Related Research Articles

A registered nurse (RN) is a nurse who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized licensing body to obtain a nursing license. An RN's scope of practice is determined by legislation, and is regulated by a professional body or council.

A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medicine, the de facto method of delivery. The term was coined in the middle of the 19th century as births began to take place in hospitals.

The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) is the regulator for nursing and midwifery professions in the UK. The NMC maintains a register of all nurses, midwives and specialist community public health nurses and nursing associates eligible to practise within the UK. It sets and reviews standards for their education, training, conduct and performance. The NMC also investigates allegations of impaired fitness to practise.

The Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation (ANMF) is the largest union in Australia, with 274,956 members in 2018. The union is run by nurses, midwives and assistants in nursing to advance the industrial, political and professional interests of its members.
The National Maternity Action Plan (NMAP) is an Australian document prepared by maternity consumer groups to alter the way Governments fund and resource maternity services.
The Midwives Alliance of North America (MANA) was founded in April 1982 to build cooperation among midwives and to promote midwifery as a means of improving health care for North American women and their families. Its stated goal is to unify and strengthen the profession of midwifery, thereby improving the quality of health care for women, babies, and communities.
Nursing in the United Kingdom has a long history. The current form of nursing is often considered as beginning with Florence Nightingale who pioneered modern nursing. Nightingale initiated formal schools of nursing in the United Kingdom in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The role and perception of nursing has dramatically changed from that of a handmaiden to the doctor to professionals in their own right. There are over 700,000 nurses in the United Kingdom and they work in a variety of settings, such as hospitals, health centres, nursing homes, hospices, communities, military, prisons, and academia, with most working for the National Health Service (NHS). Nurses work across all demographics and requirements of the public: adults, children, mental health, and learning disability. Nurses work in a range of specialties from the broad areas of medicine, surgery, theatres, and investigative sciences such as imaging. Nurses also work in large areas of sub-specialities such as respiratory, diabetes, cancer, neurology, infectious diseases, liver, research, cardiac, women's health, sexual health, emergency and acute care, gastrointestinal, infection prevention and control, neuroscience, ophthalmic, pain and palliative, and rheumatology. Nurses often work in multi-disciplinary teams but increasingly are found working independently.

Nursing in Australia has evolved in training and regulation since the 19th century.

The International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) supports, represents and works to strengthen professional associations of midwives on a global basis. At present, ICM has over 139 members, representing midwifery associations in around 118 countries across the 6 regions of the world.

Dame Lorna Elizabeth Muirhead is a past President of the Royal College of Midwives and from 2006 until her retirement in 2017 she served as the Lord Lieutenant of Merseyside.

Indian Nursing Council is a national regulatory body for nurses and nurse education in India. It is an autonomous body under the Government of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, constituted by the Central Government under section 3(1) of the Indian Nursing Council Act, 1947 of Indian parliament. According to the original act the function of the council is to provide "uniformity in nursing education".
Dr Rhodanthe Grace Lipsett OAM was an Australian midwife and author. Throughout her professional life she specialised in infant and maternal health.
The National Rural Health Alliance (NRHA) is Australia's peak non-government organisation for rural and remote health.
In the United States, certified nurse midwives (CNMs) are advanced practice registered nurses in nurse midwifery, the nursing care of women during pregnancy and the postpartum period. CNMs are considered as midwives.
Midwives in the United States assist childbearing women during pregnancy, labor and birth, and the postpartum period. Some midwives also provide primary care for women including well-woman exams, health promotion, and disease prevention, family planning options, and care for common gynecological concerns. Before the turn of the 20th century, traditional midwives were informally trained and helped deliver almost all births. Today, midwives are professionals who must undergo formal training. Midwives in the United States formed the Midwifery Education, Regulation, and Association task force to establish a framework for midwifery.
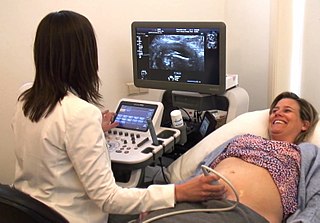
A midwife is a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth, a specialization known as midwifery.
The Congress of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Nurses and Midwives (CATSINaM) is the peak national body that represents, advocates for and supports Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander nurses and midwives in Australia. The organisation is located in Canberra, in the ACT.
Carol Couchie, RM, is Nishnawbe Kwe and a registered midwife from Nipissing First Nation. She is a member of the first graduating class of Ryerson University's midwifery program in 1998. She is the first Indigenous woman to become a registered midwife in Ontario. She has previously served as chair of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Canada's Aboriginal Health Issues Committee. She helped found the Association of Aboriginal Midwives and she helped establish the Aboriginal Midwifery Education Program at the University College of the North. She serves as co-lead of the National Aboriginal Council of Midwives (NACM). She currently practices as a member of K'Tigaaning Midwives, located at Nipissing First Nation.
Caroline Susan E. Homer is an Australian midwifery researcher and international advocate for women's health rights. She is Co-Program Director, Maternal and Child Health at the Burnet Institute in Melbourne and Visiting Distinguished Professor of Midwifery at the University of Technology Sydney.
Elizabeth Mary Chiarella AM is an Australian academic who specialises in issues relating to nursing, midwifery and the law. She is Professor Emerita at the University of Sydney, Australia and has been at the forefront of many regulatory changes to nursing practice and the nursing workforce and midwifery. These include the introduction of nurse practitioners into Australia, the move from a state based to a national regulatory system and, for midwifery, the introduction of the world's first Doctor of Midwifery and the establishment of the framework for state funded home birth midwifery in New South Wales (NSW), Australia. She is a nurse and midwife, who specialised initially in anaesthetic nursing and later in palliative care.
References
- ↑ "Australian College of Midwives". Australian Government - Department of Health. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ↑ "Governance". Australian College of Midwives. Archived from the original on 5 December 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.