Cortex or cortical may refer to:

Brodmann area 23 (BA23) is a region in the brain that lies inside the posterior cingulate cortex. It lies between Brodmann area 30 and Brodmann area 31 and is located on the medial wall of the cingulate gyrus between the callosal sulcus and the cingulate sulcus.

Brodmann area 8 is one of Brodmann's cytologically defined regions of the brain. It is involved in planning complex movements.

Brodmann area 5 is one of Brodmann's cytoarchitectural defined regions of the brain. It is involved in somatosensory processing, movement and association, and is part of the posterior parietal cortex.

Brodmann area 19, or BA 19, is part of the occipital lobe cortex in the human brain. Along with area 18, it comprises the extrastriate cortex. In humans with normal sight, extrastriate cortex is a visual association area, with feature-extracting, shape recognition, attentional, and multimodal integrating functions.

Brodmann area 20, or BA20, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the ventral temporal cortex, a region believed to play a part in high-level visual processing and recognition memory.

Brodmann area 21, or BA21, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the lateral temporal cortex and is also known as middle temporal area 21. In the human it corresponds approximately to the middle temporal gyrus.

Brodmann area 4 refers to the primary motor cortex of the human brain. It is located in the posterior portion of the frontal lobe.

Brodmann area 24 is part of the anterior cingulate in the human brain.
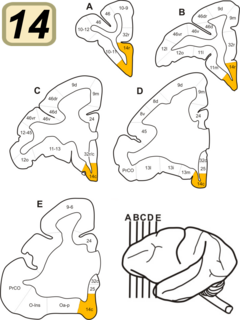
Brodmann Area 14 is one of Brodmann's subdivisions of the cerebral cortex in the brain. It was defined by Brodmann in the guenon monkey . While Brodmann, writing in 1909, argued that no equivalent structure existed in humans, later work demonstrated that area 14 has a clear homologue in the human ventromedial prefrontal cortex.
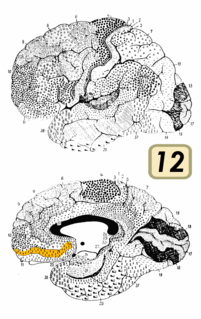
Brodmann area 12 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex of the guenon defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. It occupies the most rostral portion of the frontal lobe. Brodmann-1909 did not regard it as homologous, either topographically or cytoarchitecturally, to rostral area 12 of the human. Distinctive features (Brodmann-1905): a quite distinct internal granular layer (IV) separates slender pyramidal cells of the external pyramidal layer (III) and the internal pyramidal layer (V); the multiform layer (VI) is expanded, contains widely dispersed spindle cells and merges gradually with the underlying cortical white matter; all cells, including the pyramidal cells of the external and internal pyramidal layers are inordinately small; the internal pyramidal layer (V) also contains spindle cells in groups of two to five located close to its border with the internal granular layer (IV).

Brodmann area 13 is part of the insula, a subdivision of the cerebral cortex as defined by cytoarchitecture. The insula is covered by frontal, temporal and parietal operculum and therefore sometimes ignored as a Brodmann area.
Brodmann Area 15 is one of Brodmann's subdivisions of the cerebral cortex in the brain.
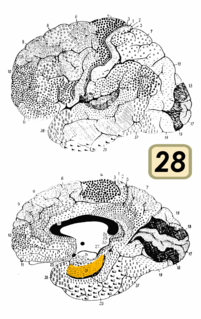
Brodmann area 28 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. It is located on the medial aspect of the temporal lobe and is part of the entorhinal cortex (Brodmann-1909).

Brodmann area 29, also known as granular retrolimbic area 29 or granular retrosplenial cortex, is a cytoarchitecturally defined portion of the retrosplenial region of the cerebral cortex. In the human it is a narrow band located in the isthmus of cingulate gyrus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the ectosplenial area 26 and externally by the agranular retrolimbic area 30 (Brodmann-1909).

Jules Baillarger, full name Jules Gabriel François Baillarger, was a French neurologist and psychiatrist.
The internal granular layer of the cortex, also commonly referred to as the granular layer of the cortex, is the layer IV in the subdivision of the mammalian cortex into 6 layers. The adjective internal is used in opposition to the external granular layer of the cortex, the term granular refers to the granule cells found here.

The line of Gennari is a band of myelinated axons that runs parallel to the surface of the cerebral cortex on the banks of the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. This formation is visible to the naked eye as a white strip running through the cortical grey matter, and is the reason the V1 in primates is also referred to as the "striate cortex." The line of Gennari is due to dense axonal input from the thalamus to layer IV of visual cortex. It is the name given to the enlarged external band of Baillarger. The structure is named for its discoverer, Francesco Gennari, who first observed it in 1776 as a medical student at the University of Parma. He described it in a book which he published six years later. Although non-primate species have areas that are designated primary visual cortex, some lack a stria of Gennari.
Granular insular cortex refers to a portion of the cerebral cortex defined on the basis of internal structure in the human and macaque, the rat, and the mouse. Classified as neocortex, it is in primates distinguished from adjacent allocortex (periallocortex) by the presence of granular layers – external granular layer (II) and internal granular layer (IV) – and by differentiation of the external pyramidal layer (III) into sublayers. In primates it occupies the posterior part of the insula. In rodents it is located on the lateral surface of the cortex rostrally, dorsal to the gustatory area or, more caudally, dorsal to the agranular insula.














