
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy. The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump includes:
Intensive insulin therapy or flexible insulin therapy is a therapeutic regimen for diabetes mellitus treatment. This newer approach contrasts with conventional insulin therapy. Rather than minimize the number of insulin injections per day, the intensive approach favors flexible meal times with variable carbohydrate as well as flexible physical activities. The trade-off is the increase from 2 or 3 injections per day to 4 or more injections per day, which was considered "intensive" relative to the older approach. In North America in 2004, many endocrinologists prefer the term "flexible insulin therapy" (FIT) to "intensive therapy" and use it to refer to any method of replacing insulin that attempts to mimic the pattern of small continuous basal insulin secretion of a working pancreas combined with larger insulin secretions at mealtimes. The semantic distinction reflects changing treatment.
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
The following is a glossary of diabetes which explains terms connected with diabetes.

Blood glucose monitoring is the use of a glucose meter for testing the concentration of glucose in the blood (glycemia). Particularly important in diabetes management, a blood glucose test is typically performed by piercing the skin to draw blood, then applying the blood to a chemically active disposable 'test-strip'. Different manufacturers use different technology, but most systems measure an electrical characteristic, and use this to determine the glucose level in the blood. The test is usually referred to as capillary blood glucose.

The glucose tolerance test is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta cell function, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In the most commonly performed version of the test, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), a standard dose of glucose is ingested by mouth and blood levels are checked two hours later. Many variations of the GTT have been devised over the years for various purposes, with different standard doses of glucose, different routes of administration, different intervals and durations of sampling, and various substances measured in addition to blood glucose.

Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it does increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and requiring a Caesarean section. Babies born to mothers with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of being too large, having low blood sugar after birth, and jaundice. If untreated, it can also result in a stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and developing type 2 diabetes.
The term diabetes includes several different metabolic disorders that all, if left untreated, result in abnormally high concentration of a sugar called glucose in the blood. Diabetes mellitus type 1 results when the pancreas no longer produces significant amounts of the hormone insulin, usually owing to the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Diabetes mellitus type 2, in contrast, is now thought to result from autoimmune attacks on the pancreas and/or insulin resistance. The pancreas of a person with type 2 diabetes may be producing normal or even abnormally large amounts of insulin. Other forms of diabetes mellitus, such as the various forms of maturity onset diabetes of the young, may represent some combination of insufficient insulin production and insulin resistance. Some degree of insulin resistance may also be present in a person with type 1 diabetes.
Many types of glucose tests exist and they can be used to estimate blood sugar levels at a given time or, over a longer period of time, to obtain average levels or to see how fast body is able to normalize changed glucose levels. Eating food for example leads to elevated blood sugar levels. In healthy people these levels quickly return to normal via increased cellular glucose uptake which is primarily mediated by increase in blood insulin levels.
Automated insulin delivery systems are automated systems designed to assist people with diabetes, primarily type 1, by automatically adjusting insulin delivery to help them control their blood glucose levels. Currently available systems can only deliver a single hormone- insulin. Other systems currently in development aim to improve on current systems by adding one or more additional hormones that can be delivered as needed, providing something closer to the endocrine functionality of a healthy pancreas.
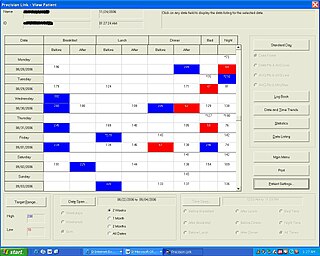
Diabetes Management Software refers to software tools that run on personal computers and personal digital assistants to help persons with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes manage the data associated with:

AIDA is a freeware computer program that permits the interactive simulation of plasma insulin and blood glucose profiles for demonstration, teaching, self-learning, and research purposes. Originally developed in 1991, it has been updated and enhanced since, and made available without charge from 1996 on the World Wide Web. The freeware software can be downloaded now from: http://www.2aida.org and http://www.2aida.net as well as from numerous freeware software repositories as a non-commercial contribution to continuing diabetes education. The program, which is still being updated, has gone through a number of revisions and developments in the 16+ years since its original internet launch. During this time over 2.5 million visits have been logged at the AIDA Websites and more than 400,000 copies of the program have been downloaded, gratis. Further copies of the simulator have been made available, in the past, on diskette by the system developers and from the British Diabetic Association (BDA) — now called 'Diabetes UK' — London, England, following the BDA's own independent evaluation of the software. More than 1,075,000 diabetes simulations have been run via a web-based version of the AIDA diabetes simulator — called AIDA on-line — accessible directly at: http://www.2aida.net.
An insulin tolerance test (ITT) is a medical diagnostic procedure during which insulin is injected into a patient's vein, after which blood glucose is measured at regular intervals. This procedure is performed to assess pituitary function, adrenal function, insulin sensitivity, and sometimes for other purposes. An ITT is usually ordered and interpreted by endocrinologists.
In medicine, a bolus is the administration of a discrete amount of medication, drug, or other compound within a specific time, generally 1–30 minutes, in order to raise its concentration in blood to an effective level. The administration can be given by injection: intravenously, intramuscularly, intrathecally, subcutaneously, or by inhalation. The article on routes of administration provides more information, as the preceding list of ROAs is not exhaustive.
Insulin is a protein hormone that is used as a medication to treat high blood glucose. This includes in diabetes mellitus type 1, diabetes mellitus type 2, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. It is also used along with glucose to treat high blood potassium levels. Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or muscle.
Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is a disease that affects an infant and their body's ability to produce or use insulin. NDM is a monogenic form of diabetes that occurs in the first 6 months of life. Infants do not produce enough insulin, leading to an increase in glucose accumulation. It is a rare disease, occurring in only one in 100,000 to 500,000 live births. NDM can be mistaken for the much more common type 1 diabetes, but type 1 diabetes usually occurs later than the first 6 months of life. There are two types of NDM: permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) is a lifelong condition. Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM) is diabetes that disappears during the infant stage but may reappear later in life.
Glucose clamp technique is a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. It is used to measure either how well an individual metabolizes glucose or how sensitive an individual is to insulin.

Insulin degludec (INN/USAN) is an ultralong-acting basal insulin analogue that was developed by Novo Nordisk under the brand name Tresiba. It is administered via subcutaneous injection once daily to help control the blood sugar level of those with diabetes. It has a duration of action that lasts up to 42 hours, making it a once-daily basal insulin, that is one that provides a base insulin level, as opposed to the fast- and short-acting bolus insulins.

Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as just diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes and cognitive impairment.
Carbohydrate counting or “carb” counting is a meal planning tool used in diabetes management to help optimize blood sugar control. It can be used with or without the use of insulin therapy. Carbohydrate counting involves determining whether a food item has carbohydrate followed by the subsequent determination of how much carbohydrate the food item has in it.







