Overview
BRFplus offers a unified modeling and runtime environment for business rules that addresses both technical users (programmers, system administrators) as well as business users who take care of operational business processes (like procurement, bidding, tax form validation, etc.). The different requirements and usage scenarios of the different target groups can be covered with the help of the SAP authorization system and a user interface that can be individually customized.
Being integrated into SAP NetWeaver, BRFplus-based applications can look at, and model, business rules from a strictly business-oriented perspective, rather than starting with the underlying technical artifacts. This is because the integration allows for direct access to the business objects available in the SAP dictionary (like customer , supplier, material, bill, etc.).
In addition to the predefined expression types (decision table, decision tree, formula, database access, loops, etc.) and actions (sending e-mails, triggering a workflow, etc.), BRFplus can be extended by custom expression types. Also, direct calls of function modules as well as ABAP OO class methods are supported so that the entire range of the ABAP programming language is available for solving business tasks.
BRFplus comes with an optional versioning mechanism. Versioning can be switched on and off for individual objects as well as for entire applications. Versioned business rules are needed in certain use cases for legal reasons, but they also allow for simulating the system behavior as it would have been at a particular point in time.
Once the rule objects are in a consistent state and active, the system automatically generates ABAP OO classes that encapsulate the functional scope of the underlying rule object. This is done on an on-demand base and speeds up processing.
The execution of functions as well as of single expressions can be simulated. The processing log of the simulation is useful for checking the implementation and for investigating problems.
BRFplus applications can be exported and imported as an XML file. This is an easy way of creating a data backup. XML files can also be used for deploying rule applications throughout the company.
Main Object Types
Application
The application object serves as a container for all the BRFplus objects that have been assembled to solve a particular business task. It is possible to define certain default settings on application level that are inherited by all objects that are created in the scope of that application.
Function
A function is used to connect a business application with the rule processing framework of BRFplus. The calling business application passes input values to the function which are then processed by the expressions and rulesets that are associated with the called function. The calculated result is then returned to the calling business application.
Expression types and action types
Ruleset
A ruleset is a container for an arbitrary number of rule objects which in turn carry out the necessary calculations with the help of assigned expressions and actions. Instead of assigning an expression to a function, it is also possible to assign any number of rulesets to a function. When the function is called, all assigned rulesets are subsequently processed.
Data Objects
BRFplus supports elementary data objects (text, number, boolean, time point, amount, quantity) as well as structures and tables. Structures can be nested. For all types of data objects it is possible to reference data objects that reside in the data dictionary of the backend system. With that, a BRFplus data object does not only inherit the type definition of the referenced object but can also access associated data like domain value lists or object documentation.
Other objects
With catalogs, it is possible to define business-specific subsets of the rule objects that reside in the system. This is helpful for hiding the complexity of a rule system, thus improving usability.
Object filters are used by system administrators to ensure that for selected users, only a predefined subset of object types is visible. This is useful to enforce access rights as well as modeling policies.
VBScript is an Active Scripting language developed by Microsoft that is modeled on Visual Basic. It allows Microsoft Windows system administrators to generate powerful tools for managing computers with error handling, subroutines, and other advanced programming constructs. It can give the user complete control over many aspects of their computing environment.
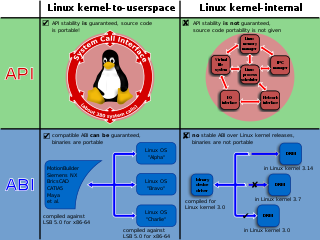
In computer software, an application binary interface (ABI) is an interface between two binary program modules. Often, one of these modules is a library or operating system facility, and the other is a program that is being run by a user.
In computer software, business logic or domain logic is the part of the program that encodes the real-world business rules that determine how data can be created, stored, and changed. It is contrasted with the remainder of the software that might be concerned with lower-level details of managing a database or displaying the user interface, system infrastructure, or generally connecting various parts of the program.
SAP R/3 is the former name of the enterprise resource planning software produced by the German corporation SAP AG. It is an enterprise-wide information system designed to coordinate all the resources, information, and activities needed to complete business processes such as order fulfillment, billing, human resource management, and production planning.
ABAP is a high-level programming language created by the German software company SAP SE. It is currently positioned, alongside Java, as the language for programming the SAP NetWeaver Application Server, which is part of the SAP NetWeaver platform for building business applications.
