Related Research Articles

British Standards (BS) are the standards produced by the BSI Group which is incorporated under a royal charter and which is formally designated as the national standards body (NSB) for the UK. The BSI Group produces British Standards under the authority of the charter, which lays down as one of the BSI's objectives to:
Set up standards of quality for goods and services, and prepare and promote the general adoption of British Standards and schedules in connection therewith and from time to time to revise, alter and amend such standards and schedules as experience and circumstances require.

The Carbon Trust was developed and launched in the UK over 1999-2001 as part of the development of the Climate Change Levy (CCL), a tax on business energy use that still operates today. The Carbon Trust was originally funded by around £50m of UK tax revenue generated from the Levy to help businesses reduce energy costs and therefore offset the additional cost of paying the CCL. The establishment of the Carbon Trust was announced in the 2000 UK White Paper "Climate Change - the UK Programme". It was launched alongside the introduction of the CCL in March–April 2001.

A carbon footprint (or greenhouse gas footprint) is a calculated value or index that makes it possible to compare the total amount of greenhouse gases that an activity, product, company or country adds to the atmosphere. Carbon footprints are usually reported in tonnes of emissions (CO2-equivalent) per unit of comparison. Such units can be for example tonnes CO2-eq per year, per kilogram of protein for consumption, per kilometer travelled, per piece of clothing and so forth. A product's carbon footprint includes the emissions for the entire life cycle. These run from the production along the supply chain to its final consumption and disposal. Similarly an organization's carbon footprint includes the direct as well as the indirect emissions that it causes. The Greenhouse Gas Protocol that is used for carbon accounting of organizations calls these Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions. There are several methodologies and online tools to calculate the carbon footprint. They depend on whether the focus is on a country, organization, product or individual person. For example, the carbon footprint of a product could help consumers decide which product to buy if they want to be climate aware. For climate change mitigation activities, the carbon footprint can help distinguish those economic activities with a high footprint from those with a low footprint. So the carbon footprint concept allows everyone to make comparisons between the climate impacts of individuals, products, companies and countries. It also helps people devise strategies and priorities for reducing the carbon footprint.

Carbon offsetting is a trading mechanism that allows entities such as governments, individuals, or businesses to compensate for (i.e. “offset”) their greenhouse gas emissions by supporting projects that reduce, avoid, and/or remove emissions elsewhere. A carbon credit or offset credit is a transferrable financial instrument, that is a derivative of an underlying commodity. It can be bought or sold after certification by a government or independent certification body. When an entity invests in a carbon offsetting program, it receives carbon credits, i.e the "tokens" used to account for net climate benefits from one entity to another. One carbon offset or credit represents a reduction, avoidance or removal of one tonne of carbon dioxide or its carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e). Offset projects that take place in the future can be considered to be a type of promissory note: The purchaser of the offset credit pays carbon market rates for the credits and in turn receives a promise that the purchaser's greenhouse emissions generated in the present (e.g. a roundtrip flight to London) will be offset by elimination of an equal amount in the near or distant future (e.g. 10-20 years for planting 110 seedlings). Offsets that were generated in the past are credible only if they were in addition to reductions that would have happened anyway.
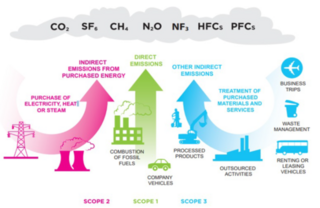
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.

The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies certification and standards-related services to businesses.
The carboNZero programme and CEMARS programme are the world’s first internationally accredited greenhouse gas (GHG) certification schemes under ISO 14065. They provide tools for organisations, products, services and events to measure and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions, and optionally offset it. The programmes are owned and operated by Toitū Envirocare - Enviro-Mark Solutions Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of Landcare Research.

