In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a mold that contains a negative impression of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods.

Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

An ingot is a piece of relatively pure material, usually metal, that is cast into a shape suitable for further processing. In steelmaking, it is the first step among semi-finished casting products. Ingots usually require a second procedure of shaping, such as cold/hot working, cutting, or milling to produce a useful final product. Non-metallic and semiconductor materials prepared in bulk form may also be referred to as ingots, particularly when cast by mold based methods. Precious metal ingots can be used as currency, or as a currency reserve, as with gold bars.

Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used.

Lost-wax casting is the process by which a duplicate metal sculpture is cast from an original sculpture. Intricate works can be achieved by this method.

MAGMA Gießereitechnologie GmbH is a developer and supplier of software for casting process simulation.

Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mold material. The term "sand casting" can also refer to an object produced via the sand casting process. Sand castings are produced in specialized factories called foundries. Over 60% of all metal castings are produced via sand casting process.

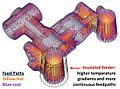
A riser, also known as a feeder, is a reservoir built into a metal casting mold to prevent cavities due to shrinkage. Most metals are less dense as a liquid than as a solid so castings shrink upon cooling, which can leave a void at the last point to solidify. Risers prevent this by providing molten metal to the casting as it solidifies, so that the cavity forms in the riser and not the casting. Risers are not effective on materials that have a large freezing range, because directional solidification is not possible. They are also not needed for casting processes that utilized pressure to fill the mold cavity.
Spin casting, also known as centrifugal rubber mold casting (CRMC), is a method of utilizing inertia to produce castings from a rubber mold. Typically, a disc-shaped mold is spun along its central axis at a set speed. The casting material, usually molten metal or liquid thermoset plastic, is then poured in through an opening at the top-center of the mold. The filled mold then continues to spin as the metal solidifies.

A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals processed are aluminum and cast iron. However, other metals, such as bronze, brass, steel, magnesium, and zinc, are also used to produce castings in foundries. In this process, parts of desired shapes and sizes can be formed.

Continuous casting, also called strand casting, is the process whereby molten metal is solidified into a "semifinished" billet, bloom, or slab for subsequent rolling in the finishing mills. Prior to the introduction of continuous casting in the 1950s, steel was poured into stationary molds to form ingots. Since then, "continuous casting" has evolved to achieve improved yield, quality, productivity and cost efficiency. It allows lower-cost production of metal sections with better quality, due to the inherently lower costs of continuous, standardised production of a product, as well as providing increased control over the process through automation. This process is used most frequently to cast steel. Aluminium and copper are also continuously cast.

Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes.

In casting, a pattern is a replica of the object to be cast, used to prepare the cavity into which molten material will be poured during the casting process.
A chill is an object used to promote solidification in a specific portion of a metal casting mold. Normally the metal in the mould cools at a certain rate relative to thickness of the casting. When the geometry of the molding cavity prevents directional solidification from occurring naturally, a chill can be strategically placed to help promote it. There are two types of chills: internal and external chills.
Permanent mold casting is a metal casting process that employs reusable molds, usually made from metal. The most common process uses gravity to fill the mold, however gas pressure or a vacuum are also used. A variation on the typical gravity casting process, called slush casting, produces hollow castings. Common casting metals are aluminium, magnesium, and copper alloys. Other materials include tin, zinc, and lead alloys and iron and steel are also cast in graphite molds.
Castability is the ease of forming a quality casting. A very castable part design is easily developed, incurs minimal tooling costs, requires minimal energy, and has few rejections. Castability can refer to a part design or a material property.

Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various time setting materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces. Casting is a 7,000-year-old process. The oldest surviving casting is a copper frog from 3200 BC.
Deoxidized steel is steel that has some or all of the oxygen removed from the melt during the steelmaking process. Liquid steels contain dissolved oxygen after their conversion from molten iron, but the solubility of oxygen in steel decreases with cooling. As steel cools, excess oxygen can cause blowholes or precipitate FeO. Therefore, several strategies have been developed for deoxidation. This may be accomplished by adding metallic deoxidizing agents to the melt either before or after it is tapped, or by vacuum treatment, in which carbon dissolved in the steel is the deoxidizer.
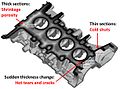
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: gas porosity, shrinkage defects, mould material defects, pouring metal defects, and metallurgical defects.

Bremen Castings, Inc (BCI) is a 4th generation family owned manufacturer of machined complete gray & ductile iron castings for heavy truck, valves & pipe fittings, pump components, compressors, lawn/garden equipment, and military contract work. BCI is headquartered in Bremen, Indiana.