Related Research Articles

A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by French radio engineer and radio manufacturer Lucien Lévy. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle.

In electronics, a varicap diode, varactor diode, variable capacitance diode, variable reactance diode or tuning diode is a type of diode designed to exploit the voltage-dependent capacitance of a reverse-biased p–n junction.

A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set, is a simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It uses only the power of the received radio signal to produce sound, needing no external power. It is named for its most important component, a crystal detector, originally made from a piece of crystalline mineral such as galena. This component is now called a diode.

Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range Station (VOR) is a type of short-range VHF radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a VOR receiver to determine the azimuth, referenced to magnetic north, between the aircraft to/from fixed VOR ground radio beacons. VOR and the first DME(1950) system to provide the slant range distance, were developed in the United States as part of a U.S. civil/military program for Aeronautical Navigation Aids in 1945. Deployment of VOR and DME(1950) began in 1949 by the U.S. CAA. ICAO standardized VOR and DME(1950) in 1950 in ICAO Annex ed.1. Frequencies for the use of VOR are standardized in the very high frequency (VHF) band between 108.00 and 117.95 MHz Chapter 3, Table A. To improve azimuth accuracy of VOR even under difficult siting conditions, Doppler VOR (DVOR) was developed in the 1960s. VOR is according to ICAO rules a primary means navigation system for commercial and general aviation, (D)VOR are gradually decommissioned and replaced by DME-DME RNAV 7.2.3 and satellite based navigation systems such as GPS in the early 21st century. In 2000 there were about 3,000 VOR stations operating around the world, including 1,033 in the US, but by 2013 the number in the US had been reduced to 967. The United States is decommissioning approximately half of its VOR stations and other legacy navigation aids as part of a move to performance-based navigation, while still retaining a "Minimum Operational Network" of VOR stations as a backup to GPS. In 2015, the UK planned to reduce the number of stations from 44 to 19 by 2020.
A variable frequency oscillator (VFO) in electronics is an oscillator whose frequency can be tuned over some range. It is a necessary component in any tunable radio transmitter and in receivers that work by the superheterodyne principle. The oscillator controls the frequency to which the apparatus is tuned.

A tuned radio frequency receiver is a type of radio receiver that is composed of one or more tuned radio frequency (RF) amplifier stages followed by a detector (demodulator) circuit to extract the audio signal and usually an audio frequency amplifier. This type of receiver was popular in the 1920s. Early examples could be tedious to operate because when tuning in a station each stage had to be individually adjusted to the station's frequency, but later models had ganged tuning, the tuning mechanisms of all stages being linked together, and operated by just one control knob. By the mid 1930s, it was replaced by the superheterodyne receiver patented by Edwin Armstrong.

In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation.
An antenna tuner, a matchbox, transmatch, antenna tuning unit (ATU), antenna coupler, or feedline coupler is a device connected between a radio transmitter or receiver and its antenna to improve power transfer between them by matching the impedance of the radio to the antenna's feedline. Antenna tuners are particularly important for use with transmitters. Transmitters feed power into a resistive load, very often 50 ohms, for which the transmitter is optimally designed for power output, efficiency, and low distortion. If the load seen by the transmitter departs from this design value due to improper tuning of the antenna/feedline combination the power output will change, distortion may occur and the transmitter may overheat.

In electronics and radio, a tuner is a type of receiver subsystem that receives RF transmissions, such as AM or FM broadcasts, and converts the selected carrier frequency into a form suitable for further processing or output, such as to an amplifier or loudspeaker. A tuner is also a standalone home audio product, component, or device called an AM/FM tuner or a stereo tuner that is part of a hi-fi or stereo system, or a TV tuner for television broadcasts. The verb tuning in radio contexts means adjusting the receiver to detect the desired radio signal carrier frequency that a particular radio station uses. Tuners were a major consumer electronics product in the 20th century but in practice are often integrated into other products in the modern day, such as stereo or AV receivers or portable radios.

A loop antenna is a radio antenna consisting of a loop or coil of wire, tubing, or other electrical conductor, that for transmitting is usually fed by a balanced power source or for receiving feeds a balanced load. Within this physical description there are two distinct types:

A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio, or as a variable reactance, e.g. for impedance matching in antenna tuners.
A radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between about 30 Hz and 300 GHz. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary parts of all systems that use radio: radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, wireless networks, radar, two way radios like walkie talkies, radio navigation systems like GPS, remote entry systems, among numerous other uses.
Body capacitance is the physical property of a human body to act as a capacitor. Like any other electrically conductive object, a human body can store electric charge if insulated. The actual amount of capacitance varies with the surroundings; it would be low when standing on top of a pole with nothing nearby, but high when leaning against an insulated, but grounded large metal surface, such as a household refrigerator, or a metal wall in a factory.

Various types of electrical transformer are made for different purposes. Despite their design differences, the various types employ the same basic principle as discovered in 1831 by Michael Faraday, and share several key functional parts.
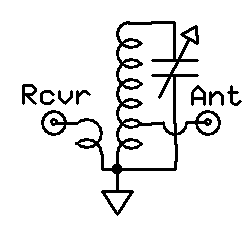
A preselector is a name for an electronic device that connects between a radio antenna and a radio receiver. The preselector is a band-pass filter that blocks troublesome out-of-tune frequencies from passing through from the antenna into the radio receiver that otherwise would be directly connected to the antenna.

Capacitors have many uses in electronic and electrical systems. They are so ubiquitous that it is rare that an electrical product does not include at least one for some purpose. Capacitors allow only AC signals to pass when they are charged blocking DC signals. The main components of filters are capacitors. Capacitors have the ability to connect one circuit segment to another. Capacitors are used by Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) devices to represent binary information as bits.

A frequency meter is an instrument that displays the frequency of a periodic electrical signal. Various types of mechanical frequency meters were used in the past, but since the 1970s these have almost universally been replaced by digital frequency counters.
Radio waves were first identified in German physicist Heinrich Hertz's 1887 series of experiments to prove James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic theory. Hertz used spark-excited dipole antennas to generate the waves and micrometer spark gaps attached to dipole and loop antennas to detect them. These precursor radio receivers were primitive devices, more accurately described as radio wave "sensors" or "detectors", as they could only receive radio waves within about 100 feet of the transmitter, and were not used for communication but instead as laboratory instruments in scientific experiments and engineering demonstrations.

A shortwave radio receiver is a radio receiver that can receive one or more shortwave bands, between 1.6 and 30 MHz. A shortwave radio receiver often receives other broadcast bands, such as FM radio, Longwave and Mediumwave. Shortwave radio receivers are often used by dedicated hobbyists called shortwave listeners.
References
- ↑ Band spreading, IEEE Standard 100 Dictionary of Standards Terms, pg 94
- ↑ Joseph J. Carr The Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook, Newnes 2000; ISBN 0750673192, page 60
- ↑ C-W and A-M Radio Transmitters and Receivers TM 11-665 United States. Dept. of the Army, 1952; page 178
- ↑ "Bush TR130". www.thevalvepage.com.