ClimateCare is a profit for purpose environmental and social impact company known for its role providing carbon offset services, with a particular focus on using carbon and other results based finance to support its 'Climate+Care Projects'. It also provides businesses and governments with sustainable development programmes, environmental and social impact measurement and project development.
A Publicly Available Specification or PAS is a standardization document that closely resembles a formal standard in structure and format but which has a different development model. The objective of a Publicly Available Specification is to speed up standardization. PASs are often produced in response to an urgent market need.

myclimate was spun off from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich in 2002 as a nonprofit climate protection organisation based in Switzerland to enable climate protection with economic mechanisms such as price-tagging carbon dioxide and integrating the externality into the market. They promote climate protection on three levels: avoidance techniques such as capacity building and teaching, reduction and carbon offsetting. myclimate advocates for the development of a carbon market while setting new standards in carbon emissions and in designing a sustainable society.
The ISO 14064 standard is the core part of the ISO 14060 family of standards that are part of the ISO 14000 series of international standards by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for environmental management. The ISO 14064 standards provides governments, businesses, regions and other organisations with a complementary set of tools for programs to quantify, monitor, report and verify greenhouse gas emissions. The ISO 14064 standards supports organisations to participate in both regulated and voluntary programs such as emissions trading schemes and public reporting using a globally recognised standard.

Airport Carbon Accreditation is a global carbon management programme for airports that independently assesses and recognises airports' efforts to manage and reduce their CO2 emissions. Aircraft emissions, which are many times greater than airport emissions, are not included in the programme. The airport industry accounts for 5% of the air transport sector’s total carbon emissions.
Carbon Clear is a sustainability consultancy. Carbon Clear is a founding member of the International Carbon Reduction and Offset Alliance (ICROA).
ISO 50001Energy management systems - Requirements with guidance for use, is an international standard created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It supports organizations in all sectors to use energy more efficiently through the development of an energy Management System. The standard specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and improving an energy management system, whose purpose is to enable an organization to follow a systematic approach in achieving continual improvement of energy performance, including energy efficiency, energy security, energy use and consumption.
Environmental certification is a form of environmental regulation and development where a company can voluntarily choose to comply with predefined processes or objectives set forth by the certification service. Most certification services have a logo which can be applied to products certified under their standards. This is seen as a form of corporate social responsibility allowing companies to address their obligation to minimise the harmful impacts to the environment by voluntarily following a set of externally set and measured objectives.
ISO 20121 is a voluntary international standard for sustainable event management, created by the International Organization for Standardization. The standard aims to help organizations improve sustainability throughout the entire event management cycle.
The Woodland Carbon Code is the UK standard for afforestation projects for climate change mitigation. It provides independent validation and verification and assurance about the levels of carbon sequestration from woodland creation projects and their contribution to climate change mitigation.

CO2balance UK Ltd is a British profit-for-purpose carbon management consultancy and project developer founded in 2003. It is known for developing carbon finance projects in developing countries that reduce carbon emissions and support the Sustainable Development Goals. CO2balance also provides businesses and individuals with carbon footprint calculation and reduction services, bestowing the label of ‘CarbonZero’ on those organisations that completely offset the footprint of their operations.

Global net zero emissions describes the state where emissions of carbon dioxide due to human activities and removals of these gases are in balance over a given period. It is often called simply net zero. In some cases, "emissions" refers to emissions of all greenhouse gases, and in others it refers only to emissions of carbon dioxide.
References
- ↑ "PAS 2060 Carbon Neutrality - BSI Group". www.bsigroup.com. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ "High Street sets standard for demonstration of carbon neutrality". Archived from the original on 2010-11-18. Retrieved 2011-02-07.
- ↑ "Demonstrate your carbon neutrality status with confidence". Archived from the original on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 2011-02-07.
- ↑ BSI (2014). PAS 2060:2014 Specification for the demonstration of carbon neutrality. BSI. ISBN 978-0-580-83670-1.
- ↑ "BS ISO 14068-1:2023 Climate change management. Transition to net zero - Carbon neutrality" . Retrieved 2023-12-19.
- 1 2 BSi. PAS 2060:2010 Specification for the demonstration of carbon neutrality. ISBN 978-0-580-66752-7, April 2010