Related Research Articles

A horoscope is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ōra and scopos meaning "time" and "observer". It is claimed by proponents of astrology that a horoscope can be used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology, although practices surrounding astrology have been recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers.

Annibale Carracci was an Italian painter and instructor, active in Bologna and later in Rome. Along with his brother and cousin, Annibale was one of the progenitors, if not founders of a leading strand of the Baroque style, borrowing from styles from both north and south of their native city, and aspiring for a return to classical monumentality, but adding a more vital dynamism. Painters working under Annibale at the gallery of the Palazzo Farnese would be highly influential in Roman painting for decades.

Bonaventura Francesco Cavalieri was an Italian mathematician and a Jesuate. He is known for his work on the problems of optics and motion, work on indivisibles, the precursors of infinitesimal calculus, and the introduction of logarithms to Italy. Cavalieri's principle in geometry partially anticipated integral calculus.

Michael Scot was a Scottish mathematician and scholar in the Middle Ages. He was educated at Oxford and Paris, and worked in Bologna and Toledo, where he learned Arabic. His patron was Frederick II of the Holy Roman Empire and Scot served as science adviser and court astrologer to him. Scot translated Averroes and was the greatest public intellectual of his day.

Astrological belief in correspondences between celestial observations and terrestrial events have influenced various aspects of human history, including world-views, language and many elements of social culture.

Astrology and astronomy were archaically treated together, but gradually distinguished through the Late Middle Ages into the Age of Reason. Developments in 17th century philosophy resulted in astrology and astronomy operating as independent pursuits by the 18th century.

Luca Gaurico was an Italian astrologer, astronomer, astrological data collector, and mathematician. He was born to a poor family in the Kingdom of Naples, and studied judicial astrology, a subject he defended in his Oratio de Inventoribus et Astrologiae Laudibus (1508). Judicial astrology concerned the fate of man as influenced by the stars. His most famous work is the Tractatus Astrologicus. Later in life he was named a bishop of the Catholic Church.

Giovanni Antonio Magini was an Italian astronomer, astrologer, cartographer, and mathematician.
La Società Entomologica Italiana, the Italian Entomological Society, is Italy's foremost society devoted to the study of insects. The society is famous for promoting applied entomology and many of its past members have saved millions from deadly diseases such as malaria.

Guido Cagnacci was an Italian painter originally from Santarcangelo di Romagna. Associated most readily with the Baroque period, his mature works are characterized by their use of chiaroscuro and their sensual subjects. He was influenced by the masters of the Bolognese School.

Guido Bonatti was an Italian mathematician, astronomer and astrologer, who was the most celebrated astrologer of the 13th century. Bonatti was advisor of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Ezzelino da Romano III, Guido Novello da Polenta and Guido I da Montefeltro. He also served the communal governments of Florence, Siena and Forlì. His employers were all Ghibellines, who were in conflict with the Guelphs, and all were excommunicated at some time or another. Bonatti's astrological reputation was also criticised in Dante's Divine Comedy, where he is depicted as residing in hell as punishment for his astrology.

GiovanniDomenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini was an Italian mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the County of Nice, part of the Savoyard state. Cassini is known for his work on astronomy and engineering. He discovered four satellites of the planet Saturn and noted the division of the rings of Saturn; the Cassini Division was named after him. Giovanni Domenico Cassini was also the first of his family to begin work on the project of creating a topographic map of France.
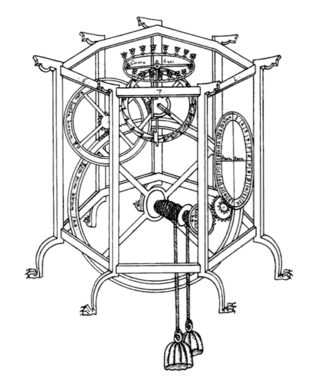
Giovanni Dondi dell'Orologio, also known as Giovanni de' Dondi, was an Italian physician, astronomer and mechanical engineer in Padua, now in Italy.

Some medieval Muslims took a keen interest in the study of astrology, partly because they considered the celestial bodies to be essential, partly because the dwellers of desert-regions often travelled at night, and relied upon knowledge of the constellations for guidance in their journeys. After the advent of Islam, the Muslims needed to determine the time of the prayers, the direction of the Kaaba, and the correct orientation of the mosque, all of which helped give a religious impetus to the study of astronomy and contributed towards the belief that the heavenly bodies were influential upon terrestrial affairs as well as the human condition. The science dealing with such influences was termed astrology, a discipline contained within the field of astronomy. The principles of these studies were rooted in Arabian, Persian, Babylonian, Hellenistic and Indian traditions and both were developed by the Arabs following their establishment of a magnificent observatory and library of astronomical and astrological texts at Baghdad in the 8th century.
Seigneur Christophe de Cattan, also called Christopher Cattan, presumed Francophone and Anglophone variants of the Italian name Cristoforo Cattaneo, was an Italian humanist author of the second quarter of the sixteenth century. Of Italian stock but Genevan origin, he served as a man-at-arms under French command in France, and wrote in French. He is known as the learned author of a work about Geomancy, which was published posthumously in 1558 in Paris as La Géomance du Seigneur Christofe de Cattan, with further printings in 1567 and 1577. Most if not all of what is known about the author derives from information in the book itself.

In astrology, planets have a meaning different from the astronomical understanding of what a planet is. Before the age of telescopes, the night sky was thought to consist of two similar components: fixed stars, which remained motionless in relation to each other, and moving objects/"wandering stars", which moved relative to the fixed stars over the course of the year(s).

The Snub-nose Painter was an Apulian pottery painter so named for his distinctive manner of painting the noses of his subjects.

Self-Portrait is a 1593 oil on canvas painting by Annibale Carracci, now in the Galleria Nazionale di Parma. It is dated 17 April 1593 on the top left of the canvas.
References
- ↑ The Origins of the Teaching of Astronomy, Museo della Specola. Accessed 6 August 2010.
- ↑ E. Narducci, I Primi due Libri del „Tractatus Sphaerae“ di Bartolomeo da Parma, astronomo del secolo XIII, Rome, 1985, 38 and 40.
- ↑ Baiada Enrica: (1988) "Il Museo della Specola e l'astronomia a Bologna", in Storia Illustrata di Bologna, vol VII, AIEP, pp. 161-180.