This article contains content that is written like an advertisement .(June 2016) |
BMJ Best Practice is an online decision-support tool made for clinical decision making support. It was created in 2009 by BMJ . [1]
This article contains content that is written like an advertisement .(June 2016) |
BMJ Best Practice is an online decision-support tool made for clinical decision making support. It was created in 2009 by BMJ . [1]
BMJ launched Best Practice in 2009.
BMJ offers personal and institutional subscriptions. Only institutional subscriptions are available to purchase in the United States and Canada. All institutional subscriptions include onsite and remote access as well as access to the mobile app for iOS and Android devices. [2] It is also included in the Clinical Information Access Portal of the New South Wales Ministry of Health.
In a 2016 article published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research , BMJ Best Practice received maximum scores for strength of volume, editorial quality, and evidence-based methodology. [3]
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. ... [It] means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research." The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of the patient, and the best available scientific information to guide decision-making about clinical management. The term was originally used to describe an approach to teaching the practice of medicine and improving decisions by individual physicians about individual patients.

An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and discussion of research. They nearly universally require peer review for research articles or other scrutiny from contemporaries competent and established in their respective fields.

The BMJ is a weekly peer-reviewed medical journal, published by BMJ Group, which in turn is wholly-owned by the British Medical Association (BMA). The BMJ has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Previously called the British Medical Journal, the title was officially shortened to BMJ in 1988, and then changed to The BMJ in 2014. The journal is published by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, a subsidiary of the British Medical Association (BMA). The current editor-in-chief of The BMJ is Kamran Abbasi, who was appointed in January 2022.
In scientific writing, IMRAD or IMRaD is a common organizational structure. IMRaD is the most prominent norm for the structure of a scientific journal article of the original research type.
MedlinePlus is an online information service produced by the United States National Library of Medicine. The service provides curated consumer health information in English and Spanish with select content in additional languages. The site brings together information from the National Library of Medicine (NLM), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), other U.S. government agencies, and health-related organizations. There is also a site optimized for display on mobile devices, in both English and Spanish. In 2015, about 400 million people from around the world used MedlinePlus. The service is funded by the NLM and is free to users.

A medical guideline is a document with the aim of guiding decisions and criteria regarding diagnosis, management, and treatment in specific areas of healthcare. Such documents have been in use for thousands of years during the entire history of medicine. However, in contrast to previous approaches, which were often based on tradition or authority, modern medical guidelines are based on an examination of current evidence within the paradigm of evidence-based medicine. They usually include summarized consensus statements on best practice in healthcare. A healthcare provider is obliged to know the medical guidelines of their profession, and has to decide whether to follow the recommendations of a guideline for an individual treatment.
An informationist provides research and knowledge management services in the context of clinical care or biomedical research.

A health or medical library is designed to assist physicians, health professionals, students, patients, consumers, medical researchers, and information specialists in finding health and scientific information to improve, update, assess, or evaluate health care. Medical libraries are typically found in hospitals, medical schools, private industry, and in medical or health associations. A typical health or medical library has access to MEDLINE, a range of electronic resources, print and digital journal collections, and print reference books. The influence of open access (OA) and free searching via Google and PubMed has a major impact on the way medical libraries operate.
Open access citation advantage (OACA), sometimes known as FUTON bias, is a type of bias whereby scholars tend to cite academic journals with open access (OA)—that is, journals that make their full text available on the Internet without charge —in preference to toll-access publications. The concept was introduced, under the FUTON bias name, by UK medical researcher Reinhard Wentz in a letter to The Lancet in 2002.
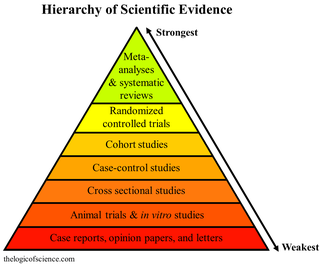
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic, then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion. For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine.
HubMed is an alternative, third-party interface to PubMed, the database of biomedical literature produced by the National Library of Medicine. It transforms data from PubMed and integrates it with data from other sources. Features include relevance-ranked search results, direct citation export, tagging and graphical display of related articles.
In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence. Some case reports also contain a literature review of other reported cases. Case reports are professional narratives that provide feedback on clinical practice guidelines and offer a framework for early signals of effectiveness, adverse events, and cost. They can be shared for medical, scientific, or educational purposes.
Index Medicus (IM) is a curated subset of MEDLINE, which is a bibliographic database of life science and biomedical science information, principally scientific journal articles. From 1879 to 2004, Index Medicus was a comprehensive bibliographic index of such articles in the form of a print index or its onscreen equivalent. Medical history experts have said of Index Medicus that it is “America's greatest contribution to medical knowledge.”
UpToDate, Inc. is a company in the Wolters Kluwer Health division of Wolters Kluwer, the main product of which is the eponymous UpToDate, a software system that is a point-of-care medical resource.
Trip is a free clinical search engine used in the United Kingdom to help clinicians identify research evidence, in part for creating systematic reviews.
E-Science librarianship refers to a role for librarians in e-Science.

The Wikipedia online encyclopedia has, since the late 2000s, served as a popular source for health information for both laypersons and, in many cases, health care practitioners. Health-related articles on Wikipedia are popularly accessed as results from search engines, which frequently deliver links to Wikipedia articles. Independent assessments have been made of the number and demographics of people who seek health information on Wikipedia, the scope of health information on Wikipedia, and the quality and reliability of the information on Wikipedia.
The NIH Public Access Policy is an open access mandate, drafted in 2004 and mandated in 2008, requiring that research papers describing research funded by the National Institutes of Health must be available to the public free through PubMed Central within 12 months of publication. PubMed Central is the self-archiving repository in which authors or their publishers deposit their publications. Copyright is retained by the usual holders, but authors may submit papers with one of the Creative Commons licenses.

Drummond Rennie is an American nephrologist and high altitude physiologist who is a contributing deputy editor of The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) and an adjunct professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco.

Estelle Brodman (1914–2007) was an American medical librarian and medical historian. She held positions at Columbia University, the National Library of Medicine and the Washington University School of Medicine (WUSM). Brodman served terms as director of the Special Libraries Association, president of the Medical Library Association, and editor of the Bulletin of the Medical Library Association. Under Brodman's leadership, the library at WUSM became known as a leader in the use of computing machines to perform library functions.