
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences, such as calculating the distance cost between strings in a natural language or in financial data.
Molecular phylogenetics is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography.
In bioinformatics, BLAST is an algorithm and program for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as the amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA and/or RNA sequences. A BLAST search enables a researcher to compare a subject protein or nucleotide sequence with a library or database of sequences, and identify database sequences that resemble the query sequence above a certain threshold. For example, following the discovery of a previously unknown gene in the mouse, a scientist will typically perform a BLAST search of the human genome to see if humans carry a similar gene; BLAST will identify sequences in the human genome that resemble the mouse gene based on similarity of sequence.
In bioinformatics and biochemistry, the FASTA format is a text-based format for representing either nucleotide sequences or amino acid (protein) sequences, in which nucleotides or amino acids are represented using single-letter codes.

Structural alignment attempts to establish homology between two or more polymer structures based on their shape and three-dimensional conformation. This process is usually applied to protein tertiary structures but can also be used for large RNA molecules. In contrast to simple structural superposition, where at least some equivalent residues of the two structures are known, structural alignment requires no a priori knowledge of equivalent positions. Structural alignment is a valuable tool for the comparison of proteins with low sequence similarity, where evolutionary relationships between proteins cannot be easily detected by standard sequence alignment techniques. Structural alignment can therefore be used to imply evolutionary relationships between proteins that share very little common sequence. However, caution should be used in using the results as evidence for shared evolutionary ancestry because of the possible confounding effects of convergent evolution by which multiple unrelated amino acid sequences converge on a common tertiary structure.
BioJava is an open-source software project dedicated to provide Java tools to process biological data. BioJava is a set of library functions written in the programming language Java for manipulating sequences, protein structures, file parsers, Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) interoperability, Distributed Annotation System (DAS), access to AceDB, dynamic programming, and simple statistical routines. BioJava supports a huge range of data, starting from DNA and protein sequences to the level of 3D protein structures. The BioJava libraries are useful for automating many daily and mundane bioinformatics tasks such as to parsing a Protein Data Bank (PDB) file, interacting with Jmol and many more. This application programming interface (API) provides various file parsers, data models and algorithms to facilitate working with the standard data formats and enables rapid application development and analysis.
FASTA is a DNA and protein sequence alignment software package first described by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985. Its legacy is the FASTA format which is now ubiquitous in bioinformatics.

