Related Research Articles

The AGM-114 Hellfire is an air-to-surface missile (ASM) first developed for anti-armor use, but later models were developed for precision drone strikes against other target types, and have been used in a number of actions aimed to "destroy high-value targets." It was originally developed under the name Heliborne laser, fire-and-forget missile, which led to the colloquial name "Hellfire" ultimately becoming the missile's formal name. It has multi-mission, multi-target precision-strike ability, and can be launched from multiple air, sea, and ground platforms, including the Predator drone. The Hellfire missile is the primary 100-pound (45 kg) class air-to-ground precision weapon for the armed forces of the United States and many other nations. It has also been fielded on surface platforms in the surface-to-surface and surface-to-air roles.
The GATOR mine system is a United States military system of air-dropped anti-tank and anti-personnel mines developed in the 1980s to be compatible with existing cluster dispensers. It is used with two dispenser systems—the Navy 230 kg (500 lb) CBU-78/B and the Air Force 450 kg (1,000 lb) CBU-89/B. Additionally the mines are used with the land- and helicopter-based Volcano mine system.
The Mark 84 or BLU-117 is an American general-purpose bomb. It is the largest of the Mark 80 series of weapons. Entering service during the Vietnam War, it became a commonly used US heavy unguided bomb to be dropped. At the time, it was the third largest bomb by weight in the US inventory behind the 15,000-pound (6,800 kg) BLU-82 "Daisy Cutter" and the 3,000-pound (1,400 kg) M118 "demolition" bomb. It is currently sixth in size due to the addition of the 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) GBU-28 in 1991, the 22,600 lb (10,300 kg) GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast bomb (MOAB) in 2003, and the 30,000 lb (14,000 kg) Massive Ordnance Penetrator.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is a type of shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity superplastic jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The jet's effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the target.

The Panzerfaust was an inexpensive, single shot, recoilless German anti-tank weapon of World War II. It consisted of a small, disposable pre-loaded launch tube firing a high-explosive anti-tank warhead, and was intended to be operated by a single soldier. The Panzerfaust's direct ancestor was the similar, smaller-warhead Faustpatrone ordnance device. The Panzerfaust was in use from 1943 until the end of the war, continuing to see service outside of Germany for a number of years.

The AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) is a glide bomb that resulted from a joint venture between the United States Navy and Air Force to deploy a standardized medium range precision guided weapon, especially for engagement of defended targets from outside the range of standard anti-aircraft defenses, thereby increasing aircraft survivability and minimizing friendly losses. The designation of the Joint Standoff Weapon as an "air-to-ground missile" is a misnomer, as it is an unpowered bomb with guidance avionics, similar to the older GBU-15.
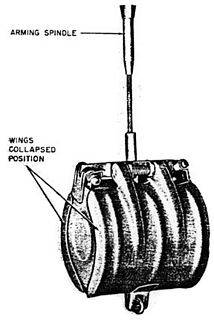
A Butterfly Bomb was a German 2-kilogram (4.4 lb) anti-personnel submunition used by the Luftwaffe during the Second World War. It was so named because the thin cylindrical metal outer shell which hinged open when the bomblet deployed gave it the superficial appearance of a large butterfly. The design was very distinctive and easy to recognise. SD 2 bomblets were not dropped individually, but were packed into containers holding between 6 and 108 submunitions e.g. the AB 23 SD 2 and AB 250-3 submunition dispensers. The SD 2 submunitions were released after the container was released from the aircraft and had burst open. Because SD 2s were always dropped in groups the discovery of one unexploded SD 2 was a reliable indication that others had been dropped nearby. This bomb type was one of the first cluster bombs ever used in combat and it proved to be a highly effective weapon. The bomb containers that carried the SD 2 bomblets and released them in the air were nicknamed the "Devil's Eggs" by Luftwaffe air and ground crew.
The CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon is a United States Air Force 1,000-pound (450 kg)-class freefall Cluster Bomb Unit. It was developed and produced by Textron Defense Systems. A CBU-97 used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit is converted to a precision-guided weapon, and the combination is designated CBU-105.
The AGM-124 Wasp is a missile developed by the United States. The Wasp grew out of the 1975 WAAM program initiated by the US Air Force in order to develop a series of new air-to-ground anti-armour weapons for close-support aircraft. The three-pronged program led to the CBU-92/B ERAM, the CBU-90/B ACM, and the Wasp anti-armour missile. The Wasp is regarded as the most advanced of these weapons.

