
The Urnfield culture was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and placing their ashes in urns, which were then buried in fields. The first usage of the name occurred in publications over grave sites in southern Germany in the late 19th century. Over much of Europe, the Urnfield culture followed the Tumulus culture and was succeeded by the Hallstatt culture. Some linguists and archaeologists have associated this culture with a pre-Celtic language or Proto-Celtic language family. By the end of the 2nd millennium BC, the Urnfield Tradition had spread through Italy, northwestern Europe, and as far west as the Pyrenees. It is at this time that fortified hilltop settlements and sheet‐bronze metalworking also spread widely across Europe, leading some authorities to equate these changes with the expansion of the Celts. These links are no longer accepted. The Italic peoples, including the Latins, from which the Romans emerged, come from the Urnfield culture of central Europe.
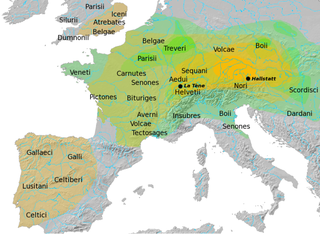
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations.
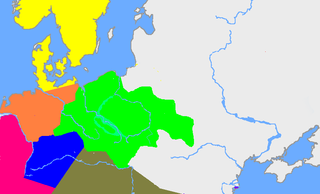
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III to V of the Northern European chronological scheme. It has been associated or closely linked with the Nordic Bronze Age. Hallstatt influences can also be seen particularly in ornaments and weapons.
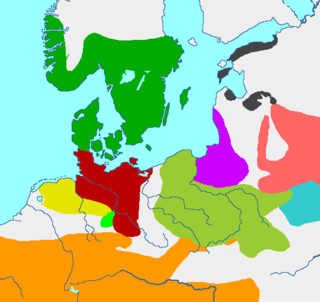
The Pomeranian culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture was an Iron Age culture with origins in parts of the area south of the Baltic Sea, from the 7th century BC to the 3rd century BC, which eventually covered most of today's Poland.

The Jastorf culture was an Iron Age material culture in what is now northern Germany and the southern Scandinavian Peninsula, spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming the southern part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The culture evolved out of the Nordic Bronze Age.

The area known as Croatia today has been inhabited throughout the prehistoric period, ever since the Stone Age, up to the Migrations Period and the arrival of the White Croats.
The history of Hungarybefore the Hungarian conquest spans the time period before the Hungarian conquest in the 9th century of the territories that would become the Principality of Hungary and the Kingdom of Hungary.

The Tumulus culture was the dominant material culture in Central Europe during the Middle Bronze Age.

Situla, from the Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Bronze Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types may be highly decorated, most characteristically with reliefs in bands or friezes running round the vessel.
The archaeology of Northern Europe studies the prehistory of Scandinavia and the adjacent North European Plain, roughly corresponding to the territories of modern Sweden, Norway, Denmark, northern Germany, Poland and the Netherlands.

Prehistoric France is the period in the human occupation of the geographical area covered by present-day France which extended through prehistory and ended in the Iron Age with the Roman conquest, when the territory enters the domain of written history.
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods, which initially meant descriptions of a particular area by Greek and Roman writers. For much of Europe, the period came to an abrupt end after conquest by the Romans, though ironworking remained the dominant technology until recent times. Elsewhere, the period lasted until the early centuries AD, and either Christianization or a new conquest in the Migration Period. Iron working was introduced to Europe in the late 11th century BC, probably from the Caucasus, and slowly spread northwards and westwards over the succeeding 500 years. For example, the Iron Age of Prehistoric Ireland begins around 500 BC, when the Greek Iron Age had already ended, and finishes around 400 AD. The use of iron and iron-working technology became widespread concurrently in Europe and Asia.

The Bronze and Iron Age cultures in Poland are known mainly from archeological research. Early Bronze Age cultures in Poland began around 2400–2300 BCE, while the Iron Age commenced in approximately 750–700 BCE. The Iron Age archeological cultures no longer existed by the start of the Common Era. The subject of the ethnicity and linguistic affiliation of the groups living in Central Europe at that time is, given the absence of written records, speculative, and accordingly there is considerable disagreement. In Poland the Lusatian culture, spanning both the Bronze and Iron Ages, became particularly prominent. The most famous archeological finding from that period is the Biskupin fortified settlement (gord) on the lake from which it takes its name, representing the Lusatian culture of the early Iron Age.

The Dacian bracelets are bracelets associated with the ancient people known as the Dacians, a distinct branch of the Thracians. These bracelets were used as ornaments, currency, high rank insignia and votive offerings Their ornamentations consist of many elaborate regionally distinct styles. Bracelets of various types were worn by Dacians, but the most characteristic piece of their jewelry was the large multi-spiral bracelets; engraved with palmettes towards the ends and terminating in the shape of an animal head, usually that of a snake.

The Strettweg cult wagon, or Strettweg sacrificial wagon, or Strettweg chariot is a bronze cult wagon from ca. 600 BC, which was found as part of a princely grave of the Hallstatt culture in Strettweg near Judenburg, Austria in 1851. Besides the wagon, other grave goods, like jewelry, bronze amphorae, iron weapons, and horse tack were found.

Židovar is an archeological site and settlement near Vršac, Serbia. This site is famous by the treasure that was found here.

The Prehistory of Transylvania describes what can be learned about the region known as Transylvania through archaeology, anthropology, comparative linguistics and other allied sciences.

Gonsenheim is a borough in the northwest corner of Mainz, Germany. With about 25,000 inhabitants, it is the second-most populated borough of Mainz, before Oberstadt and after Neustadt.

Romanian archaeology begins in the 19th century.
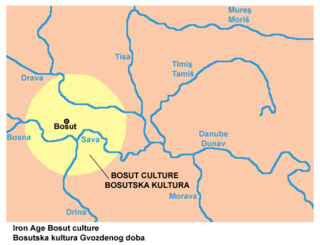
Bosut culture is a name of a prehistoric Iron Age culture, which was named after the Bosut Gradina archaeological site in Serbia. It is sometimes grouped with related Basarabi culture into Bosut-Basarabi complex. There are different views about ethnic identity of the people of Bosut culture; according to one view, they were Triballi, while according to another view, they were Daco-Getaes. The culture flourished in the first half of the 1st millennium BC, until the arrival of the Scythian tribes.



















