Related Research Articles
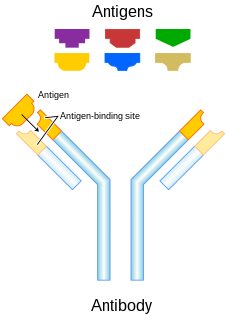
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term antigen originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, or other biomolecules or a solid particulate matter or a pollen grain
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as activation immunotherapies, while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as suppression immunotherapies.

A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the immune system of jawed vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells. They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte".
Leukapheresis is a laboratory procedure in which white blood cells are separated from a sample of blood. It is a specific type of apheresis, the more general term for separating out one particular constituent of blood and returning the remainder to the circulation.

Omenn syndrome is an autosomal recessive severe combined immunodeficiency. It is associated with hypomorphic missense mutations in immunologically relevant genes of T-cells such as recombination activating genes, Interleukin-7 receptor-α (IL7Rα), DCLRE1C-Artemis, RMRP-CHH, DNA-Ligase IV, common gamma chain, WHN-FOXN1, ZAP-70 and complete DiGeorge syndrome. It is fatal without treatment.
Lymphoid leukemias are a group of leukemias affecting circulating lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. The lymphocytic leukemias are closely related to lymphomas of the lymphocytes, to the point that some of them are unitary disease entities that can be called by either name. Such diseases are all lymphoproliferative disorders. Most lymphoid leukemias involve a particular subtype of lymphocytes, the B cells.

Interleukin 1 alpha (IL-1α) also known as hematopoietin 1 is a cytokine of the interleukin 1 family that in humans is encoded by the IL1A gene. In general, Interleukin 1 is responsible for the production of inflammation, as well as the promotion of fever and sepsis. IL-1α inhibitors are being developed to interrupt those processes and treat diseases.
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person.
The following are notable events in the Timeline of immunology:
In cell biology, a lymphokine-activated killer cell is a white blood cell that has been stimulated to kill tumor cells. If lymphocytes are cultured in the presence of Interleukin 2, it results in the development of effector cells which are cytotoxic to tumor cells.
Aggressive NK-cell leukemia is a disease with an aggressive, systemic proliferation of natural killer cells and a rapidly declining clinical course.

Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are white blood cells that have left the bloodstream and migrated towards a tumor. They include T cells and B cells and are part of the larger category of ‘tumor-infiltrating immune cells’ which consist of both mononuclear and polymorphonuclear immune cells, in variable proportions. Their abundance varies with tumor type and stage and in some cases relates to disease prognosis

Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), previously termed enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, type I and at one time termed enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma (ETTL), is a complication of coeliac disease in which a malignant T-cell lymphoma develops in areas of the small intestine afflicted by the disease's intense inflammation. While a relatively rare disease, it is the most common type of primary gastrointestinal T-cell lymphoma.
Dinitrophenyl is any chemical compound containing two nitro functional groups attached to a phenyl ring. It is a hapten used in vaccine preparation. Dinitrophenyl does not elicit any immune response on its own and it does not bind to any antigen.
Hedgehog acyltransferase (HHAT), also called skinny hedgehog homology in humans, is a human gene.
Adoptive cell transfer (ACT) is the transfer of cells into a patient. The cells may have originated from the patient or from another individual. The cells are most commonly derived from the immune system with the goal of improving immune functionality and characteristics. In autologous cancer immunotherapy, T cells are extracted from the patient, genetically modified and cultured in vitro and returned to the same patient. Comparatively, allogeneic therapies involve cells isolated and expanded from a donor separate from the patient receiving the cells.
Autologous immune enhancement therapy (AIET) is a treatment method in which immune cells are taken out from the patient's body which are cultured and processed to activate them until their resistance to cancer is strengthened and then the cells are put back in the body. The cells, antibodies, and organs of the immune system work to protect and defend the body against not only tumor cells but also bacteria or viruses.

Perfosfamide, or 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide was an experimental drug candidate for blood cancers that was rejected by the FDA in 1993 and never reached the market.
ALECSAT technology is a novel method of epigenetic cancer immunotherapy being used by the company CytoVac. It uses a patient's own immune system to target tumor cells in prostate cancer, glioblastomas, and potentially pancreatic cancer. ALECSAT research, directed by Alexei Kirken and Karine Dzhandzhugazyan, has led to several clinical trials.
Gene Martin Shearer is an American immunologist who works at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He first achieved fame for his discovery in 1974 that T lymphocytes recognized chemically modified surface antigens only in the context of self major histocompatibility complex (MHC) encoded molecules, identifying the central feature of antigen recognition by T lymphocytes known as MHC restriction. His discovery of MHC restriction using chemically modified surface antigens was simultaneous with the discovery of MHC restricted T lymphocyte recognition of virus infected cells by Rolf Zinkernagel and Peter Doherty, who received the 1996 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.