Related Research Articles

Trichuris trichiura, Trichocephalus trichiuris or whipworm, is a parasitic roundworm that causes trichuriasis when it infects a human large intestine. It is commonly known as the whipworm which refers to the shape of the worm; it looks like a whip with wider "handles" at the posterior end. The helminth is also known to cause rectal prolapse.
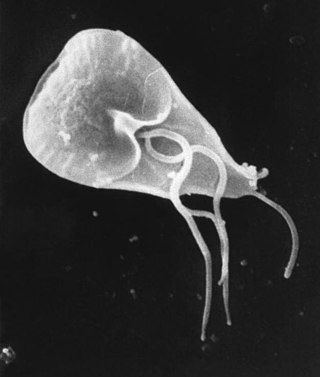
Giardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between a swimming trophozoite and an infective, resistant cyst. Giardia were first described by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1681. The genus is named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard.

Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology.
Veterinary parasitology is a branch of veterinary medicine that deals with the study of morphology, life-cycle, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and control of eukaryotic invertebrates of the kingdom Animalia and the taxon Protozoa that depend upon other invertebrates and higher vertebrates for their propagation, nutrition, and metabolism without necessarily causing the death of their hosts. Modern parasitology focuses on responses of animal hosts to parasitic invasion. Parasites of domestic animals,, as well as wildlife animals are considered. Data obtained from parasitological research in animals helps in veterinary practice and improves animal breeding. The major goal of veterinary parasitology is to protect animals and improve their health, but because a number of animal parasites are transmitted to humans, veterinary parasitology is also important for public health.
Bacillary dysentery is a type of dysentery, and is a severe form of shigellosis. It is associated with species of bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. The term is usually restricted to Shigella infections.

Helminthic therapy, an experimental type of immunotherapy, is the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune disorders by means of deliberate infestation with a helminth or with the eggs of a helminth. Helminths are parasitic worms such as hookworms, whipworms, and threadworms that have evolved to live within a host organism on which they rely for nutrients. These worms are members of two phyla: nematodes, which are primarily used in human helminthic therapy, and flat worms (trematodes).
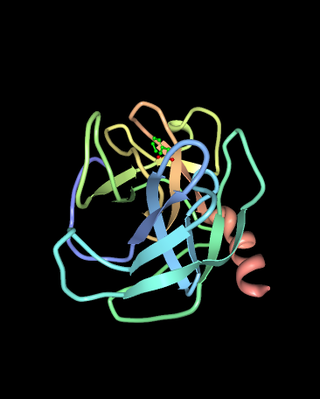
Chymases are a family of serine proteases found primarily in mast cells, though also present in basophil granulocytes. Recently, Derakhshan et al. reported that a specific mast cell population expressed transcripts for Mcpt8. They show broad peptidolytic activity and are involved in a variety of functions. For example, chymases are released by connective tissue-type mast cells upon challenge with parasites and parasite antigens promoting an inflammatory response, and chymase mcp1 and mcp2 are used for marker for mast cell degranulation in parasite infection such as Nematode, Trichuris muris Chymases are also known to convert angiotensin I to angiotensin II and thus play a role in hypertension and atherosclerosis.

Leucocytozoon is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa.

Theileria is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to Plasmodium. Two Theileria species, T. annulata and T. parva, are important cattle parasites. T. annulata causes tropical theileriosis and T. parva causes East Coast fever. Theileria species are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of T. orientalis Shintoku, Theileria equi WA, Theileria annulata Ankara and Theileria parva Muguga have been sequenced and published.

Trichuris, often referred to as whipworms or the silent serpent, is a genus of parasitic helminths from the roundworm family Trichuridae. The name whipworm refers to the shape of the worm; they look like whips with wider "handles" at the posterior end.

Blastocystis is a genus of single-celled parasites belonging to the Stramenopiles that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds. There are several species, living in the gastrointestinal tracts of species as diverse as humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and cockroaches. Blastocystis has low host specificity, and many different species of Blastocystis can infect humans, and by current convention, any of these species would be identified as Blastocystis hominis.