In biology, a substitution model, also called models of DNA sequence evolution, are Markov models that describe changes over evolutionary time. These models describe evolutionary changes in macromolecules represented as sequence of symbols. Substitution models are used to calculate the likelihood of phylogenetic trees using multiple sequence alignment data. Thus, substitution models are central to maximum likelihood estimation of phylogeny as well as Bayesian inference in phylogeny. Estimates of evolutionary distances are typically calculated using substitution models. Substitution models are also central to phylogenetic invariants because they are necessary to predict site pattern frequencies given a tree topology. Substitution models are also necessary to simulate sequence data for a group of organisms related by a specific tree.
Clustal is a series of widely used computer programs used in bioinformatics for multiple sequence alignment. There have been many versions of Clustal over the development of the algorithm that are listed below. The analysis of each tool and its algorithm is also detailed in their respective categories. Available operating systems listed in the sidebar are a combination of the software availability and may not be supported for every current version of the Clustal tools. Clustal Omega has the widest variety of operating systems out of all the Clustal tools.
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is an intergovernmental organization (IGO) which, as part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) family, focuses on research and services in bioinformatics. It is located on the Wellcome Genome Campus in Hinxton near Cambridge, and employs over 600 full-time equivalent (FTE) staff. Institute leaders such as Rolf Apweiler, Alex Bateman, Ewan Birney, and Guy Cochrane, an adviser on the National Genomics Data Center Scientific Advisory Board, serve as part of the international research network of the BIG Data Center at the Beijing Institute of Genomics.
Computational phylogenetics, phylogeny inference, or phylogenetic inference focuses on computational and optimization algorithms, heuristics, and approaches involved in phylogenetic analyses. The goal is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of genes, species, or taxa. Maximum likelihood, parsimony, Bayesian, and minimum evolution are typical optimality criteria used to assess how well a phylogenetic tree topology describes the sequence data. Nearest Neighbour Interchange (NNI), Subtree Prune and Regraft (SPR), and Tree Bisection and Reconnection (TBR), known as tree rearrangements, are deterministic algorithms to search for optimal or the best phylogenetic tree. The space and the landscape of searching for the optimal phylogenetic tree is known as phylogeny search space.
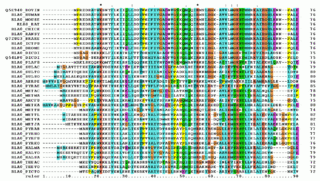
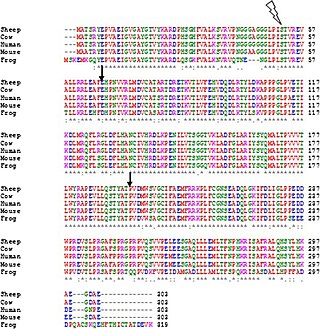
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a linkage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino acids or nucleotides.
T-Coffee is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can also combine multiple sequences alignments obtained previously and in the latest versions can use structural information from PDB files (3D-Coffee). It has advanced features to evaluate the quality of the alignments and some capacity for identifying occurrence of motifs (Mocca). It produces alignment in the aln format (Clustal) by default, but can also produce PIR, MSF, and FASTA format. The most common input formats are supported.
PHYLogeny Inference Package (PHYLIP) is a free computational phylogenetics package of programs for inferring evolutionary trees (phylogenies). It consists of 65 portable programs, i.e., the source code is written in the programming language C. As of version 3.696, it is licensed as open-source software; versions 3.695 and older were proprietary software freeware. Releases occur as source code, and as precompiled executables for many operating systems including Windows, Mac OS 8, Mac OS 9, OS X, Linux ; and FreeBSD from FreeBSD.org. Full documentation is written for all the programs in the package and is included therein. The programs in the phylip package were written by Professor Joseph Felsenstein, of the Department of Genome Sciences and the Department of Biology, University of Washington, Seattle.
In bioinformatics, MAFFT is a program used to create multiple sequence alignments of amino acid or nucleotide sequences. Published in 2002, the first version of MAFFT used an algorithm based on progressive alignment, in which the sequences were clustered with the help of the Fast Fourier Transform. Subsequent versions of MAFFT have added other algorithms and modes of operation, including options for faster alignment of large numbers of sequences, higher accuracy alignments, alignment of non-coding RNA sequences, and the addition of new sequences to existing alignments.
Distance matrices are used in phylogeny as non-parametric distance methods and were originally applied to phenetic data using a matrix of pairwise distances. These distances are then reconciled to produce a tree. The distance matrix can come from a number of different sources, including measured distance or morphometric analysis, various pairwise distance formulae applied to discrete morphological characters, or genetic distance from sequence, restriction fragment, or allozyme data. For phylogenetic character data, raw distance values can be calculated by simply counting the number of pairwise differences in character states.
In bioinformatics, Stemloc is an open source software for multiple RNA sequence alignment and RNA structure prediction based on probabilistic models of RNA structure known as Pair stochastic context-free grammars. Stemloc attempts to simultaneously predict and align the structure of RNA sequences with an improved time and space cost compared to previous methods with the same motive. The resulting software implements constrained versions of the Sankoff algorithm by introducing both fold and alignment constraints, which reduces processor and memory usage and allows for larger RNA sequences to be analyzed on commodity hardware. Stemloc was written in 2004 by Ian Holmes.

Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) is computer software for conducting statistical analysis of molecular evolution and for constructing phylogenetic trees. It includes many sophisticated methods and tools for phylogenomics and phylomedicine. It is licensed as proprietary freeware. The project for developing this software was initiated by the leadership of Masatoshi Nei in his laboratory at the Pennsylvania State University in collaboration with his graduate student Sudhir Kumar and postdoctoral fellow Koichiro Tamura. Nei wrote a monograph (pp. 130) outlining the scope of the software and presenting new statistical methods that were included in MEGA. The entire set of computer programs was written by Kumar and Tamura. The personal computers then lacked the ability to send the monograph and software electronically, so they were delivered by postal mail. From the start, MEGA was intended to be easy-to-use and include solid statistical methods only.

Tandy Warnow is an American computer scientist and Grainger Distinguished Chair in Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. She is known for her work on the reconstruction of evolutionary trees, both in biology and in historical linguistics, and also for multiple sequence alignment methods.
T-REX is a freely available web server, developed at the department of Computer Science of the Université du Québec à Montréal, dedicated to the inference, validation and visualization of phylogenetic trees and phylogenetic networks. The T-REX web server allows the users to perform several popular methods of phylogenetic analysis as well as some new phylogenetic applications for inferring, drawing and validating phylogenetic trees and networks.