Related Research Articles
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the forms of decisions. Understanding in this context means the transformation of visual images into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory.

Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide imaging-based automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision refers to many technologies, software and hardware products, integrated systems, actions, methods and expertise. Machine vision as a systems engineering discipline can be considered distinct from computer vision, a form of computer science. It attempts to integrate existing technologies in new ways and apply them to solve real world problems. The term is the prevalent one for these functions in industrial automation environments but is also used for these functions in other environment vehicle guidance.

The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) is the largest trade association of electrical equipment manufacturers in the United States. Founded in 1926, it advocates for the industry, and publishes standards for electrical products. Notably, the form of US household electrical outlets and plugs is specified by NEMA.

A smart camera (sensor) or intelligent camera (sensor) or (smart) vision sensor or intelligent vision sensor or smart optical sensor or intelligent optical sensor or smart visual sensor or intelligent visual sensor is a machine vision system which, in addition to image capture circuitry, is capable of extracting application-specific information from the captured images, along with generating event descriptions or making decisions that are used in an intelligent and automated system. A smart camera is a self-contained, standalone vision system with built-in image sensor in the housing of an industrial video camera. The vision system and the image sensor can be integrated into one single piece of hardware known as intelligent image sensor or smart image sensor. It contains all necessary communication interfaces, e.g. Ethernet, as well as industry-proof 24V I/O lines for connection to a PLC, actuators, relays or pneumatic valves, and can be either static or mobile. It is not necessarily larger than an industrial or surveillance camera. A capability in machine vision generally means a degree of development such that these capabilities are ready for use on individual applications. This architecture has the advantage of a more compact volume compared to PC-based vision systems and often achieves lower cost, at the expense of a somewhat simpler (or omitted) user interface. Smart cameras are also referred to by the more general term smart sensors.
The Aerospace Industries Association (AIA) -- originally the Aeronautical Chamber of Commerce (1922-1945), then Aircraft Industries Association (1945-1960) -- is an American trade association representing manufacturers and suppliers of civil, military, and business aircraft, helicopters, UAVs, space systems, aircraft engines, missiles, material, and related components, equipment, services, and information technology in the United States. It also co-sponsors, with the National Association of Rocketry, the America Rocketry Challenge (TARC), an annual competition for high school students. Member companies also give awards and scholarships to top placing teams at the TARC national finals each year, and it is funded through sponsoring companies. AIA also develops the manufacturing standards called National Aerospace Standards, which are available to aerospace manufacturers that conform to United States Military Standard's for equipment manufacturing and provide standards for other various components.
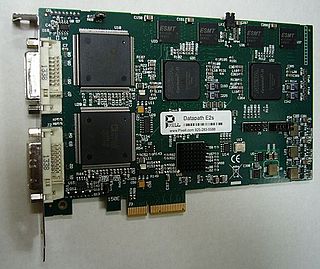
A frame grabber is an electronic device that captures individual, digital still frames from an analog video signal or a digital video stream. It is usually employed as a component of a computer vision system, in which video frames are captured in digital form and then displayed, stored, transmitted, analyzed, or combinations of these.
The following are common definitions related to the machine vision field.

Integrated Micro-electronics, Inc. provides electronics manufacturing services (EMS) and power semiconductor assembly and test services (SATS) with manufacturing facilities in Asia, Europe, and North America. Its headquarters is located in Biñan, Laguna.
Camera Link is a serial communication protocol standard designed for camera interface applications based on the National Semiconductor interface Channel-link. It was designed for the purpose of standardizing scientific and industrial video products including cameras, cables and frame grabbers. The standard is maintained and administered by the Automated Imaging Association or AIA, the global machine vision industry's trade group.
Pleora Technologies Inc. is a privately held Canadian company that specializes in video transmitters and receivers that enable the streaming of data or video in real-time over standard Gigabit Ethernet networks. The company was founded in 2000 by George Chamberlain and Alain Rivard.

