Related Research Articles

Clozapine is a psychiatric medication and is the first atypical antipsychotic. It is primarily used to treat people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorders who have had an inadequate response to other antipsychotics or who have been unable to tolerate other drugs due to extrapyramidal side effects. It is also used for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's Disease. Clozapine is regarded as the gold-standard treatment when other medication has been insufficiently effective and its use is recommended by multiple international treatment guidelines.

Typical antipsychotics are a class of antipsychotic drugs first developed in the 1950s and used to treat psychosis. Typical antipsychotics may also be used for the treatment of acute mania, agitation, and other conditions. The first typical antipsychotics to come into medical use were the phenothiazines, namely chlorpromazine which was discovered serendipitously. Another prominent grouping of antipsychotics are the butyrophenones, an example of which is haloperidol. The newer, second-generation antipsychotics, also known as atypical antipsychotics, have largely supplanted the use of typical antipsychotics as first-line agents due to the higher risk of movement disorders in the latter.

Benzatropine (INN), known as benztropine in the United States and Japan, is a medication used to treat a type of movement disorder due to antipsychotics known as dystonia and parkinsonism. It is not useful for tardive dyskinesia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein or muscle. Benefits are seen within two hours and last for up to ten hours.
Akathisia is a movement disorder characterized by a subjective feeling of inner restlessness accompanied by mental distress and an inability to sit still. Usually, the legs are most prominently affected. Those affected may fidget, rock back and forth, or pace, while some may just have an uneasy feeling in their body. The most severe cases may result in aggression, violence or suicidal thoughts.
Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a disorder that results in involuntary, repetitive body movements, which may include grimacing, sticking out the tongue, or smacking the lips. Additionally, there may be rapid jerking movements or slow writhing movements. In about 20% of people with TD, the disorder interferes with daily functioning.
Metoclopramide is a medication used for stomach and esophageal problems. It is commonly used to treat and prevent nausea and vomiting, to help with emptying of the stomach in people with delayed stomach emptying, and to help with gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is also used to treat migraine headaches.

Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks, but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of Mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

Clonazepam, sold under the brand Klonopin among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat seizures, panic disorder, anxiety, and the movement disorder known as akathisia. It is a tranquilizer of the benzodiazepine class. It is taken by mouth. Effects begin within one hour and last between six and twelve hours.
Psychomotor agitation is a symptom related to a spectrum of disorders characterized by unintentional and purposeless motions and restlessness, often but not always accompanied by emotional distress. Typical manifestations include pacing around, wringing of the hands, uncontrolled tongue movement, pulling off clothing and putting it back on, and other similar actions. In more severe cases, the motions may become harmful to the individual, and may involve things such as ripping, tearing, or chewing at the skin around one's fingernails, lips, or other body parts to the point of bleeding. Psychomotor agitation is typically found in major depressive disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder, and sometimes the manic phase in bipolar disorder, though it can also be a result of an excess intake of stimulants. It can also be caused by severe hyponatremia. The middle-aged and the elderly are more at risk to express it.
Biperiden, sold under the brand name Akineton among others, is a medication used to treat Parkinson disease and certain drug-induced movement disorders. It is not recommended for tardive dyskinesias. It is taken by mouth, injection into a vein, or muscle.
Lunsers refers to the Liverpool University Neuroleptic Side Effect Rating Scale.

Cyproheptadine, sold under the brand name Periactin among others, is a first-generation antihistamine with additional anticholinergic, antiserotonergic, and local anesthetic properties.

Mesoridazine(Serentil) is a piperidine neuroleptic drug belonging to the class of drugs called phenothiazines, used in the treatment of schizophrenia. It is a metabolite of thioridazine. The drug's name is derived from the methylsulfoxy and piperidine functional groups in its chemical structure.
The term dysphrenia was coined by the German medical specialist Karl Kahlbaum to designate a clinical picture in 19th-century psychiatry. Today the concept is still used in the western world as a lay generic synonym for mental disorder in adults, and as a term to describe different cognitive/verbal/behavioral deficits in children and adolescents. It is also used in the People's Republic of China, controversially, to identify a local medical diagnostic category. A number of followers of Falun Gong and other social movements considered insurrectionary by the regime are said to have been diagnosed with dysphrenia.
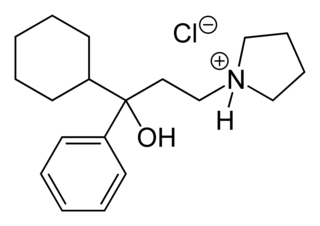
Procyclidine is an anticholinergic drug principally used for the treatment of drug-induced parkinsonism, akathisia and acute dystonia; Parkinson disease; and idiopathic or secondary dystonia.
Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) are symptoms that are archetypically associated with the extrapyramidal system of the brain's cerebral cortex. When such symptoms are caused by medications or other drugs, they are also known as extrapyramidal side effects (EPSE). The symptoms can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). They include movement dysfunction such as dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism characteristic symptoms such as rigidity, bradykinesia, tremor, and tardive dyskinesia. Extrapyramidal symptoms are a reason why subjects drop out of clinical trials of antipsychotics; of the 213 (14.6%) subjects that dropped out of one of the largest clinical trials of antipsychotics, 58 (27.2%) of those discontinuations were due to EPS.

Zuclopenthixol, also known as zuclopentixol, is a medication used to treat schizophrenia and other psychoses. It is classed, pharmacologically, as a typical antipsychotic. Chemically it is a thioxanthene. It is the cis-isomer of clopenthixol. Clopenthixol was introduced in 1961, while zuclopenthixol was introduced in 1978.
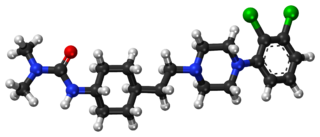
Cariprazine, sold under the brand names Vraylar in the United States and Reagila in the European Union, is an atypical antipsychotic which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, and bipolar depression. It acts primarily as a D3 receptor and D2 receptor partial agonist, with high selectivity for the D3 receptor. Positive Phase III study results were published for schizophrenia and mania in early 2012, and for bipolar disorder I depression from a Phase II trial in 2015. It is also potentially useful as an add-on therapy in major depressive disorder.
Perminder Sachdev is a neuropsychiatrist based in Australia. He is the Scientia Professor of Neuropsychiatry at the University of New South Wales (UNSW), Australia, the director of the Centre for Healthy Brain Ageing (CHeBA), UNSW, and the Clinical Director of the Neuropsychiatric Institute (NPI) at the Prince of Wales Hospital, Sydney, Australia.