
Fax, sometimes called telecopying or telefax, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material, normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device. The original document is scanned with a fax machine, which processes the contents as a single fixed graphic image, converting it into a bitmap, and then transmitting it through the telephone system in the form of audio-frequency tones. The receiving fax machine interprets the tones and reconstructs the image, printing a paper copy. Early systems used direct conversions of image darkness to audio tone in a continuous or analog manner. Since the 1980s, most machines transmit an audio-encoded digital representation of the page, using data compression to transmit areas that are all-white or all-black, more quickly.

An MFP, multi-functional, all-in-one (AIO), or multi-function device (MFD), is an office machine which incorporates the functionality of multiple devices in one, so as to have a smaller footprint in a home or small business setting, or to provide centralized document management/distribution/production in a large-office setting. A typical MFP may act as a combination of some or all of the following devices: email, fax, photocopier, printer, scanner.

An image scanner is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object and converts it to a digital image. The most common type of scanner used in offices and in the home is the flatbed scanner, where the document is placed on a glass window for scanning. A sheetfed scanner, which moves the page across an image sensor using a series of rollers, may be used to scan one document at a time or multiple, as in an automatic document feeder. A handheld scanner is a portable version of an image scanner that can be used on any flat surface. Scans are usually downloaded to the computer that the scanner is connected to, although some scanners are able to store scans on standalone flash media.

DeskJet is a brand name for inkjet printers manufactured by Hewlett-Packard. These printers range from small domestic to large industrial models, although the largest models in the range have generally been dubbed DesignJet. The Macintosh-compatible equivalent was branded as the Deskwriter and competed with Apple's StyleWriter, and the all-in-one equivalent is called OfficeJet.

LaserJet is a line of laser printers sold by HP Inc. since 1984. The LaserJet was the world's first commercially successful laser printer. Canon supplies both mechanisms and cartridges for most HP laser printers; some larger A3 models use Samsung print engines.
Internet fax, e-fax, or online fax is the use of the internet and internet protocols to send a fax (facsimile), rather than using a standard telephone connection and a fax machine. A distinguishing feature of Internet fax, compared to other Internet communications such as email, is the ability to exchange fax messages with traditional telephone-based fax machines.
Duplex printing is a feature of some computer printers and multi-function printers (MFPs) that allows the printing of a sheet of paper on both sides automatically. Print devices without this capability can only print on a single side of paper, sometimes called single-sided printing or simplex printing.

Book scanning or book digitization is the process of converting physical books and magazines into digital media such as images, electronic text, or electronic books (e-books) by using an image scanner. Large scale book scanning projects have made many books available online.
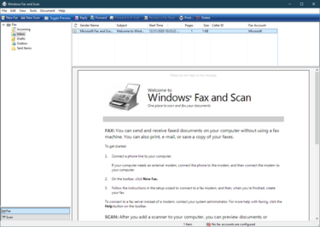
Windows Fax and Scan is an integrated faxing and scanning application introduced in Windows Vista and included in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate Windows Vista editions as the replacement for the Fax Console of Windows XP; it is available in all versions of Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 (x86/x64) and Windows 11 (x64), but not on ARM64 versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11.
DocuTech is the name given to a line of electronic production-publishing systems produced by Xerox Corporation. It allowed paper documents to be scanned, electronically edited, and then printed on demand. DocuTech systems were the last known to use the XNS protocol for networking.
Document cameras, also known as visual presenters, visualizers, digital overheads, or docucams, are real-time image capture devices for displaying an object to a large audience. Document cameras have also been used as replacements for image scanners. Like an opaque projector, a document camera is able to magnify and project the images of actual, three-dimensional objects, as well as transparencies. They are, in essence, high resolution web cams, mounted on arms so as to facilitate their placement over a page. This allows a teacher, lecturer or presenter to write on a sheet of paper or to display a two or three-dimensional object while the audience watches. Theoretically, all objects can be displayed by a document camera. Most objects are simply placed under the camera, and the camera takes the picture, which in turn produces a live image using a projector or monitor. Different types of document camera/visualizer allow great flexibility in terms of placement of objects. Larger objects, for example, can simply be placed in front of the camera and the camera rotated as necessary, or a ceiling mounted document camera can also be used to allow a larger working area to be used.

Duplex scanning is a feature of some computer scanners, and multifunction printers (MFPs) that support duplex printing. A duplex scanner can automatically scan a sheet of paper on both sides. Scanners without this capability can only scan both sides of a sheet of paper by reinserting it manually the other way up.

A photocopier is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called xerography, a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying.
Forms processing is a process by which one can capture information entered into data fields and convert it into an electronic format. This can be done manually or automatically, but the general process is that hard copy data is filled out by humans and then "captured" from their respective fields and entered into a database or other electronic format.
Avision is a Taiwan based company founded in 1991 that designs and produces image scanners and multifunction printers. The company was established in Hsinchu Science and Industrial Park in 1991.

The IBM 3800 is a discontinued laser printer designed and manufactured by IBM. It was the first commercially available laser printer. It was a continuous form laser printer, meaning that it printed onto a continuous long sheet of paper.
{{subst:Proposed deletion|concern=vague name put detailed information about this concept in articlePhotocopier}}

The IBM 6670 Information Distributor (6670-001) was a combination laser printer and photocopier introduced by IBM. Announced on February 14, 1979, as part of Office System/6, its feature set included two-sided printing.
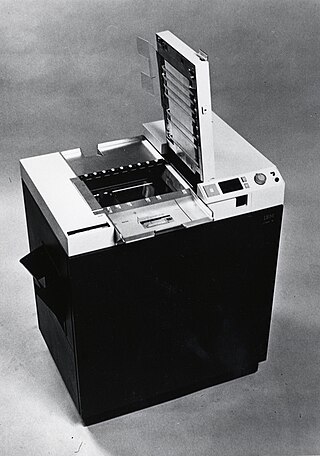
IBM Office Products Division (OPD) manufactured and sold copier equipment and supplies from 1970 till IBM withdrew from the copier market in 1988. IBM's decision to compete in this market resulted in the first commercial use of an organic photoconductor now widely used in most photocopiers. It is often held up as an example of a corporate u-turn, where a company rejects a technology and then adopts it. It showed that despite the size of IBM's sales and engineering organisations, this did not guarantee success in every market it chose to compete in. The development effort that resulted in the IBM Copier helped in the development of IBMs first laser printer, the IBM 3800.`

ScanJet is a line of desktop flatbed and sheetfed image scanners originally sold by Hewlett-Packard (HP), later HP Inc., since 1987. It was the first commercially widespread image scanner on the market, as well as one of the first scanners aimed at the small office/home office market. It was originally designed to compliment the company's LaserJet series of laser printers and allowed HP to compete in the burgeoning desktop publishing market of the early 1980s.