SAP Business Warehouse is SAP’s Enterprise Data Warehouse product. It can transform and consolidate business information from virtually any source system. It ran on industry standard RDBMS until version 7.3 at which point it began to transition onto SAP's HANA in-memory DBMS, particularly with the release of version 7.4.
SAP NetWeaver is a software stack for many of SAP SE's applications. The SAP NetWeaver Application Server, sometimes referred to as WebAS, is the runtime environment for the SAP applications and all of the mySAP Business Suite runs on SAP WebAS: supplier relationship management (SRM), customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), product lifecycle management (PLM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), transportation management system (TMS).
Systems Applications Products audit is an audit of a computer system from SAP to check its security and data integrity. SAP is the acronym for Systems, Applications, Products. It is a system that provides users with a soft real-time business application. It contains a user interface and is considered very flexible. In an SAP audit the two main areas of concern are security and data integrity.
Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) is a query language for online analytical processing (OLAP) using a database management system. Much like SQL, it is a query language for OLAP cubes. It is also a calculation language, with syntax similar to spreadsheet formulas.
SAP GUI is the graphical user interface client in SAP ERP's 3-tier architecture of database, application server and client. It is software that runs on a Microsoft Windows, Apple Macintosh or Unix desktop, and allows a user to access SAP functionality in SAP applications such as SAP ERP and SAP Business Information Warehouse (BW). It is used for remote access to the SAP central server in a company network.
SAP NetWeaver Application Server or SAP Web Application Server is a component of SAP NetWeaver which works as a web application server for SAP products. All ABAP application servers including the message server represent the application layer of the multitier architecture of an ABAP-based SAP system. These application servers execute ABAP applications and communicate with the presentation components, the database, and also with each other, using the message server.
Kinetic Rule Language (KRL) is a rule-based programming language for creating applications on the Live Web. KRL programs, or rulesets, comprise a number of rules that respond to particular events. KRL has been promoted as language for building personal clouds.
SAP Composite Application Framework is a composition tool in NWDS and runtime on SAP Web Application Server Java for developing, testing, deploying, running and configuring composite applications. It is tightly integrated in the NetWeaver stack and is currently the tool of choice of SAP customers for developing an enterprise application's business logic layer, along with the pure JEE development tools provided in NWDS. The CAF IDE tool has a strong model-driven architecture approach to development, resulting in rapid development of a system 's business logic layer.
IDoc, short for Intermediate Document, is a SAP document format for business transaction data transfers. Non SAP-systems can use IDocs as the standard interface (computing) for data transfer. IDoc is similar to XML in purpose, but differs in syntax. Both serve the purpose of data exchange and automation in computer systems, but the IDoc-Technology takes a different approach.
Web Dynpro (WD) is a web application technology developed by SAP SE that focuses on the development of server-side business applications. For modern releases the user interface is rendered according to the HTML5 web standard. Since Netweaver 754 a touch enabled user interface is available. The newly released versions usually follow the SAP Fiori design principles. One of its main design features is that the user interface is defined in an entirely declarative manner. Web Dynpro applications can be developed using either the Java or ABAP development infrastructure.
SAP Logon Tickets represent user credentials in SAP systems. When enabled, users can access multiple SAP applications and services through SAP GUI and web browsers without further username and password inputs from the user. SAP Logon Tickets can also be a vehicle for enabling single sign-on across SAP boundaries; in some cases, logon tickets can be used to authenticate into 3rd party applications such as Microsoft-based web applications.

SAP HANA is an in-memory, column-oriented, relational database management system developed and marketed by SAP SE. Its primary function as the software running a database server is to store and retrieve data as requested by the applications. In addition, it performs advanced analytics and includes extract, transform, load (ETL) capabilities as well as an application server.
In business analysis, the Decision Model and Notation (DMN) is a standard published by the Object Management Group. It is a standard approach for describing and modeling repeatable decisions within organizations to ensure that decision models are interchangeable across organizations.
ERP Security is a wide range of measures aimed at protecting Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems from illicit access ensuring accessibility and integrity of system data. ERP system is a computer software that serves to unify the information intended to manage the organization including Production, Supply Chain Management, Financial Management, Human Resource Management, Customer Relationship Management, Enterprise Performance Management. Common ERP systems are SAP, Oracle E-Business Suite, Microsoft Dynamics, Priority Software.


