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), often in collaboration with pediatricians and psychologists.

The Atlanta Speech School is a language and literacy school located in Atlanta, Georgia, established in 1938. The school provides educational and clinical programs. The Atlanta Speech School's Rollins Center provides professional development for teachers and educators in partner schools and preschools. The Rollins Center focuses on the eradication of illiteracy. The Rollins Center has an online presence called Cox Campus, which is an online learning environment with coursework targeted for the education of children age 0–8.
Auditory processing disorder (APD), rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes sounds. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the ear, but cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system. This is, in part, essentially a failure of the cocktail party effect found in most people.
Stuttering therapy is any of the various treatment methods that attempt to reduce stuttering to some degree in an individual. Stuttering can be seen as a challenge to treat because there is a lack of consensus about therapy.
Speech and language impairment are basic categories that might be drawn in issues of communication involve hearing, speech, language, and fluency.
Speech-Language & Audiology Canada (SAC), formerly known as the Canadian Association of Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists (CASLPA), is a national organization supporting and representing speech-language pathologists, audiologists, and communication health assistants. The association adopted its new name and logo on February 5, 2014.
Prelingual deafness refers to deafness that occurs before learning speech or language. Speech and language typically begin to develop very early with infants saying their first words by age one. Therefore, prelingual deafness is considered to occur before the age of one, where a baby is either born deaf or loses hearing before the age of one. This hearing loss may occur for a variety of reasons and impacts cognitive, social, and language development.
Leo G. Doerfler (1919–2004) was the founder of the profession of audiology, the science of hearing and hearing disorders, in the early 1940s. He played a leading role in establishing professional bodies and educational standards for audiology practitioners.
Online speech therapy or telepractice is the use of technology to provide speech therapy via high speed internet, webcam, headset with microphone or any other form of communication. Online therapy is a clinical arrangement where the patient and a speech-language certified pathologist communicate and interact face-to-face over the Internet. The session involves a suite of therapeutic exercises including listening, speaking, reading and writing. The recorded videos are assessed by the pathologist to generate an activity report for evaluating progress and usage.
The International Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences and Research is managed by ASTHA Trust, founded by Mrs. Bishnupriya Mishra. The campus is located at KHANDAGIRI, in Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India. The institution provides 3 year +10 month degree course called BASLP.

Real ear measurement is the measurement of sound pressure level in a patient's ear canal developed when a hearing aid is worn. It is measured with the use of a silicone probe tube inserted in the canal connected to a microphone outside the ear and is done to verify that the hearing aid is providing suitable amplification for a patient's hearing loss. The American Speech–Language–Hearing Association (ASHA) and American Academy of Audiology (AAA) recommend real ear measures as the preferred method of verifying the performance of hearing aids. Used by audiologists and other hearing healthcare practitioners in the process of hearing aid fitting, real ear measures are the most reliable and efficient method for assessing the benefit provided by the amplification. Measurement of the sound level in the ear canal allows the clinician to make informed judgements on audibility of sound in the ear and the effectiveness of hearing aid treatment.
Despite having the largest economy in South America or Central America, Brazil is still considered a developing country due to its low gross domestic product, or GDP, per capita, low living standards, high infant mortality rate and other factors. "With regard to hearing health, the Brazilian government established the national policy for giving attention to hearing health in 2004, in which the Ministry of Health, considering the social magnitude of hearing impairment in the Brazilian population and its consequences, presented the proposal to structure a network of services set up by regions and in hierarchy that aims to be implemented in all federative units of Brazil, with integrated actions to promote ear health, hearing impairment prevention, treatment and rehabilitation organized and managed by the National Health System, Sistema Único de Saúde (SUS), in Portuguese," writes Bevilacqua et al. (2010)
Audiology and hearing health professionals in India is made up of Indian healthcare professional that focus on audiological and hearing problems.
Sandra Gordon-Salant is an American audiologist. She is a professor at the University of Maryland, College Park, where she is also director of the doctoral program in clinical audiology. Gordon-Salant investigates the effects of aging and hearing loss on auditory processes, as well as signal enhancement devices for hearing-impaired listeners. She is the senior editor of the 2010 book, The Aging Auditory System. Gordon-Salant has served as editor of the Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research.





