Related Research Articles

The Bangalore Development Authority (BDA) of Bangalore, India, is a governmental organization and the principal planning authority for Bangalore in accordance with the Karnataka Municipal Corporation Act. Its functions, carried out under the Karnataka Town and Country Planning Act of 1961, include preparing a Comprehensive Development Plan for the Bangalore Metropolitan Region. It also oversees planning and development of infrastructure, provision of development-related sites and services, the housing needs of underprivileged citizens in Bangalore and is currently the city's largest land developer. No other authority or person may undertake development within the Bangalore Metropolitan Region without the permission of the BDA.

Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) is the administrative body responsible for civic amenities and some infrastructural assets of the Greater Bengaluru metropolitan area. It is the fourth largest Municipal Corporation in India and is responsible for a population of 8.4 million in an area of 741 km2. Its boundaries have expanded more than 10 times over the last six decades.

The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as GoK or GoKA, formerly known as Government of Mysore (1956–1974), is a democratically elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints their council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and their council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested.

Vibuthipura Lake is a lake in the suburb of Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, in the southeast of the city of Bengaluru. The lake is the part of Bellandur-Varthur Lake series.
Greater Bengaluru is a metropolitan area in the state of Karnataka and it including Bangalore as well as its neighbouring urban cities. It occupies an area of 741 sq km.
A municipal corporation is a type of local government in India which administers urban areas with a population of more than one million. The growing population and urbanization of various Indian cities highlighted the need for a type of local governing body that could provide services such as healthcare, education, housing and transport by collecting property taxes and administering grants from the state government.
Ramanjaneyanagar is a locality belonging to the assembly constituency of Bangalore South which is the biggest assembly constituency in Bangalore with 3,79,870 voters. This area is also referred to as Sriramanjaneyanagar.
Yelahanka Lake is a water body near Yelahanka, a suburb of Bangalore.
G. Padmavathi is an Indian politician. She was 50th and also the seventh female Mayor of Bangalore.
In 2007, for administrative purposes, the city of Bangalore was divided into nine zones, which were further subdivided into a total of 198 wards administered by the Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP). After delimitation in 2023, BBMP increased the number of wards to 225.
The Kempegowda Award or Nadaprabhu Kempegowda Award is a civilian award presented annually by Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP), Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.

M Goutham Kumar is an Indian politician who was the 53rd Mayor of Bangalore. He is currently the Lok Sabha Convenor for BJP, Bangalore Central Lok Sabha constituency. He was elected from Jogupalya Ward, belonging to Shanti Nagar Assembly constituency from Bharatiya Janata Party. He was elected as Mayor on 1 October 2019. While Kumar secured 129 votes, R Satyanarayana from the Congress got 110 votes. He is also currently the General Secretary of Bharatiya Janata Party, Bangalore Central Lok Sabha constituency

Yelahanka Ward, officially known as Kempegowda Ward is one of the 225 Wards of Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike, an administrative body responsible for civic amenities and some infrastructural assets of the Greater Bangalore metropolitan area in the Indian state of Karnataka.

The 2010 Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike election was held on 4 April 2010 in all 198 Wards of Bangalore

The 2015 Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike election was held on 22 April 2015 in all 198 Wards of Bangalore (Bengaluru).
The 1996 Bangalore Mahanagara Palike election was held in October 1996 in all 100 Wards of Bangalore
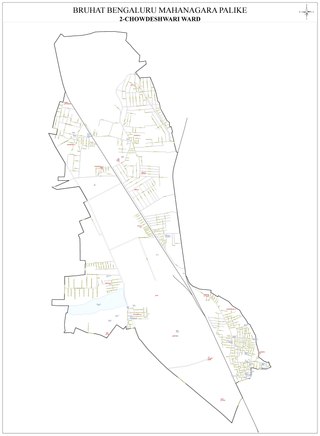
Chowdeshwari Ward, is one of the 198 Wards of Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike, an administrative body responsible for civic amenities and some infrastructural assets of the Greater Bangalore metropolitan area in the Indian state of Karnataka.

Attur Ward, is one of the 198 Wards of Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike, an administrative body responsible for civic amenities and some infrastructural assets of the Greater Bangalore metropolitan area in the Indian state of Karnataka.
References
- 1 2 Shree, D N (21 November 2013). "Will Bangalore get Maths, Physics and Chemistry right this time?". Citizen Matters.
- 1 2 "Metropolitan planning panel rules notified". The Hindu. 7 January 2014. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- 1 2 Murali, Janaki (11 May 2016). "Doomed to repeat past mistakes? Bengaluru Vision Group runs into trouble over absentees". First Post.
- ↑ "No. UDD 356 MNJ 2005 (P)". Urban Development Seretariat. 7 November 2013.
- ↑ Chamaraj, Kathyayini (16 September 2014). "How Siddaramaiah's government crippled Bengaluru in 11 ways recently". Citizen Matters.
- ↑ "Metropolitan planning panel meets for second time, members complain of short notice". The Hindu. 17 December 2016.
- ↑ Bureau, ET (3 October 2017). "Bangalore Metropolitan plan panel meets only for chai, not charcha". The Economic Times. Retrieved 23 January 2020.
{{cite news}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ↑ Chatterjee, Soumya (12 June 2018). "Thanks to K'taka HC, Bengaluru may not get another unwanted 'expert committee'". The News Minute. Retrieved 23 January 2020.
- ↑ JHA, Ramanath (30 January 2021). "The Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike Act, 2020: A critical appreciation". ORF. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ↑ P K, Naya (7 January 2021). "Karnataka's new municipal law tightens Govt grip on BBMP". Citizen Matters. Retrieved 6 April 2021.