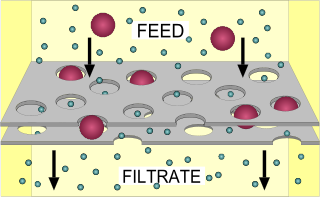
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms.

Water purification means the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for human consumption, but water purification may also be carried out for a variety of other purposes, including medical, pharmacological, chemical, and industrial applications. The history of water purification includes a wide variety of methods. The methods used include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation; biological processes such as slow sand filters or biologically active carbon; chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination; and the use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light.

Water is the most crucial compound for life on Earth, and having drinkable water is a key worldwide concern for the twenty-first century. All living things require clean, uncontaminated water as a basic requirement. Water covers more than 71 percent of the earth’s surface, but only around 1% of it is drinkable according to international standards due to various contaminations. Waste water discharge from industries, agricultural pollution, municipal wastewater, environmental and global changes are the main sources of water contamination. Even trace levels of heavy metals, dyes, and microbes are hazardous to human health, aquatic systems, and the environment. According to a Food and Agriculture Organization assessment from 2007, absolute water scarcity will affect 1.8 billion people living in countries, and water stress might affect two-thirds of the global population.

Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a variety of membrane filtration in which forces like pressure or concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained in the so-called retentate, while water and low molecular weight solutes pass through the membrane in the permeate (filtrate). This separation process is used in industry and research for purifying and concentrating macromolecular (103–106 Da) solutions, especially protein solutions.
Microfiltration is a type of filtration physical process where a contaminated fluid is passed through a special pore-sized membrane to separate microorganisms and suspended particles from process liquid. It is commonly used in conjunction with various other separation processes such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis to provide a product stream which is free of undesired contaminants.

Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes. The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater, the treatment plant is called a sewage treatment plant. For industrial wastewater, treatment either takes place in a separate industrial wastewater treatment plant, or in a sewage treatment plant. Further types of wastewater treatment plants include agricultural wastewater treatment plants and leachate treatment plants.

Waste stabilization ponds are ponds designed and built for wastewater treatment to reduce the organic content and remove pathogens from wastewater. They are man-made depressions confined by earthen structures. Wastewater or "influent" enters on one side of the waste stabilization pond and exits on the other side as "effluent", after spending several days in the pond, during which treatment processes take place.

Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter, toxic pollutants or nutrients such as ammonia. Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants, and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system.

Physical plant, mechanical plant or industrial plant refers to the necessary infrastructure used in operation and maintenance of a given facility. The operation of these facilities, or the department of an organization which does so, is called "plant operations" or facility management. Industrial plant should not be confused with "manufacturing plant" in the sense of "a factory". This is a holistic look at the architecture, design, equipment, and other peripheral systems linked with a plant required to operate or maintain it.
Electrocoagulation (EC) is a technique used for wastewater treatment, wash water treatment, industrially processed water, and medical treatment. Electrocoagulation has become a rapidly growing area of wastewater treatment due to its ability to remove contaminants that are generally more difficult to remove by filtration or chemical treatment systems, such as emulsified oil, total petroleum hydrocarbons, refractory organics, suspended solids, and heavy metals. There are many brands of electrocoagulation devices available and they can range in complexity from a simple anode and cathode to much more complex devices with control over electrode potentials, passivation, anode consumption, cell REDOX potentials as well as the introduction of ultrasonic sound, ultraviolet light and a range of gases and reactants to achieve so-called Advanced Oxidation Processes for refractory or recalcitrant organic substances.

The rapid sand filter or rapid gravity filter is a type of filter used in water purification and is commonly used in municipal drinking water facilities as part of a multiple-stage treatment system.

