
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.

A corrective lens is a transmissive optical device that is worn on the eye to improve visual perception. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes.

Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct vision or for cosmetic or therapeutic reasons. In 2010, the worldwide market for contact lenses was estimated at $6.1 billion, while the US soft lens market was estimated at $2.1 billion. Multiple analysts estimated that the global market for contact lenses would reach $11.7 billion by 2015. As of 2010, the average age of contact lens wearers globally was 31 years old, and two-thirds of wearers were female.

A dioptre or diopter, symbol dpt, is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dpt = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at 1⁄3 metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams.

Keratoconus (KC) is a disorder of the eye that results in progressive thinning of the cornea. This may result in blurry vision, double vision, nearsightedness, irregular astigmatism, and light sensitivity leading to poor quality-of-life. Usually both eyes are affected. In more severe cases a scarring or a circle may be seen within the cornea.

Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead of on, the retina due to insufficient accommodation by the lens. Minor hypermetropia in young patients is usually corrected by their accommodation, without any defects in vision. But, due to this accommodative effort for distant vision, people may complain of eye strain during prolonged reading. If the hypermetropia is high, there will be defective vision for both distance and near. People may also experience accommodative dysfunction, binocular dysfunction, amblyopia, and strabismus. Newborns are almost invariably hypermetropic, but it gradually decreases as the newborn gets older.

An eyeglass prescription is an order written by an eyewear prescriber, such as an optometrist, that specifies the value of all parameters the prescriber has deemed necessary to construct and/or dispense corrective lenses appropriate for a patient. If an eye examination indicates that corrective lenses are appropriate, the prescriber generally provides the patient with an eyewear prescription at the conclusion of the exam.

An optical system with astigmatism is one where rays that propagate in two perpendicular planes have different foci. If an optical system with astigmatism is used to form an image of a cross, the vertical and horizontal lines will be in sharp focus at two different distances. The term comes from the Greek α- (a-) meaning "without" and στίγμα (stigma), "a mark, spot, puncture".

Orthokeratology, also referred to as Night lenses, Ortho-K, OK, Overnight Vision Correction, Corneal Refractive Therapy (CRT), Accelerated Orthokeretology, Cornea Corrective Contacts, Eccentricity Zero Molding, and Gentle Vision Shaping System (GVSS), is the use of gas-permeable contact lenses that temporarily reshape the cornea to reduce refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.

A spherometer is an instrument used for the precise measurement of the radius of curvature of a curved surface. Originally, these instruments were primarily used by opticians to measure the curvature of the surface of a lens.

An aspheric lens or asphere is a lens whose surface profiles are not portions of a sphere or cylinder. In photography, a lens assembly that includes an aspheric element is often called an aspherical lens.

In ophthalmology, gonioscopy is a routine procedure that measures the angle between the iris and the cornea, using a goniolens together with a slit lamp or operating microscope. Its use is important in diagnosing and monitoring various eye conditions associated with glaucoma.

Corneal topography, also known as photokeratoscopy or videokeratography, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique for mapping the anterior curvature of the cornea, the outer structure of the eye. Since the cornea is normally responsible for some 70% of the eye's refractive power, its topography is of critical importance in determining the quality of vision and corneal health.

Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often occurs at birth and can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia.

A lens clock is a mechanical dial indicator that is used to measure the dioptric power of a lens. It is a specialized version of a spherometer. A lens clock measures the curvature of a surface, but gives the result as an optical power in diopters, assuming the lens is made of a material with a particular refractive index.

A toric lens is a lens with different optical power and focal length in two orientations perpendicular to each other. One of the lens surfaces is shaped like a "cap" from a torus, and the other one is usually spherical. Such a lens behaves like a combination of a spherical lens and a cylindrical lens. Toric lenses are used primarily in eyeglasses, contact lenses and intraocular lenses to correct astigmatism.
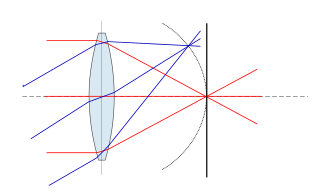
Petzval field curvature, named for Joseph Petzval, describes the optical aberration in which a flat object normal to the optical axis cannot be brought properly into focus on a flat image plane. Field curvature can be corrected with the use of a field flattener, designs can also incorporate a curved focal plane like in the case of the human eye in order to improve image quality at the focal surface.

Long-term contact lens use can lead to alterations in corneal thickness, stromal thickness, curvature, corneal sensitivity, cell density, and epithelial oxygen uptake, etc. Other changes may include the formation of epithelial vacuoles and microcysts as well as the emergence of polymegethism in the corneal endothelium. Decreased corneal sensitivity, vision loss, and photophobia have also been observed in patients who have worn contact lenses for an extended period of time. Many contact lens-induced changes in corneal structure are reversible if contact lenses are removed for an extended period of time.
The aim of an accurate intraocular lens power calculation is to provide an intraocular lens (IOL) that fits the specific needs and desires of the individual patient. The development of better instrumentation for measuring the eye's axial length (AL) and the use of more precise mathematical formulas to perform the appropriate calculations have significantly improved the accuracy with which the surgeon determines the IOL power.
Corneal ectatic disorders or corneal ectasia are a group of uncommon, noninflammatory, eye disorders characterised by bilateral thinning of the central, paracentral, or peripheral cornea.
