The Unrotated Projectile (UP) was a British anti-aircraft and ground-bombardment rocket of the Second World War. A 7 in (180 mm) version was developed for the Royal Navy by Alwyn Crow of the Projectile Development Establishment of the Ministry of Supply at Fort Halstead. It proved unreliable and ineffective and was withdrawn from use in 1941. Development of the concept led to the UP-2 and UP-3, which had smaller diameters of 2 in (51 mm) and 3 in (76 mm) respectively but were longer. The latter was used as the basis of the Z Battery anti-aircraft weapons and later developed in air-to-ground form as the RP-3, used against ground forces and shipping by aircraft like the Hawker Typhoon and the Bristol Beaufighter. In 1944–1945 several adaptations for general bombardment were produced, including Sea Mattress, Land Mattress, LILO and Tulip.
RS-82 and RS-132 were unguided rockets used by Soviet military aircraft in World War II.
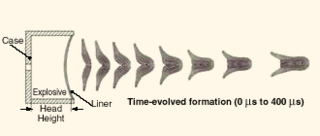
An explosively formed penetrator (EFP), also known as an explosively formed projectile, a self-forging warhead, or a self-forging fragment, is a special type of shaped charge designed to penetrate armor effectively. As the name suggests, the effect of the explosive charge is to deform a metal plate into a slug or rod shape and accelerate it toward a target. They were first developed as oil well perforators by American oil companies in the 1930s, and were deployed as weapons in World War II.

Project Sense and Destroy ARMor, or SADARM, is a United States 'smart' submunition capable of searching for, and destroying tanks within a given target area.
The CBU-87 Combined Effects Munition (CEM) is a cluster bomb used by the United States Air Force, developed by Aerojet General/Honeywell and introduced in 1986 to replace the earlier cluster bombs used in the Vietnam War. CBU stands for Cluster Bomb Unit. When the CBU-87 is used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit, it becomes much more accurate, and is designated CBU-103.

The BLU-97/B Combined Effects Bomb is the submunition used in several cluster bomb type weapon systems, mainly the CBU-87 and its precision-guided version CBU-103. When the bomblets fall, they separate from the main bomb and independently free fall to the ground. They contain an inflatable bag (ballute) on the top of them, which slows them down and spreads them out. Once the bomblets reach a force of 6 Gs they arm themselves. As the bomblets fall, they are also spinning. Arming takes about 2.6 seconds. They have a combined shaped charge, fragmentation and incendiary effect on the target. It is very effective against and mainly used for anti-personnel, anti-materiel, and anti-armor.

The Low Cost Autonomous Attack System (LOCAAS) was a loitering attack munition developed for the United States Air Force. In 1998 the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Army Lockheed Martin began to examine the feasibility of a small, affordable cruise missile weapon for use against armoured and unarmoured vehicles, materiel and personnel, and if so develop a demonstration program. The program cost approximately $150,000,000; the cost per unit was calculated to be $30,000 based on a production of 12,000 units before cancellation.
The CBU-107 Passive Attack Weapon is an air-dropped guided bomb containing metal penetrator rods of various sizes. It was designed to attack targets where an explosive effect may be undesirable, such as fuel storage tanks or chemical weapon stockpiles in civilian areas.
The S-TEC Sentry is a reconnaissance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), developed in the United States in the 1980s. Built by S-TEC systems of Texas, it is a battlefield mini-UAV in roughly the same class as the BAI Dragon drone. In fact, the Sentry looks something like an Exdrone with a twin-boom raised tail. It is built of carbon composition and Kevlar, and powered by a 19.5 kW (26 hp) piston engine in a tractor configuration.

The MW-1 is a German munitions dispenser similar to the British JP233. It is designed to be carried on the Tornado IDS, although it can be carried on the F-104 Starfighter and the F-4 Phantom. The MW-1 started to be phased out after the German Government ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions in 2009.

A precision-guided munition is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets. During the First Gulf War guided munitions accounted for only 9% of weapons fired, but accounted for 75% of all successful hits. Despite guided weapons generally being used on more difficult targets, they were still 35 times more likely to destroy their targets per weapon dropped.
References
- ↑ "BAK to BSU/BSG - Equipment Listing". www.designation-systems.net.