Related Research Articles
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.

A root canal is the naturally occurring anatomic space within the root of a tooth. It consists of the pulp chamber, the main canal(s), and more intricate anatomical branches that may connect the root canals to each other or to the surface of the root.

Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.

The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour.

In dentistry, a crown most commonly refers to a dental cap, a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large dental cavity threatens the health of a tooth. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using indirect methods. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly.

A dental drill or handpiece is a hand-held, mechanical instrument used to perform a variety of common dental procedures, including removing decay, polishing fillings, performing cosmetic dentistry, and altering prostheses. The handpiece itself consists of internal mechanical components which initiate a rotational force and provide power to the cutting instrument, usually a dental burr. The type of apparatus used clinically will vary depending on the required function dictated by the dental procedure. It is common for a light source and cooling water-spray system to also be incorporated into certain handpieces; this improves visibility, accuracy and overall success of the procedure. The burrs are usually made of tungsten carbide or diamond.
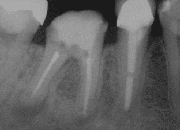
A root end surgery, also known as apicoectomy, apicectomy, retrograde root canal treatment or root-end filling, is an endodontic surgical procedure whereby a tooth's root tip is removed and a root end cavity is prepared and filled with a biocompatible material. It is an example of a periradicular surgery.

Veterinary dentistry is the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals. It is the art and science of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions, diseases, and disorders of the oral cavity, the maxillofacial region, and its associated structures as it relates to animals.

Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.
Focal infection theory is the historical concept that many chronic diseases, including systemic and common ones, are caused by focal infections. In present medical consensus, a focal infection is a localized infection, often asymptomatic, that causes disease elsewhere in the host, but focal infections are fairly infrequent and limited to fairly uncommon diseases. Focal infection theory, rather, so explained virtually all diseases, including arthritis, atherosclerosis, cancer, and mental illnesses.
A post and core crown is a type of dental restoration required where there is an inadequate amount of sound tooth tissue remaining to retain a conventional crown. A post is cemented into a prepared root canal, which retains a core restoration, which retains the final crown.

Root canal treatment is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.
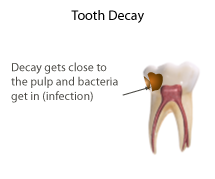
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a primary tooth with extensive caries but without evidence of root pathology. The minimally invasive endodontic techniques of vital pulp therapy (VPT) are based on improved understanding of the capacity of pulp (nerve) tissues to heal and regenerate plus the availability of advanced endodontic materials. During the caries removal, this results in a carious or mechanical pulp exposure (bleeding) from the cavity. During pulpotomy, the inflamed/diseased pulp tissue is removed from the coronal pulp chamber of the tooth leaving healthy pulp tissue which is dressed with a long-term clinically-successful medicament that maintains the survival of the pulp and promotes repair. There are various types of medicament placed above the vital pulp such as Buckley's Solution of formocresol, ferric sulfate, calcium hydroxide or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). MTA is a more recent material used for pulpotomies with a high rate of success, better than formocresol or ferric sulfate. It is also recommended to be the preferred pulpotomy agent in the future. After the coronal pulp chamber is filled, the tooth is restored with a filling material that seals the tooth from microleakage, such as a stainless steel crown which is the most effective long-term restoration. However, if there is sufficient remaining supporting tooth structure, other filling materials such as amalgam or composite resin can provide a functional alternative when the primary tooth has a life span of two years or less. The medium- to long-term treatment outcomes of pulpotomy in symptomatic permanent teeth with caries, especially in young people, indicate that pulpotomy can be a potential alternative to root canal therapy (RCT).
Dental pulpal testing is a clinical and diagnostic aid used in dentistry to help establish the health of the dental pulp within the pulp chamber and root canals of a tooth. Such investigations are important in aiding dentists in devising a treatment plan for the tooth being tested.
Endodontic files and reamers are surgical instruments used by dentists when performing root canal treatment. These tools are used to clean and shape the root canal, with the concept being to perform complete chemomechanical debridement of the root canal to the length of the apical foramen. Preparing the canal in this way facilitates the chemical disinfection to a satisfactory length but also provides a shape conducive to obturation.
In dentistry, the smear layer is a layer found on root canal walls after root canal instrumentation. It consists of microcrystalline and organic particle debris. It was first described in 1975 and research has been performed since then to evaluate its importance in bacteria penetration into the dentinal tubules and its effects on endodontic treatment. More broadly, it is the organic layer found over all hard tooth surfaces.

Regenerative endodontic procedures is defined as biologically based procedures designed to replace damaged structures such as dentin, root structures, and cells of the pulp-dentin complex. This new treatment modality aims to promote normal function of the pulp. It has become an alternative to heal apical periodontitis. Regenerative endodontics is the extension of root canal therapy. Conventional root canal therapy cleans and fills the pulp chamber with biologically inert material after destruction of the pulp due to dental caries, congenital deformity or trauma. Regenerative endodontics instead seeks to replace live tissue in the pulp chamber. The ultimate goal of regenerative endodontic procedures is to regenerate the tissues and the normal function of the dentin-pulp complex.

Pulp capping is a technique used in dental restorations to prevent the dental pulp from necrosis, after being exposed, or nearly exposed during a cavity preparation, from a traumatic injury, or by a deep cavity that reaches the center of the tooth causing the pulp to die. When dental caries is removed from a tooth, all or most of the infected and softened enamel and dentin are removed. This can lead to the pulp of the tooth either being exposed or nearly exposed which causes pulpitis (inflammation). Pulpitis, in turn, can become irreversible, leading to pain and pulp necrosis, and necessitating either root canal treatment or extraction. The ultimate goal of pulp capping or stepwise caries removal is to protect a healthy dental pulp and avoid the need for root canal therapy.
Biofilling, also known as orthograde canal grafting technique or 4D sealing, is an endodontic root canal obturation technique with a Bioceramic material after root canal preparation and enlargement procedure.
Apexification is a method of dental treatment to induce a calcific barrier in a root with incomplete formation or open apex of a tooth with necrotic pulp. Pulpal involvement usually occurs as a consequence of trauma or caries involvement of young or immature permanent teeth. As a sequelae of untreated pulp involvement, loss of pulp vitality or necrotic pulp took place for the involved teeth.
References
- 1 2 3 Journal of the National Dental Association. National Dental Association. 1918. pp. 138–140. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ Torabinejad, Mahmoud; Walton, Richard E. (2009). Endodontics: Principles and Practice. Saunders/Elsevier. ISBN 9781416038511 . Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ The Minneapolis District Dental Journal. 1917. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ Gupta, Ruchi; Hegde, Jayshree; Prakash, Vijay; Srirekha, A (30 May 2009). Concise Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 543. ISBN 9788131253441 . Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ Taylor, J. A. (1922). History of Dentistry: A Practical Treatise for the Use of Dental Students and Practitioners. New York: Lea & Febiger.