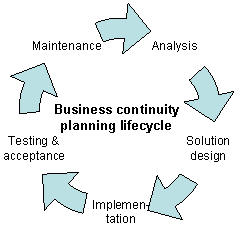
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.
ISO/IEC 20000 is the international standard for IT service management. It was developed in 2005 by ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7 and revised in 2011 and 2018. It was originally based on the earlier BS 15000 that was developed by BSI Group.
Information security standards or cyber security standards are techniques generally outlined in published materials that attempt to protect the cyber environment of a user or organization. This environment includes users themselves, networks, devices, all software, processes, information in storage or transit, applications, services, and systems that can be connected directly or indirectly to networks.

The Standard of Good Practice for Information Security (SOGP), published by the Information Security Forum (ISF), is a business-focused, practical and comprehensive guide to identifying and managing information security risks in organizations and their supply chains.
ISO/IEC 27000 is one of the ISO/IEC technical standards in the ISO/IEC 27000 series of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)-related standards. The formal title for ISO/IEC 27000 is Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management systems — Overview and vocabulary.

The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies certification and standards-related services to businesses.
Information security management (ISM) defines and manages controls that an organization needs to implement to ensure that it is sensibly protecting the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of assets from threats and vulnerabilities. The core of ISM includes information risk management, a process that involves the assessment of the risks an organization must deal with in the management and protection of assets, as well as the dissemination of the risks to all appropriate stakeholders. This requires proper asset identification and valuation steps, including evaluating the value of confidentiality, integrity, availability, and replacement of assets. As part of information security management, an organization may implement an information security management system and other best practices found in the ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27002, and ISO/IEC 27035 standards on information security.
ISO/IEC 27002 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), titled Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Information security controls.
The ISO/IEC 27000-series comprises information security standards published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO/IEC 27006 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Part of the ISO/IEC 27000 series of ISO/IEC Information Security Management System (ISMS) standards, it is titled Information technology - Security techniques - Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of information security management systems.
ISO/IEC 27003 Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management systems — Guidance. It is part of a family of standards of information security management system (ISMS), which is a systematic approach to securing sensitive information, of ISO/IEC. It provides standards for a robust approach to managing information security (infosec) and building resilience. It was published on February 1, 2010, and revised in April 2017. It is currently not certifiable and is not translated into Spanish.
ISO/IEC 27004 Information Technology – Security techniques – Information Security Management – Measurement. It is part of a family of standards of information security management system (ISMS), which is a systematic approach to securing sensitive information, of ISO/IEC. It provides standards for a robust approach to managing information security (infosec) and building resilience. It was published on December 7, 2009 and revised in December 2016. It is currently not certifiable and is not translated into Spanish.
ISO/IEC 27007 is a standard on Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection that provides guidance on managing an information security management system (ISMS) audit programme, on conducting audits, and on the competence of ISMS auditors, in addition to the guidance contained in ISO 19011. This standard is applicable to those needing to understand or conduct internal or external audits of an ISMS or to manage an ISMS audit programme. It was published on November 14, 2011, and revised on January 21, 2020.
Information technology risk, IT risk, IT-related risk, or cyber risk is any risk relating to information technology. While information has long been appreciated as a valuable and important asset, the rise of the knowledge economy and the Digital Revolution has led to organizations becoming increasingly dependent on information, information processing and especially IT. Various events or incidents that compromise IT in some way can therefore cause adverse impacts on the organization's business processes or mission, ranging from inconsequential to catastrophic in scale.
The IT baseline protection approach from the German Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) is a methodology to identify and implement computer security measures in an organization. The aim is the achievement of an adequate and appropriate level of security for IT systems. To reach this goal the BSI recommends "well-proven technical, organizational, personnel, and infrastructural safeguards". Organizations and federal agencies show their systematic approach to secure their IT systems by obtaining an ISO/IEC 27001 Certificate on the basis of IT-Grundschutz.
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard to manage information security. The standard was originally published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2005, revised in 2013, and again most recently in 2022. There are also numerous recognized national variants of the standard. It details requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS) – the aim of which is to help organizations make the information assets they hold more secure. Organizations that meet the standard's requirements can choose to be certified by an accredited certification body following successful completion of an audit. The effectiveness of the ISO/IEC 27001 certification process and the overall standard has been addressed in a large-scale study conducted in 2020.
ISO/IEC 27701:2019 is a privacy extension to ISO/IEC 27001. The design goal is to enhance the existing Information Security Management System (ISMS) with additional requirements in order to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS). The standard outlines a framework for Personally Identifiable Information (PII) Controllers and PII Processors to manage privacy controls to reduce the risk to the privacy rights of individuals.
ISO/IEC 27017 is a security standard developed for cloud service providers and users to make a safer cloud-based environment and reduce the risk of security problems. It was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under the joint ISO and IEC subcommittee, ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 27. It is part of the ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards, standards which provides best practice recommendations on information security management. This standard was built from ISO/IEC 27002, suggesting additional security controls for the cloud which were not completely defined in ISO/IEC 27002.
ISO/IEC 27018 is a security standard part of the ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards. It was the first international standard about the privacy in cloud computing services which was promoted by the industry. It was created in 2014 as an addendum to ISO/IEC 27001, the first international code of practice for cloud privacy. It helps cloud service providers who process personally identifiable information (PII) to assess risk and implement controls for protecting PII. It was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under the joint ISO and IEC subcommittee, ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 27.


