
A veterinarian (vet) is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine. They manage a wide range of health conditions and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, veterinarians also play a role in animal reproduction, health management, conservation, husbandry and breeding and preventive medicine like nutrition, vaccination and parasitic control as well as biosecurity and zoonotic disease surveillance and prevention.
Degree abbreviations are used as an alternative way to specify an academic degree instead of spelling out the title in full, such as in reference books such as Who's Who and on business cards. Many degree titles have more than one possible abbreviation, with the abbreviation used varying between different universities. In the UK it is normal not to punctuate abbreviations for degrees with full stops, although this is done at some universities.

The Royal Veterinary College is a veterinary school located in London and a member institution of the federal University of London. The RVC was founded in 1791 and joined the University of London in 1949. It is the oldest and largest Veterinary school in the United Kingdom, and one of only nine in the country where students can study to become a vet.

The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), founded in 1863, is a not-for-profit association representing more than 99,500 veterinarians in the US.
A Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery is an undergraduate medical degree awarded by medical schools in countries that follow the tradition of the United Kingdom. The historical degree nomenclature states that they are two separate undergraduate degrees. In practice, however, they are usually combined as one and conferred together, and may also be awarded at graduate-level medical schools. It usually takes five to six years to complete this degree.

Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI) is located at Izatnagar, Bareilly in Uttar Pradesh state. It is an advanced research facility in the field of veterinary medicine and allied branches. It has regional campuses at Mukteshwar, Bangalore, Palampur, Pune, Kolkata and Srinagar.

The University of Veterinary Science, Yezin, located in Yezin in the outskirts of Naypyidaw, is the only university of veterinary science in Myanmar (Burma). The university offers a six-year Bachelor of Veterinary Science (BVSc) program. Since 2014, UVS renamed its BVSc degree to DVM and, since then, all new graduates received DVM title instead. It accepts about 100 students a year. It has launched a four-year Bachelor of Animal Science (BASc) program since 2014. It accepts about 100 students a year.<The global new light of Myanmar, daily news paper, December 30,2018,https://www.burmalibrary.org/en/category/the-global-new-light-of-myanmar-2018> It also offers graduate degree programs. The language of instruction at UVS is English.

Veterinary education is the tertiary education of veterinarians. To become a veterinarian, one must first complete a degree in veterinary medicine Doctor of Veterinary Medicine.

The Royal (Dick) School of Veterinary Studies, commonly referred to as the Dick Vet, is the veterinary school of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland and part of the College of Medicine and Veterinary Medicine the head of which is David Argyle. Dylan Clements has been Dean and Interim Head of School since May 2023.
Ross University School of Veterinary Medicine (RUSVM), founded in 1982, is a university offering the Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree. As of 2014, RUSVM began offering Master of Science and PhD degrees in public health, global animal health, conservation medicine, and other research areas supported by the school. The school is located in St. Kitts. Administrative offices are located in Downers Grove, IL. RUSVM is accredited by the American Veterinary Medical Association Council on Education.
The Sydney School of Veterinary Science is a constituent body of the University of Sydney, Australia. Initially established on 22 March 1910, it is the second oldest established veterinary school in Australia, the longest running veterinary school in Australia and one of two universities offering veterinary degrees in New South Wales. The faculty offers a joint Bachelor of Veterinary Biology/Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (BVetBiol/DVM), having retired the former Bachelor of Veterinary Science (BVSc), and the Bachelor of Animal and Veterinary Bioscience (BAnVetBioSc). The Faculty is established across both Camperdown and Camden campuses. The faculty is usually associated with the Roundhouse or Centaur as a logo and celebrated its centenary in 2010. The Faculty will be incorporated into the Faculty of Science in 2017.
The Faculty of Veterinary Science is a faculty of the University of Pretoria. Founded in 1920, it is the second oldest veterinary faculty in Africa. With the exception of the faculties in Khartoum, and Cairo, all the other African faculties were established after 1960. It is the only one of its kind in South Africa and is one of 33 veterinary faculties in Africa.

WikiVet is a wiki of veterinary content based on the MediaWiki platform. The website is a collaborative initiative between various veterinary schools, and its content covers the entire veterinary curriculum. WikiVet is part of the WikiVet Educational Foundation.
Veterinary ethics is a system of moral principles that apply values and judgements to the practice of veterinary medicine. As a scholarly discipline, veterinary ethics encompasses its practical application in clinical settings as well as work on its history, philosophy, theology, and sociology. Veterinary ethics combines veterinary professional ethics and the subject of animal ethics. The subject of veterinary ethics can be interpreted as an extension of critical thinking skills necessary to make the decisions in veterinary care in order to support the profession's responsibilities to animal kind and mankind.
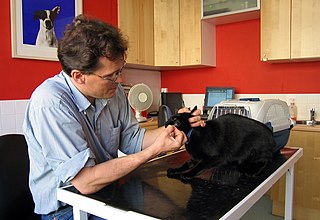
Veterinary medicine in the United Kingdom is the performance of veterinary medicine by licensed professionals. It is strictly regulated by the statute law, notably the Veterinary Surgeons Act 1966. Veterinary medicine is led by veterinary physicians, termed "veterinary surgeons", normally referred to as "vets".

Veterinary medicine in the United States is the performance of veterinary medicine in the United States, normally performed by licensed professionals, and subject to provisions of statute law which vary by state. Veterinary medicine is normally led by veterinary physicians, termed veterinarians or vets, but also by paraveterinary workers, such as veterinary technicians, and veterinary assistants. This can be augmented by other paraprofessionals with specific specialties, such as animal physiotherapy or dentistry, and species-relevant roles such as farriers.

Alexander John "Sandy" Trees, Baron Trees is a Professor of veterinary parasitology and a Crossbench member of the House of Lords.
Albert Edward Mettam MRCVS, MRIA, was inaugural Principal of the Royal Veterinary College of Ireland in Dublin. He went there from the Royal (Dick) Veterinary College where he had been Professor of Anatomy and Histology from 1892.
Joan Olive Joshua was an English veterinary surgeon, dog breeder and feminist. She worked at her one-person private practice in Finchley, London from 1939 to 1962. Joshua was the first female fellow of the Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons (RCVP) and the first woman to serve on the RCVP council. She served as a councillor for the National Veterinary Medical Association and successfully campaigned for the Animal Health Trust to be founded. Joshua was a reader at the University of Liverpool School of Veterinary Science's Department of Clinical Studies. She was the first woman to receive each of the RCVS Francis Hogg Prize and the Victory Medal of the Central Veterinary Society.