GigE Vision is an interface standard introduced in 2006 for high-performance industrial cameras. It provides a framework for transmitting high-speed video and related control data over Ethernet networks. The distribution of software or development, manufacture or sale of hardware that implement the standard, require the payment of annual licensing fees. The standard was initiated by a group of 12 companies, and the committee has since grown to include more than 50 members. The 12 founding members were: Adimec, Atmel, Basler AG, CyberOptics, Teledyne DALSA, JAI A/S, JAI PULNiX, Matrox, National Instruments, Photonfocus, Pleora Technologies and Stemmer Imaging. The Association for Advancing Automation (A3) oversees the ongoing development and administration of the standard.
GenICam is a generic programming interface for machine vision (industrial) cameras. The goal of the standard is to decouple industrial camera interfaces technology from the user application programming interface (API). GenICam is administered by the European Machine Vision Association (EMVA). The work on the standard began in 2003 and the first module in GenICam, i.e., GenApi, was ratified in 2006 whereas the final module, i.e., GenTL was ratified in 2008.

Promotional merchandise are products branded with a logo or slogan and distributed at little or no cost to promote a brand, corporate identity, or event. Such products, which are often informally called promo products, swag, tchotchkes, or freebies, are used in marketing and sales. They are given away or sold at a loss to promote a company, corporate image, brand, or event. They are often distributed as handouts at trade shows, at conferences, on sales calls, and as bonus items in shipped orders. They are often used in guerrilla marketing campaigns.
CoaXPress (CXP) is a digital interface standard developed for high speed image data transmission in machine vision applications. The name is a portmanteau of 'express' and 'coaxial' to emphasize CoaXPress is faster than other standards and uses 75 ohm coaxial cables as the physical transmission medium. CoaXPress is mostly used in digital imaging applications but it is also suitable for high-speed transmission of universal digital data.

Clothing industry or garment industry summarizes the types of trade and industry along the production and value chain of clothing and garments, starting with the textile industry, embellishment using embroidery, via the fashion industry to apparel retailers up to trade with second-hand clothes and textile recycling. The producing sectors build upon a wealth of clothing technology some of which, like the loom, the cotton gin, and the sewing machine heralded industrialization not only of the previous textile manufacturing practices. Clothing industries are also known as allied industries, fashion industries, garment industries, or soft goods industries.
The Association for Advancing Automation (A3) is an international trade group that serves the robotics industry. It was founded in 1974 and is headquartered in Ann Arbor, Michigan. The organization is involved in safety standards for robots, and sponsors robotics conferences. On April 14, 2021 the Robotic Industries Association, AIA-Advancing Vision + Imaging (AIA), the Motion Control and Motors Association (MCMA), and A3 Mexico merged into A3, which had long acted as a long acted as an umbrella organisation for the individual trade organizations.
Mikrotron GmbH develops, produces, distributes, and rents high-speed cameras, recording systems, software and image processing components. The company, based near Munich, Germany, employs about 35 people, and has 35 distributors operating in over 30 countries.
Pedestrian crash avoidance mitigation (PCAM) systems, also known as pedestrian protection or detection systems, use computer and artificial intelligence technology to recognize pedestrians and bicycles in an automobile's path to take action for safety. PCAM systems are often part of a pre-collision system available in several high end car manufacturers, such as Volvo and Mercedes and Lexus, and used less widely in lower end cars such as Ford and Nissan. As of 2018 using 2016 data, more than 6,000 pedestrians and 800 cyclists are killed every year in the US in car crashes. Effective systems deployed widely could save up to 50% of these lives. More than 270,000 pedestrians are killed every year in the world. An excellent analysis of technology capabilities and limitations is provided in Death of Elaine Herzberg. Pedestrian safety has traditionally taken a secondary role to passenger safety.

USB3 Vision is an interface standard introduced in 2013 for industrial cameras. It describes a specification on top of the USB standard, with a particular focus on supporting high-performance cameras based on USB 3.0. It is recognized as one of the fastest growing machine vision camera standards. As of October 2019, version 1.1 is the latest version of the standard.
The Processing and Packaging Machinery Association (PPMA) is a UK trade membership organisation headquartered in Wallington, Surrey.
References
- ↑ AIA – Vision Online – About AIA. Vision Online.