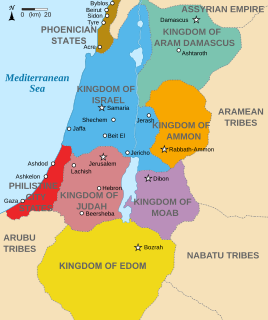
Ammon was an ancient Semitic-speaking nation occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Arnon and Jabbok, in present-day Jordan. The chief city of the country was Rabbah or Rabbat Ammon, site of the modern city of Amman, Jordan's capital. Milcom and Molech are named in the Hebrew Bible as the gods of Ammon. The people of this kingdom are called "Children of Ammon" or "Ammonites".

The Book of Amos is the third of the Twelve Minor Prophets in the Old Testament (Tanakh) and the second in the Greek Septuagint tradition. Amos, an older contemporary of Hosea and Isaiah, was active c. 750 BC during the reign of Jeroboam II of Samaria, making Amos the first prophetic book of the Bible to be written. Amos lived in the kingdom of Judah but preached in the northern kingdom of Israel. His major themes of social justice, God's omnipotence, and divine judgment became staples of prophecy.

Hezekiah, or Ezekias, was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Judah.

Zephaniah is the name of several people in the Hebrew Bible and Jewish Tanakh; the most prominent one being the prophet who prophesied in the days of Josiah, king of Judah and is attributed a book bearing his name among the Twelve Minor Prophets. His name is commonly transliterated Sophonias in Bibles translated from the Vulgate or Septuagint. The name might mean "Yah has concealed", "[he whom] Yah has hidden", or "Yah lies in wait".

Canaan was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur, and Gezer.

The Book of Jubilees, sometimes called Lesser Genesis (Leptogenesis), is an ancient Jewish religious work of 50 chapters, considered canonical by the Ethiopian Orthodox Church as well as Beta Israel, where it is known as the Book of Division. Jubilees is considered one of the pseudepigrapha by Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, and Protestant Churches. It is also not considered canonical within Judaism outside of Beta Israel.
The New Chronology is an alternative chronology of the ancient Near East developed by English Egyptologist David Rohl and other researchers beginning with A Test of Time: The Bible - from Myth to History in 1995. It contradicts mainstream Egyptology by proposing a major revision of the established Egyptian chronology, in particular by re-dating Egyptian kings of the Nineteenth through Twenty-fifth Dynasties, bringing forward conventional dating by up to 350 years. Rohl asserts that the New Chronology allows him to identify some of the characters in the Hebrew Bible with people whose names appear in archaeological finds.

Magnus Magnusson, was an Icelandic-born British-based journalist, translator, writer and television presenter. Born in Reykjavík, he lived in Scotland for almost all his life, although he never took British citizenship. He came to prominence as a BBC television journalist and was the presenter of the BBC television quiz programme Mastermind for 25 years. His catchphrase "I've started so I'll finish" was said whenever the time ran out while he was reading a question on the show.

According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Asher was one of the Tribes of Israel descended from Asher, the eighth son of Jacob. It is one of the ten lost tribes.
James Bennett Pritchard was an American archeologist whose work explicated the interrelationships of the religions of ancient Palestine, Canaan, Egypt, Assyria, and Babylon. Pritchard was honored with the Gold Medal Award for Distinguished Archaeological Achievement in 1983 from the Archaeological Institute of America.

The United Monarchy is the name given to the united Israelite kingdom of Israel and Judah during the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon, as depicted in the Hebrew Bible. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between 1047 BCE and 930 BCE. The Biblical account reports that, on the succession of Solomon's son Rehoboam, the country split into two kingdoms: the Kingdom of Israel in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south. To date, no proof of the existence of the United Monarchy has been found.
An Asherah pole is a sacred tree or pole that stood near Canaanite religious locations to honor the Ugaritic mother goddess Asherah, consort of El. The relation of the literary references to an asherah and archaeological finds of Judaean pillar-figurines has engendered a literature of debate.
Bryant G. Wood is an American biblical archaeologist and young earth creationist. Wood is known for arguing that the destruction of Jericho could be accorded with the biblical literalist chronology of c. 1400 BC. This date is some 150 years later than the accepted date of c. 1550 BC, first determined by Kathleen Kenyon and subsequently confirmed with a variety of methods including radiocarbon dating.

The Twelve Tribes of Israel are, according to Hebrew scriptures, the descendants of the biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, through his twelve sons through his wives, Leah and Rachel, and his concubines, Bilhah and Zilpah, who collectively form the Israelite nation. Some modern scholars dispute whether there ever were twelve Israelite tribes, and think that the number 12 more likely signifies a symbolic invented tradition as part of a national founding myth.

Criticism of the Bible is an interdisciplinary field of study concerning the factual accuracy of the claims and the moral tenability of the commandments made in the Bible, the holy book of Christianity. Devout Christians have long regarded their Bible as the perfect word of God. Scholars and scientists have endeavored for centuries to scrutinise biblical texts to establish their origins and validity. In addition to concerns about ethics in the Bible, about biblical inerrancy, or about the historicity of the Bible, there remain some questions of biblical authorship and as to what material to include in the biblical canon.
Biblical archaeology, occasionally known as Palestinology, is the school of archaeology which concerns itself with the biblical world.

Edom was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east. Most of its former territory is now divided between present-day southern Israel and Jordan. Edom appears in written sources relating to the late Bronze Age and to the Iron Age in the Levant.

The Bible makes reference to various pharaohs of Egypt. These include unnamed pharaohs in events described in the Torah, as well as several later named pharaohs, some of whom were historical or can be identified with historical pharaohs.








