Related Research Articles

Paraponera clavata, commonly known as the bullet ant, is a species of ant named for its extremely painful sting. It inhabits humid lowland rainforests in Central and South America.

Adetomyrma is a genus of ants endemic to Madagascar. Workers of this genus are blind. The type species Adetomyrma venatrix was described in 1994, with the genus being an atypical member of its tribe, the Amblyoponini. This tribe includes the Dracula ants, members of which can feed on the hemolymph of larvae and pupae.
In ants, the traditional subfamily Ponerinae has been subdivided into several Poneromorph subfamilies, with several former tribes now elevated to subfamily rank. According to this analysis, some ponerine groups may be more closely related to other subfamilies than to each other. The subfamilies of "poneromorph" Formicidae include:
Leptothorax pocahontas is a threatened species of ant endemic to Alberta, Canada, facing a high risk of extinction.
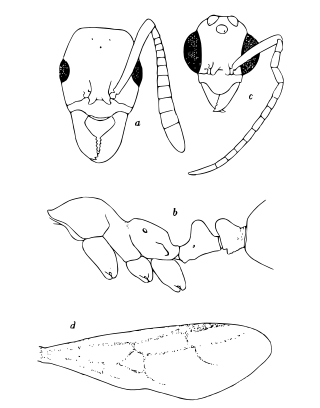
Megalomyrmex is a genus of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus is known only from the Neotropics, where some of the species are specialized parasites or predators of Attini.

Myrmoteras is a genus of ants in the subfamily Formicinae and the sole member of the tribe Myrmoteratini. They have enormous eyes, a character found in other ancient genera, and extremely elongated mandibles with eight to 16 teeth. These work as trap-jaws and can open up to 270°.

Amblyoponinae is a subfamily of ants in the poneromorph subfamilies group containing 13 extant genera and one extinct genus. The ants in this subfamily are mostly specialized subterranean predators. Adult workers pierce the integument of their larvae and pupa to imbibe haemolymph, earning them the common name Dracula ant.

Agroecomyrmecinae is a subfamily of ants containing two extant and two fossil genera. The subfamily was originally classified in 1930 by Carpenter as Agroecomyrmecini, a Myrmicinae tribe. Bolton raised the tribe to subfamily status in 2003, suggesting that Agroecomyrmecinae might be the sister taxon to Myrmicinae. It has since been discovered to be one of the earliest lineages of ants, a clade from the basal polytomy for all ants. In 2014, the subfamily was expanded to two tribes. The tribe Ankylomyrmini was moved from the subfamily Myrmicinae to Agroemyrmecinae.

Brownimecia is an extinct genus of ants, the only genus in the tribe Brownimeciini and subfamily Brownimeciinae of the Formicidae. Fossils of the single identified species, Brownimecia clavata, are known from the Middle Cretaceous of North America. The genus is one of several ants described from Middle Cretaceous ambers of New Jersey. Brownimecia was initially placed in the subfamily Ponerinae, until it was transferred to its own subfamily in 2003; it can be distinguished from other ants due to its unusual sickle-like mandibles and other morphological features that makes this ant unique among the Formicidae. The ant is also small, measuring 3.43 millimetres (0.135 in), and a stinger is present in almost all of the specimens collected. The morphology of the mandibles suggest a high level of feeding specialization.

Gauromyrmex is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus contains two species, known from the Indomalayan realm. According to Bolton (2003), there are a further five or six undescribed species in the collections of the Natural History Museum in London.
Meranoplus parviumgulatus is a species of ant in the genus Meranoplus. It is known from New Guinea and Papua New Guinea.

Santschiella is an Afrotropical genus of ants in the subfamily Formicinae. It contains the single species Santschiella kohli, described by Forel in 1916 from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The genus is known only from workers, measuring about 3 mm in length and with large eyes. Forel (1917) placed Santschiella in its own tribe, Santschiellini, where it remain until Bolton (2003) moved it to Gesomyrmecini.

Promyopias is an Afrotropical genus of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae containing the single species Promyopias silvestrii. The rare genus has previously been regarded as a separate genus, as a subgenus and as a provisional synonymy, but was reinstated at genus-rank in 2008.

Burmomyrma is an extinct genus of aculeate hymenopteran, suggested to be an ant. The genus contains a single described species, Burmomyrma rossi. Burmomyrma is known from a single Middle Cretaceous fossil which was found in Asia.

Stigmatomma pluto is a species of ant in the subfamily Amblyoponinae. The species was first described as Amblyopone pluto by Gotwald and Levieux in 1972 and moved to the genus Stigmatomma in 2012.
Kotshkorkia is an extinct genus of ants of the subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus contains a single described species Kotshkorkia laticeps. It was described by Dlussky in 1981, where the first fossils of the ant were found in Russia.

Stenamma impar is a species of ant in the family Formicidae.

Myrmelachistini is a tribe of ants in the family Formicidae. There are at least 2 genera and 50 described species in Myrmelachistini.
References
- ↑ Snelling, Roy R. (Summer 1997). "A New General Catalogue of the Ants of the World". American Entomologist (Book Review). 43 (2): 127. doi: 10.1093/ae/43.2.127 .