Related Research Articles

Gene therapy is a medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
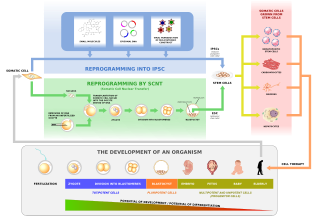
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissue. It does not refer to the natural conception and delivery of identical twins. The possibilities of human cloning have raised controversies. These ethical concerns have prompted several nations to pass laws regarding human cloning.

Leukemia is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy.

In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking a denucleated oocyte and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. In 1996, Dolly the sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. In January 2018, a team of scientists in Shanghai announced the successful cloning of two female crab-eating macaques from foetal nuclei.

Haemophilia B, also spelled hemophilia B, is a blood clotting disorder causing easy bruising and bleeding due to an inherited mutation of the gene for factor IX, and resulting in a deficiency of factor IX. It is less common than factor VIII deficiency.

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severity in alcoholic hepatitis is determined several clinical prediction models such as the Maddrey's Discriminant Function and the MELD score.

Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency also known as OTC deficiency is the most common urea cycle disorder in humans. Ornithine transcarbamylase, the defective enzyme in this disorder, is the final enzyme in the proximal portion of the urea cycle, responsible for converting carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine into citrulline. OTC deficiency is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, meaning males are more commonly affected than females.

Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are small viruses that infect humans and some other primate species. They belong to the genus Dependoparvovirus, which in turn belongs to the family Parvoviridae. They are small replication-defective, nonenveloped viruses and have linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genome of approximately 4.8 kilobases (kb).
Pharmacotherapy, also known as pharmacological therapy or drug therapy, is defined as medical treatment that utilizes one or more pharmaceutical drugs to improve ongoing symptoms, treat the underlying condition, or act as a prevention for other diseases (prophylaxis).
An artificial cell, synthetic cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, liposomes, polymersomes, nanoparticles, microcapsules and a number of other particles can qualify as artificial cells.
Follistatin, also known as activin-bindings protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FST gene. Follistatin is an autocrine glycoprotein that is expressed in nearly all tissues of higher animals.
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) is a form of lymphoproliferative disorder (LPDs). It affects lymphocyte apoptosis.

Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX), also called cerebral cholesterosis, is a rare inborn bile acid metabolism disorder caused by autosomal-recessive mutations in the CYP27A1 gene. CTX is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including neurological and non-neurological issues.

Niemann–Pick type C (NPC) is a lysosomal storage disease associated with mutations in NPC1 and NPC2 genes. Niemann–Pick type C affects an estimated 1:150,000 people. Approximately 50% of cases present before ten years of age, but manifestations may first be recognized as late as the sixth decade.
Adenovirus varieties have been explored extensively as a viral vector for gene therapy and also as an oncolytic virus.
James M. Wilson is an American biomedical researcher and CEO of two biotech companies, Gemma Biotherapeutics and Franklin Biolabs, focused on gene therapies. He previously served as the Director of the Gene Therapy Program, Rose H. Weiss Professor and Director of the Orphan Disease Center, and Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Previously, he held the John Herr Musser endowed professorship at the Perelman School of Medicine.

Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company involved in the research and development of novel products for treatment of rare and ultra-rare genetic diseases for which there are typically no approved treatments and high unmet medical need. The company works with multiple drug modalities including biologics, small molecule, gene therapies, and ASO and mRNAs in the disease categories of bone, endocrine, metabolic, muscle and CNS diseases.
Precision BioSciences, Inc. is a publicly traded American clinical stage gene editing company headquartered in Durham, North Carolina. Founded in 2006, Precision is focused on developing both in vivo and ex vivo gene editing therapies using its proprietary "ARCUS" genome editing platform.
Richard P. Novick is an American microbiologist best known for his work in the fields of plasmid biology, staphylococcal pathobiology and antimicrobial resistance. He is the Recanati Family Professor of Science, Emeritus, at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and is a member of the American National Academy of Sciences. Novick has published over 250 peer-reviewed articles, and several book reviews for the Times Literary Supplement, and is a member of the Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Dirloctogene samoparvovec, also known as SPK-8011, is an experimental gene therapy developed for hemophilia A by Roche and Spark Therapeutics. It uses an engineered AAV vector to cause liver cells to produce the Factor VIII blood clotting protein.
References
- ↑ Wang, Lili; Warzecha, Claude C.; Kistner, Alexander; Chichester, Jessica A.; Bell, Peter; Buza, Elizabeth L.; He, Zhenning; Pampena, M. Betina; Couthouis, Julien; Sethi, Sunjay; McKeever, Kathleen; Betts, Michael R.; Kakkis, Emil; Wilson, James M.; Wadsworth, Samuel; Sullivan, Barbara A. (2022). "Prednisolone reduces the interferon response to AAV in cynomolgus macaques and may increase liver gene expression". Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development. 24. Elsevier BV: 292–305. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.01.007 . ISSN 2329-0501. PMC 8841522 . PMID 35211641.
- ↑ Kistner, Alexander; Chichester, Jessica A.; Wang, Lili; Calcedo, Roberto; Greig, Jenny A.; Cardwell, Leah N.; Wright, Margaret C.; Couthouis, Julien; Sethi, Sunjay; McIntosh, Brian E.; McKeever, Kathleen; Wadsworth, Samuel; Wilson, James M.; Kakkis, Emil; Sullivan, Barbara A. (2023-10-13). "Prednisolone and rapamycin reduce the plasma cell gene signature and may improve AAV gene therapy in cynomolgus macaques". Gene Therapy. 31 (3–4). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 128–143. doi: 10.1038/s41434-023-00423-z . ISSN 0969-7128. PMC 10940161 . PMID 37833563.
- ↑ Nathwani, Amit C.; McIntosh, Jenny; Sheridan, Rose (1 September 2022). "Liver Gene Therapy". Human Gene Therapy. 33 (17–18): 879–888. doi:10.1089/hum.2022.169. PMID 36082993. S2CID 252160990.