An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse, contain the necessary compiler, interpreter, or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and Lazarus, do not.
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is an implementation of Microsoft's event-driven programming language Visual Basic 6.0 built into most desktop Microsoft Office applications. Although based on pre-.NET Visual Basic, which is no longer supported or updated by Microsoft, the VBA implementation in Office continues to be updated to support new Office features. VBA is used for professional and end-user development due to its perceived ease-of-use, Office's vast installed userbase, and extensive legacy in business.
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple Inc. that facilitates automated control over scriptable Mac applications. First introduced in System 7, it is currently included in all versions of macOS as part of a package of system automation tools. The term "AppleScript" may refer to the language itself, to an individual script written in the language, or, informally, to the macOS Open Scripting Architecture that underlies the language.
In computing, an icon is a pictogram or ideogram displayed on a computer screen in order to help the user navigate a computer system. The icon itself is a quickly comprehensible symbol of a software tool, function, or a data file, accessible on the system and is more like a traffic sign than a detailed illustration of the actual entity it represents. It can serve as an electronic hyperlink or file shortcut to access the program or data. The user can activate an icon using a mouse, pointer, finger, or voice commands. Their placement on the screen, also in relation to other icons, may provide further information to the user about their usage. In activating an icon, the user can move directly into and out of the identified function without knowing anything further about the location or requirements of the file or code.
Computer accessibility refers to the accessibility of a computer system to all people, regardless of disability type or severity of impairment. The term accessibility is most often used in reference to specialized hardware or software, or a combination of both, designed to enable the use of a computer by a person with a disability or impairment. Computer accessibility often has direct positive effects on people with disabilities.

Apache Ant is a software tool for automating software build processes which originated from the Apache Tomcat project in early 2000 as a replacement for the Make build tool of Unix. It is similar to Make, but is implemented using the Java language and requires the Java platform. Unlike Make, which uses the Makefile format, Ant uses XML to describe the code build process and its dependencies.

AutoHotkey is a free and open-source custom scripting language for Microsoft Windows, initially aimed at providing easy keyboard shortcuts or hotkeys, fast macro-creation and software automation that allows users of most levels of computer skill to automate repetitive tasks in any Windows application. User interfaces can easily be extended or modified by AutoHotkey. The AutoHotkey installation includes its own extensive help file, and web-based documentation is also available.
A voice-user interface (VUI) makes spoken human interaction with computers possible, using speech recognition to understand spoken commands and answer questions, and typically text to speech to play a reply. A voice command device is a device controlled with a voice user interface.
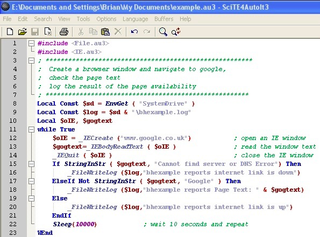
AutoIt is a freeware programming language for Microsoft Windows. In its earliest release, it was primarily intended to create automation scripts for Microsoft Windows programs but has since grown to include enhancements in both programming language design and overall functionality.
Mobile app development is the act or process by which a mobile app is developed for one or more mobile devices, which can include personal digital assistants (PDA), enterprise digital assistants (EDA), or mobile phones. Such software applications are specifically designed to run on mobile devices, taking numerous hardware constraints into consideration. Common constraints include CPU architecture and speeds, available memory (RAM), limited data storage capacities, and considerable variation in displays and input methods. These applications can be pre-installed on phones during manufacturing or delivered as web applications, using server-side or client-side processing to provide an "application-like" experience within a web browser.
Microsoft Build Engine, or MSBuild, is a set of free and open-source build tools for managed code under the Common Language Infrastructure as well as native C and C++ code. It was first released in 2003 and was a part of .NET Framework. MSBuild is included with Visual Studio, but can also be run independently through MSBuild's command-line interface.

Workbench is the desktop environment and graphical file manager of AmigaOS developed by Commodore International for their Amiga line of computers. Workbench provides the user with a graphical interface to work with file systems and launch applications. It uses a workbench metaphor for representing file system organisation.

Adobe AIR is a cross-platform runtime system currently developed by Harman International, in collaboration with Adobe Inc., for building desktop applications and mobile applications, programmed using Adobe Animate, ActionScript, and optionally Apache Flex. It was originally released in 2008. The runtime supports installable applications on Windows, macOS, and mobile operating systems, including Android, iOS, and BlackBerry Tablet OS.
FinalBuilder is a commercial Windows build automation tool that provides a unified graphical interface to author and execute build projects. Once defined, a project can only be run either via the graphical interface or command line program to execute build projects. A project consists of actions, of which there are around 650 types defined as of version 6. Projects are stored in a zipped XML format.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
The Wing Python IDE family of integrated development environments (IDEs) from Wingware was created specifically for the Python programming language, with support for editing, testing, debugging, inspecting/browsing, and error checking Python code.

Hollywood is a commercially distributed programming language developed by Andreas Falkenhahn which mainly focuses on the creation of multimedia-oriented applications. Hollywood is available for AmigaOS, MorphOS, WarpOS, AROS, Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Hollywood has an inbuilt cross compiler that can automatically save executables for all platforms supported by the software. The generated executables are completely stand-alone and do not have any external dependencies, so they can also be started from a USB flash drive. An optional add-on also allows users to compile projects into APK files.
FastTrack Automation Studio, often referred to as just FastTrack, is a scripting language for Windows IT System Administrators. The product’s goal is to handle any kind of scripting that might be required to automate processes with Microsoft Windows networks. The web site of the product is located at www.fasttrackscript.com.