Trichuris suis is a whipworm; the variations in thickness of the anterior and posterior segments give the parasite the characteristic "whip-like" appearance. Adult females measure 6 to 8 cm and adult males 3 to 4 cm. T. suis eggs are oval and yellow-brown with bipolar plugs. T. suis is also used in helminthic therapy studies.

Archaeoparasitology, a multi-disciplinary field within paleopathology, is the study of parasites in archaeological contexts. It includes studies of the protozoan and metazoan parasites of humans in the past, as well as parasites which may have affected past human societies, such as those infesting domesticated animals.

Trichuris vulpis is a whipworm that lives in the large intestine of canines in its adult stages. Out of different types of worms, Trichuris vulpis is one of the smaller worms with a size ranging from 30–50 mm in length. As the name suggests, the worm has a whip-like shape with distinct features including a small, narrow anterior head, which is the digestive part of the worm, and a larger posterior tail, which is the reproductive part of the worm. Eggs from T. vulpis are oval shaped with bipolar plugs and contain a thick outer shell. Their sizes range from 72–90 μm in length and 32–40 μm in width. Because of their thick outer shell, T. vulpis eggs are very resistant to environmental extremes such as freezing or hot temperatures, thus allowing for their long viability in the outside world.
Tegument is a term in helminthology for the outer body covering of members of the phylum Platyhelminthes. The name is derived from a Latin word tegumentum or tegere, meaning "to cover". It is characteristic of flatworms including the broad groups of tapeworms and flukes. Once considered to be a non-living component, it is now known to be a dynamic cellular structure. In fact it is a living structure consisting of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and RNA. It forms the protective layer and the host-parasite interface of the worms, serving both secretory and absorptive functions.

Stichosome is a multicellular organ that is very prominent in some stages of nematodes and consists of a longitudinal series of glandular unicellular cells (stichocytes) arranged in a row along the oesophagus that form the posterior esophageal glands. It opens into the esophageal lumen and apparently functions as a secretory gland and storage organ.

Stichocytes are glandular unicellular cells arranged in a row along the posterior portion of the oesophagus, each of which communicates by a single pore with the lumen of the oesophagus. They contain mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum, abundant Golgi apparatuses, and usually 1 of 2 types of secretory granules, α-granules and β-granules, indicating secretory function. Collectively stichocytes form the stichosome. Characteristic of Trichocephalida and Mermithida, two groups of nematodes.
Trichuris serrata, commonly known as a whipworm, is a nematode of the genus Trichuris first discovered in domestic Brazilian cats by Dr. Otto Friedrich Bernhard von Linstow in 1879. Since then, there have been reports of this species in North and South America, Australia, and the Caribbean islands. Information regarding the species' general life cycle and egg development can be seen in the Trichuris page.
Trichuris ovis, commonly known as a whipworm, is a nematode belonging to the genus Trichuris. This whipworm species was first discovered in 1795 and is known to infect sheep and goats. These organisms are capable of inhabiting any region that has the aforementioned hosts, as can be attested by the numerous reports of T. ovis findings throughout North and South America, Australia, Europe, and Asia. Information regarding the species' general life cycle and egg development can be seen in the Trichuris page.
Ostertagia ostertagi, commonly known as the medium stomach worm or brown stomach worm, is a parasitic nematode of cattle. O. ostertagi can also be found to a lesser extent in sheep, goats, wild ruminants, and horses. It causes ostertagiosis, which is potentially fatal in cattle. It is found worldwide and is economically important to cattle industries, particularly those found in temperate climates.
References
- ↑ Peter J. Gosling. Dictionary of Parasitology. 2005
- ↑ Heinz Mehlhorn. Encyclopedia of Parasitology. 3rd Edition 2008
- ↑ Larry Roberts, John Janovy. Foundations of Parasitology. 8th edition 2008
- ↑ Michael Hutchins, Donna Olendorf. Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia: Lower metazoans and lesser deuterosomes. 2004
- ↑ Wright, K. A. 1968. Structure of the bacillary band of Trichuris myocastoris. J. Parasitol. 54:1106–1110.
- ↑ Sheffield, H. G. 1963. Electron microscopy of the bacillary band and stichosome of Trichuris muris and T. vulpes, J. Parasitol. 49:998–1009.