Sanitary engineering, also known as public health engineering or wastewater engineering, is the application of engineering methods to improve sanitation of human communities, primarily by providing the removal and disposal of human waste, and in addition to the supply of safe potable water. Traditionally a branch of civil engineering and now a subset of environmental engineering, in the mid-19th century, the discipline concentrated on the reduction of disease, then thought to be caused by miasma. This was accomplished mainly by the collection and segregation of sewerage flow in London specifically, and Great Britain generally. These and later regulatory improvements were reported in the United States as early as 1865.
A lamella clarifier or inclined plate settler (IPS) is a type of settler designed to remove particulates from liquids.

Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water pollution from raw sewage discharges. Sewage contains wastewater from households and businesses and possibly pre-treated industrial wastewater. There are a high number of sewage treatment processes to choose from. These can range from decentralized systems to large centralized systems involving a network of pipes and pump stations which convey the sewage to a treatment plant. For cities that have a combined sewer, the sewers will also carry urban runoff (stormwater) to the sewage treatment plant. Sewage treatment often involves two main stages, called primary and secondary treatment, while advanced treatment also incorporates a tertiary treatment stage with polishing processes and nutrient removal. Secondary treatment can reduce organic matter from sewage, using aerobic or anaerobic biological processes.
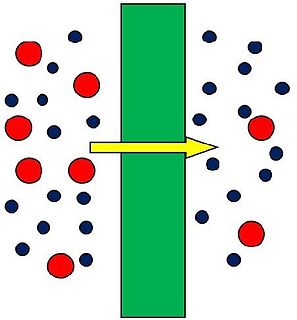
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Biological membranes include cell membranes ; nuclear membranes, which cover a cell nucleus; and tissue membranes, such as mucosae and serosae. Synthetic membranes are made by humans for use in laboratories and industry.
Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) is the concentration of suspended solids, in an aeration tank during the activated sludge process, which occurs during the treatment of waste water. The units MLSS is primarily measured in milligram per litre (mg/L), but for activated sludge its mostly measured in gram per litre [g/L] which is equal to kilogram per cubic metre [kg/m3]. Mixed liquor is a combination of raw or unsettled wastewater or pre-settled wastewater and activated sludge within an aeration tank. MLSS consists mostly of microorganisms and non-biodegradable suspended matter. MLSS is an important part of the activated sludge process to ensure that there is a sufficient quantity of active biomass available to consume the applied quantity of organic pollutant at any time. This is known as the food to microorganism ratio, more commonly notated as the F/M ratio. By maintaining this ratio at the appropriate level the biomass will consume high percentages of the food. This minimizes the loss of residual food in the treated effluent. In simple terms, the more the biomass consumes the lower the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) will be in the discharge. It is important that MLSS removes COD and BOD in order to purify water for clean surface waters, and subsequently clean drinking water and hygiene. Raw sewage enters in the water treatment process with a concentration of sometimes several hundred mg/L of BOD. Upon being treated by screening, pre-settling, activated sludge processes or other methods of treatment, the concentration of BOD in water can be lowered to less than 2 mg/L, which is considered to be clean, safe to discharge to surface waters or to reuse water.
A marine sanitation device (MSD) is a piece of machinery or a mechanical system that is dedicated to treat, process, and/or store raw, untreated sewage that can accumulate onboard water vessels. It does not refer to portable devices such as portable toilets.

Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) are used in home aquaria and for fish production where water exchange is limited and the use of biofiltration is required to reduce ammonia toxicity. Other types of filtration and environmental control are often also necessary to maintain clean water and provide a suitable habitat for fish. The main benefit of RAS is the ability to reduce the need for fresh, clean water while still maintaining a healthy environment for fish. To be operated economically commercial RAS must have high fish stocking densities, and many researchers are currently conducting studies to determine if RAS is a viable form of intensive aquaculture.

A vermifilter is an aerobic treatment system, consisting of a biological reactor containing media that filters organic material from wastewater. The media also provides a habitat for aerobic bacteria and composting earthworms that purify the wastewater by removing pathogens and oxygen demand. The "trickling action" of the wastewater through the media dissolves oxygen into the wastewater, ensuring the treatment environment is aerobic for rapid decomposition of organic substances.














