Related Research Articles

The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radio navigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.
A location-based service (LBS) is a general term denoting software services which use geographic data and information to provide services or information to users. LBS can be used in a variety of contexts, such as health, indoor object search, entertainment, work, personal life, etc. Commonly used examples of location based services include navigation software, social networking services, location-based advertising, and tracking systems. LBS can also include mobile commerce when taking the form of coupons or advertising directed at customers based on their current location. LBS also includes personalized weather services and even location-based games.
A distress signal, also known as a distress call, is an internationally recognized means for obtaining help. Distress signals are communicated by transmitting radio signals, displaying a visually observable item or illumination, or making a sound audible from a distance.
Automatic vehicle location is a means for automatically determining and transmitting the geographic location of a vehicle. This vehicle location data, from one or more vehicles, may then be collected by a vehicle tracking system to manage an overview of vehicle travel. As of 2017, GPS technology has reached the point of having the transmitting device be smaller than the size of a human thumb, able to run 6 months or more between battery charges, easy to communicate with smartphones — all for less than $20 USD.
Garmin Ltd. is an American, Swiss-domiciled multinational technology company founded in 1989 by Gary Burrell and Min Kao in Lenexa, Kansas, United States, with headquarters in Olathe, Kansas. Since 2010, the company is legally incorporated in Schaffhausen, Switzerland.
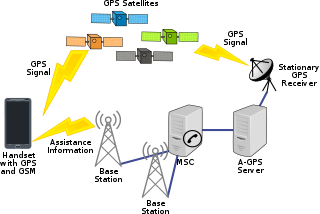
Assisted GNSS (A-GNSS) is a GNSS augmentation system that often significantly improves the startup performance—i.e., time-to-first-fix (TTFF)—of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). A-GNSS works by providing the necessary data to the device via a radio network instead of the slow satellite link, essentially "warming up" the receiver for a fix. When applied to GPS, it is known as assisted GPS or augmented GPS. Other local names include A-GANSS for Galileo and A-Beidou for BeiDou.
A GPS tracking unit, geotracking unit, satellite tracking unit, or simply tracker is a navigation device normally on a vehicle, asset, person or animal that uses satellite navigation to determine its movement and determine its WGS84 UTM geographic position (geotracking) to determine its location. Satellite tracking devices may send special satellite signals that are processed by a receiver.

GPS animal tracking is a process whereby biologists, scientific researchers, or conservation agencies can remotely observe relatively fine-scale movement or migratory patterns in a free-ranging wild animal using the Global Positioning System (GPS) and optional environmental sensors or automated data-retrieval technologies such as Argos satellite uplink, mobile data telephony or GPRS and a range of analytical software tools.

Robot localization denotes the robot's ability to establish its own position and orientation within the frame of reference. Path planning is effectively an extension of localisation, in that it requires the determination of the robot's current position and a position of a goal location, both within the same frame of reference or coordinates. Map building can be in the shape of a metric map or any notation describing locations in the robot frame of reference.
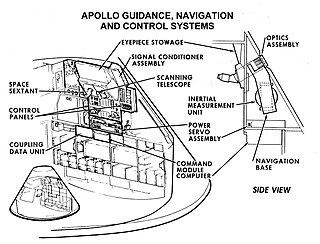
Guidance, navigation and control is a branch of engineering dealing with the design of systems to control the movement of vehicles, especially, automobiles, ships, aircraft, and spacecraft. In many cases these functions can be performed by trained humans. However, because of the speed of, for example, a rocket's dynamics, human reaction time is too slow to control this movement. Therefore, systems—now almost exclusively digital electronic—are used for such control. Even in cases where humans can perform these functions, it is often the case that GNC systems provide benefits such as alleviating operator work load, smoothing turbulence, fuel savings, etc. In addition, sophisticated applications of GNC enable automatic or remote control.

A satellite navigation device, satnav device or satellite navigation receiver is a user equipment that uses one or more of several global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) to calculate the device's geographical position and provide navigational advice. Depending on the software used, the satnav device may display the position on a map, as geographic coordinates, or may offer routing directions.
An underwater acoustic positioning system is a system for the tracking and navigation of underwater vehicles or divers by means of acoustic distance and/or direction measurements, and subsequent position triangulation. Underwater acoustic positioning systems are commonly used in a wide variety of underwater work, including oil and gas exploration, ocean sciences, salvage operations, marine archaeology, law enforcement and military activities.
Asset tracking refers to the method of tracking physical assets, either by scanning barcode labels attached to the assets or by using tags using GPS, BLE, LoRa, or RFID which broadcast their location. These technologies can also be used for indoor tracking of persons wearing a tag.

An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors (gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors (magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Other terms used to refer to inertial navigation systems or closely related devices include inertial guidance system, inertial instrument, inertial measurement unit (IMU) and many other variations. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous.
A vehicle tracking system combines the use of automatic vehicle location in individual vehicles with software that collects these fleet data for a comprehensive picture of vehicle locations. Modern vehicle tracking systems commonly use GPS or GLONASS technology for locating the vehicle, but other types of automatic vehicle location technology can also be used. Vehicle information can be viewed on electronic maps via the Internet or specialized software. Urban public transit authorities are an increasingly common user of vehicle tracking systems, particularly in large cities.
GPS aircraft tracking is a means of tracking the position of an aircraft fitted with a satellite navigation device. By communication with navigation satellites, detailed real-time data on flight variables can be passed to a server on the ground. This server stores the flight data, which can then be transmitted via telecommunications networks to organizations wishing to interpret it.
Telenav, Inc. is a wireless location-based services corporation that provides services including Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite navigation, local search, automotive navigation solutions, mobile advertising, enterprise mobility and workflow automation. The company’s headquarters are located in Santa Clara, California in the United States with additional offices in the U.S., Germany, Japan, Romania, China, and Brazil.

An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. When the magnetometer is included, IMUs are referred to as IMMUs. IMUs are typically used to maneuver modern vehicles including motorcycles, missiles, aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), among many others, and spacecraft, including satellites and landers. Recent developments allow for the production of IMU-enabled GPS devices. An IMU allows a GPS receiver to work when GPS-signals are unavailable, such as in tunnels, inside buildings, or when electronic interference is present.
Blue Sky Network is a global satellite technology company headquartered in San Diego, California. Founded in 2001, Blue Sky Network offers satellite tracking solutions to support fleet managers and operators monitoring their assets on land, sea, and in the air. Blue Sky Network solutions use the satellite network from Iridium Communications to provide customers with 100 percent global coverage. The company has also been an authorized Tier 1 Iridium Communications partner since 2002.

Flightradar24 is a Swedish internet-based service that shows real-time aircraft flight tracking information on a map. It includes flight tracking information, origins and destinations, flight numbers, aircraft types, positions, altitudes, headings and speeds. It can also show time-lapse replays of previous tracks and historical flight data by airline, aircraft, aircraft type, area, or airport. It aggregates data from multiple sources, but, outside of the United States, mostly from crowdsourced information gathering by volunteers with ADS-B receivers and from satellite-based ADS-B receivers.
References
- ↑ "Set Up AFF". Spidertracks.
- ↑ "Guardian Mobility". Guardian Mobility.
- ↑ "Firefighting". TracPlus.
- ↑ "Automated Flight Following (AFF)". AFF Govt Website.