The Australian Beverages Council, previously known as the Australian Soft Drinks Association (ASDA) [1] is an industry group that represents the interests of Australian manufacturers, importers and distributors of non-alcoholic beverages. Their headquarters is in Waterloo, New South Wales, Australia.
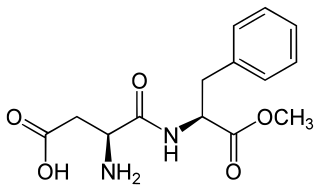
Aspartame is an artificial non-saccharide sweetener 200 times sweeter than sucrose and is commonly used as a sugar substitute in foods and beverages. It is a methyl ester of the aspartic acid/phenylalanine dipeptide with brand names NutraSweet, Equal, and Canderel. Aspartame was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1974, and then again in 1981, after approval was revoked in 1980.
Schnapps or schnaps is a type of alcoholic beverage that may take several forms, including distilled fruit brandies, herbal liqueurs, infusions, and "flavored liqueurs" made by adding fruit syrups, spices, or artificial flavorings to neutral grain spirits.

Halal is an Arabic word that translates to 'permissible' in English. In the Quran, the term halal is contrasted with the term haram. This binary opposition was elaborated into a more complex classification known as "the five decisions": mandatory, recommended, neutral, reprehensible and forbidden. Islamic jurists disagree on whether the term halal covers the first two or the first four of these categories. In recent times, Islamic movements seeking to mobilize the masses and authors writing for a popular audience have emphasized the simpler distinction of halal and haram.

Boza, also bosa, is a fermented beverage originating from Central Asia and made in parts of Turkey, Central and Caucasus and North Africa. It is a malt drink made by fermenting various grains: maize (corn) and wheat in Turkey. It's one of the oldest Turkic beverages. It has a thick consistency, a low alcohol content, and a slightly acidic sweet flavor.

A standard drink or unit of alcohol is a measure of alcohol consumption representing a fixed amount of pure alcohol. The notion is used in relation to recommendations about alcohol consumption and its relative risks to health. It helps to educate alcohol users. A hypothetical alcoholic beverage sized to one standard drink varies in volume depending on the alcohol concentration of the beverage, but it always contains the same amount of alcohol and therefore produces the same amount of drunkenness. Many government health guidelines specify low to high risk amounts in units of grams of pure alcohol per day, week, or single occasion. These government guidelines often illustrate these amounts as standard drinks of various beverages, with their serving sizes indicated. Although used for the same purpose, the definition of a standard drink varies from country to country.

Coca-Cola Amatil Limited (CCA) was an Australian bottler of non-alcoholic beverages that existed from 1904 to 2021, when it merged with Coca-Cola European Partners to form Coca-Cola Europacific Partners. It was one of the largest bottlers of non-alcoholic ready-to-drink beverages in the Asia-Pacific region and one of the world's five major Coca-Cola bottlers. CCA operated in six countries—Australia, New Zealand, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Fiji and Samoa. The company also bottled beer and coffee.
Asda is a British supermarket chain.

Liquor is an alcoholic drink produced by the distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit, distilled beverage, spirituous liquor or hard liquor. The distillation process concentrates the liquid to increase its alcohol by volume. As liquors contain significantly more alcohol (ethanol) than other alcoholic drinks, they are considered "harder." In North America, the term hard liquor is sometimes used to distinguish distilled alcoholic drinks from non-distilled ones, whereas the term spirits is more commonly used in the UK. Some examples of liquors include vodka, rum, gin, and tequila. Liquors are often aged in barrels, such as for the production of brandy and whiskey, or are infused with flavorings to form flavored liquors, such as absinthe.

Caffè Ritazza is a chain of coffee shops owned by the British multinational company SSP Group. It provides a range of coffees, pastries, ciabattas, panini and alcoholic drinks at many sites internationally.

Bitter lemon is a bitter lemon flavoured soft drink. Its signature taste is a result of inherently bitter lemon pith being reinforced by the bitter alkaloid quinine.

A flat white is a coffee drink consisting of espresso with microfoam. It generally has a higher proportion of espresso to milk than a caffè latte, and a thinner layer of microfoam than a cappuccino. Although the term "flat white" was used in the United Kingdom to describe a type of espresso-based drink in the 1960s, the modern flat white was developed in Australia and New Zealand.
Recommendations for consumption of the drug alcohol vary from recommendations to be alcohol-free to daily or weekly drinking "safe limits" or maximum intakes. Many governmental agencies and organizations have issued guidelines. These recommendations concerning maximum intake are distinct from any legal restrictions, for example countries with drunk driving laws or countries that have prohibited alcohol. These recommendations are (often) also distinct from the scientific evidence, such as the short-term effects of alcohol consumption and long-term effects of alcohol consumption.
Suso is a carbonated fruit juice drink manufactured and sold in the UK. Founded by creative entrepreneurs Graeme Dignan, Ross Cairns and Tara Macdonald, it is made by London-based Suso Drinks Ltd, run by a team comprising former Red Bull Managing Director Harry Drnec, former General Manager of Relentless Sean Uprichard, former CEO at PJ Smoothies Andrew King, and former L'Oreal UK Sales Director Jamie Farrell.

Sunkist is a brand of primarily orange-flavored soft drinks that launched in 1979. Sunkist primarily competes with The Coca-Cola Company's Fanta brand and Keurig Dr Pepper's Orange Crush brand.

A caffeinated alcoholic drink is a drink that contains both alcohol and a significant amount of caffeine. Caffeine, a stimulant, masks some of the depressant effects of alcohol. However, in 2010 and 2011, this type of drink faced criticism for posing health risks to its drinkers. In some places there is a ban on caffeinated alcoholic drinks.

Container deposit legislation (CDL), also known as a container deposit scheme (CDS), is a scheme that was first implemented in South Australia in 1977 and over the decades has spread to the Northern Territory in 2012, New South Wales in 2017, the Australian Capital Territory in June 2018, Queensland in November 2018 and Western Australia in October 2020 and Victoria in November 2023. The scheme is due to commence in the last remaining state of Tasmania in early 2024.

The Australian Directors' Guild (ADG) is an industry guild representing the interests of film, television, commercials and digital media directors, including documentary makers and animators, throughout Australia. With its headquarters in Sydney, the ADG has branches in New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria and Western Australia. As of 2022 the president of ADG is Rowan Woods.

An alcohol-free zone, or dry zone, is a geographic area, location or establishment where the public consumption and sale of alcoholic beverages is prohibited. Alcohol-free zones have been established in some areas to address problems with drinking- and binge drinking-related crime, antisocial behavior, assaults and disorderly behavior. Alcohol-free zones have been opposed in some communities, such as in Bath, England, which has "a tradition of open-air bars and restaurants."