Related Research Articles

Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997, its official name was Shaba Province.

The Niger–Congo languages are the world's third largest language family in terms of number of speakers and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area, number of speakers, and number of distinct languages. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.

The Congo River, formerly known as the Zaire River during the dictatorship of Mobutu Sese Seko, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge volume, following only the Amazon. It is also the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths in excess of 220 m (720 ft). The Congo-Lualaba-Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,920 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,120 mi).

Kinshasa, formerly Léopoldville, is the capital and the largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The city is situated alongside the Congo River.

Leopold II was the second King of the Belgians from 1865 to 1909 and, through his own efforts, the owner and absolute ruler of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908.

The Belgian Congo was a Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960. The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964.
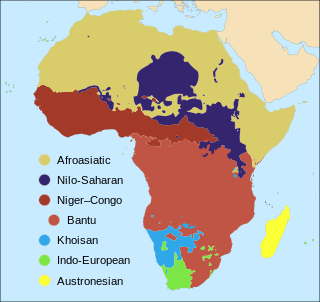
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families:

The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Kinshasa, Zaire, DR Congo, DRC, the DROC, or simply the Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It was formerly called Zaire (1971–1997). It is, by area, the largest country in sub-Saharan Africa, the second-largest in all of Africa, and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of over 101 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world, as well as the fourth-most-populous in Africa, and the 15th-most-populous country in the world. Since 2015, the Eastern DR Congo has been the scene of an ongoing military conflict in Kivu.

Benue–Congo is a major subdivision of the Niger–Congo language family which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. It consists of two main branches:

The Second Congo War began in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in August 1998, little more than a year after the First Congo War, and involved some of the same issues. The war officially ended in July 2003, when the Transitional Government of the Democratic Republic of the Congo took power. Although a peace agreement was signed in 2002, violence has continued in many regions of the country, especially in the east. Hostilities have continued since the ongoing Lord's Resistance Army insurgency, and the Kivu and Ituri conflicts.

The DR Congo national football team, recognised by FIFA as Congo DR, represents DR Congo in men's international football and it is controlled by the Congolese Association Football Federation. They are nicknamed the Leopards., The team represents FIFA and Confederation of African Football (CAF).

The Congo Crisis was a period of political upheaval and conflict in the Republic of the Congo between 1960 and 1965. The crisis began almost immediately after the Congo became independent from Belgium and ended, unofficially, with the entire country under the rule of Joseph-Désiré Mobutu. Constituting a series of civil wars, the Congo Crisis was also a proxy conflict in the Cold War, in which the Soviet Union and the United States supported opposing factions. Around 100,000 people are believed to have been killed during the crisis.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family of the Benue-Congo language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.

The Congolese Association Football Federation is the governing body of football in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was founded in 1919 and affiliated to the FIFA in 1964 and CAF in 1964. It organizes the national football league Linafoot and the national team.

Islam is a minority religion within the Democratic Republic of the Congo where the large majority is affiliated to various Christian denominations and sects. Though estimates vary, it is generally believed that approximately 10 percent of the country's population identify as Muslim. It was first introduced from the East African coast during the Arab slave trade in the 19th century and remains largely concentrated in parts of Eastern Congo, notably Maniema Province. Most Congolese Muslims are Sunni and follow the Shaafi and maliki school of jurisprudence (fiqh).

Republic of the Congo passports are issued to Congolese citizens to travel outside the Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville.

The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa. It is bordered by five countries: Gabon to its west; Cameroon to its northwest and the Central African Republic to its northeast; the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the southeast and the Angolan exclave of Cabinda to its south; and the Atlantic Ocean to its southwest. The official language is French.
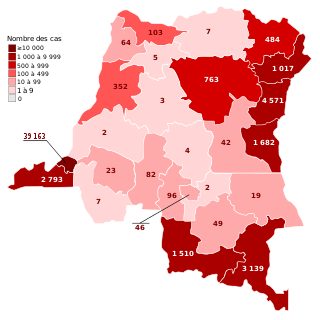
The COVID-19 pandemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 10 March 2020. The first few confirmed cases were all outside arrivals.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the Republic of the Congo in March 2020.
References
- ↑ "Découpage administratif de la République Démocratique du Congo" (PDF). Référentiel Géographique Commun - RGC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 April 2010. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
| This article related to a river in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |