Banu Abd Shams refers to a clan within the Meccan tribe of Quraysh.

Marwan ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya, commonly known as Marwan I, was the fourth Umayyad caliph, ruling for less than a year in 684–685. He founded the Marwanid ruling house of the Umayyad dynasty, which replaced the Sufyanid house after its collapse in the Second Muslim Civil War and remained in power until 750.

The Banu Thaqif is an Arab tribe which inhabited, and still inhabits, the city of Ta'if and its environs, in modern Saudi Arabia, and played a prominent role in early Islamic history.
The Azd, or Al-Azd, are a tribe of Ancient Arabs.

Ubayd Allah ibn Ziyad was the Umayyad governor of Basra, Kufa and Khurasan during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I and Yazid I, and the leading general of the Umayyad army under caliphs Marwan I and Abd al-Malik.

Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam was the leader of a caliphate based in Mecca that rivaled the Umayyads from 683 until his death.
Abu Abd Allah al-Mughira ibn Shu'ba ibn Abi Amir ibn Mas'ud al-Thaqafi ; c. 600–671), was a prominent companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was known as one of the four 'shrewds of the Arabs'. He belonged to the tribe of Thaqif of Ta'if, who were part of the early Islamic elite. He served as governor of Kufa, one of the two principal Arab garrisons and administrative centers of Iraq, under Caliph Umar in 642–645. In his old age, al-Mughira was again made governor of Kufa, serving under the Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I from 661 until his death in 671. During his second governorship, he ruled with virtual independence from the caliph.
The Judham was a large Arab tribe that inhabited the southern Levant and northwestern Arabia during the late antique and early Islamic eras. Under the Byzantine Empire, the tribe was nominally Christian and fought against the Muslim armies between 629 and 636, until the Byzantines and their Arab allies were defeated at the Battle of Yarmouk. Afterward, the Judham converted to Islam and became the largest tribal faction of Jund Filastin.
Qays ʿAylān, often referred to simply as Qays were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe appears to have functioned as a unit in the pre-Islamic era (pre-630). However, by the early Umayyad period (661-750), its constituent tribes consolidated into one of the main tribo-political factions of the caliphate.
The Umayyad dynasty or Umayyads was an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe who were the ruling family of the Caliphate between 661 and 750 and later of al-Andalus between 756 and 1031. In the pre-Islamic period, they were a prominent clan of the Meccan tribe of Quraysh, descended from Umayya ibn Abd Shams. Despite staunch opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the Umayyads embraced Islam before the latter's death in 632. Uthman, an early companion of Muhammad from the Umayyad clan, was the third Rashidun caliph, ruling in 644–656, while other members held various governorships. One of these governors, Mu'awiya I of Syria, opposed Caliph Ali in the First Muslim Civil War (656–661) and afterward founded the Umayyad Caliphate with its capital in Damascus. This marked the beginning of the Umayyad dynasty, the first hereditary dynasty in the history of Islam, and the only one to rule over the entire Islamic world of its time.
Abū Muḥammad Maʿdīkarib ibn Qays ibn Maʿdīkarib (599–661), better known as al-Ashʿath, was a chief of the Kinda tribe of Hadhramawt and founder of a leading noble Arab household in Kufa, one of the two main garrison towns and administrative centers of Iraq under the Rashidun (632–661) and Umayyad (661–750) caliphs.
Abu al-Hudhayl Zufar ibn al-Harith al-Kilabi was a Muslim commander, a chieftain of the Arab tribe of Banu Amir, and the preeminent leader of the Qays tribal–political faction in the late 7th century. During the First Muslim Civil War he commanded his tribe in A'isha's army against Caliph Ali's forces at the Battle of the Camel near Basra in 656. The following year, he relocated from Iraq to the Jazira and fought under Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan, future founder of the Umayyad Caliphate, against Ali at the Battle of Siffin. During the Second Muslim Civil War he served Mu'awiya's son, Caliph Yazid I, leading the troops of Jund Qinnasrin against anti-Umayyad rebels in the 683 Battle of al-Harra.
Hassan ibn Malik ibn Bahdal al-Kalbi (Arabic: حسان بن مالك بن بحدل الكلبي, romanized: Ḥassān ibn Mālik ibn Baḥdal al-Kalbī, commonly known as Ibn Bahdal, was the Umayyad governor of Palestine and Jordan during the reigns of Mu'awiya I and Yazid I, a senior figure in the caliph's court, and a chieftain of the Banu Kalb tribe. He owed his position both to his leadership of the powerful Kalb, a major source of troops, and his kinship with the Umayyads through his aunt Maysun bint Bahdal, the wife of Mu'awiya and mother of Yazid. Following Yazid's death, Ibn Bahdal served as the guardian of his son and successor, Mu'awiya II, until the latter's premature death in 684. Amid the political instability and rebellions that ensued in the caliphate, Ibn Bahdal attempted to secure the succession Mu'awiya II's brother Khalid, but ultimately threw his support behind Marwan I, who hailed from a different branch of the Umayyads. Ibn Bahdal and his tribal allies defeated Marwan's opponents at the Battle of Marj Rahit and secured for themselves the most prominent roles in the Umayyad administration and military.
Ibrahim ibn Malik al-Ashtar ibn al-Harith al-Nakha'i, better known as Ibrahim ibn al-Ashtar was an Arab commander who fought in the service of Caliph Ali and later served the pro-Alid leader al-Mukhtar al-Thaqafi. He led al-Mukhtar's forces to a decisive victory at the Battle of Khazir (686) against the Umayyads under Ubayd Allah ibn Ziyad, who was personally slain by Ibn al-Ashtar.
Abū Zurʿa Rawḥ ibn Zinbāʿ al-Judhāmī was the Umayyad governor of Palestine, one of the main advisers of Caliph Abd al-Malik and the chieftain of the Judham tribe.
Nu'man ibn Bashir ibn Sa'd al-Ansari was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was also a commander and statesman of the Umayyad Caliphate. A supporter of Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan during the First Muslim Civil War, he was appointed by him governor of Kufa in 678–680. Afterward, he was made governor of Homs by Caliph Yazid I. After the latter's death, he gave allegiance to the Mecca-based, Caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. When pro-Umayyad forces routed Ibn al-Zubayr's supporters in Syria, he fled Homs but was slain during his escape.
Natil ibn Qays ibn Zayd al-Judhami was the chieftain of the Banu Judham tribe and a prominent tribal leader in Palestine during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I and Yazid I. In 684, he revolted against the Umayyads, took control of Palestine and gave his allegiance to Caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. He joined the latter in Mecca after pro-Zubayrid forces were routed at the Battle of Marj Rahit. He may have renewed his rebellion in Palestine in 685/86 and was slain during the hostilities.
Taym Allah, known as Taym Allat in the pre-Islamic period or before their conversion to Christianity, were an Arab tribe in eastern Arabia and the lower Euphrates valley, belonging to the Banu Bakr confederation. They were a relatively minor branch and most of their pre-Islamic history pertains to their role in the Lahazim alliance of Bakrite tribes in the alliance's conflicts with the Tamim tribe and the Lakhmids, the main Arab vassals of the Sasanian Empire. They fought against the Muslims during the conquest of Iraq, but afterward embraced Islam and eventually, a number of their tribesmen held important military positions in the eastern provinces of the Caliphate. A small section of the tribe settled the Wadi al-Taym valley, which is called after them, in modern Lebanon.
ʿAbd Allāh ibn Yazīd ibn Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān, commonly known as al-Uswār, was an Umayyad prince from the Sufyanid line of the dynasty. He was the son of Caliph Yazid I. After the death of his brother, Caliph Mu'awiya II, in 684, he and his brother, Khalid ibn Yazid, were deemed too young to succeed by the pro-Umayyad tribes of Syria and Umayyad rule was vested in the line of a distant kinsman, Marwan I. Abd Allah was a famed archer and horseman and commanded part of the army which took over Iraq from anti-Umayyad forces during the Second Fitna in 691.
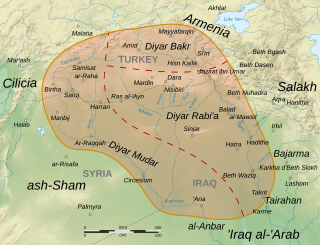
Al-Jazira, also known as Jazirat Aqur or Iqlim Aqur, was a province of the Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates, spanning at minimum most of Upper Mesopotamia, divided between the districts of Diyar Bakr, Diyar Rabi'a and Diyar Mudar, and at times including Mosul, Arminiya and Adharbayjan as sub-provinces. Following its conquest by the Muslim Arabs in 639/40, it became an administrative unit attached to the larger district of Jund Hims. It was separated from Hims during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I or Yazid I and came under the jurisdiction of Jund Qinnasrin. It was made its own province in 692 by Caliph Abd al-Malik. After 702, it frequently came to span the key districts of Arminiya and Adharbayjan along the Caliphate's northern frontier, making it a super-province. The predominance of Arabs from the Qays/Mudar and Rabi'a groups made it a major recruitment pool of tribesmen for the Umayyad armies and the troops of the Jazira played a key military role under the Umayyad caliphs in the 8th century, peaking under the last Umayyad caliph, Marwan II, until the toppling of the Umayyads by the Abbasids in 750.






