Related Research Articles

PostgreSQL, also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance. It was originally named POSTGRES, referring to its origins as a successor to the Ingres database developed at the University of California, Berkeley. In 1996, the project was renamed to PostgreSQL to reflect its support for SQL. After a review in 2007, the development team decided to keep the name PostgreSQL and the alias Postgres.

File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems. It is also the component of the operating system that presents many user interface items on the screen such as the taskbar and desktop. Controlling the computer is possible without Windows Explorer running.
In the context of SQL, data definition or data description language (DDL) is a syntax for creating and modifying database objects such as tables, indices, and users. DDL statements are similar to a computer programming language for defining data structures, especially database schemas. Common examples of DDL statements include CREATE, ALTER, and DROP.
PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintain the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval.
The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records, from one or more tables.
A query string is a part of a uniform resource locator (URL) that assigns values to specified parameters. A query string commonly includes fields added to a base URL by a Web browser or other client application, for example as part of an HTML, choosing the appearance of a page, or jumping to positions in multimedia content.
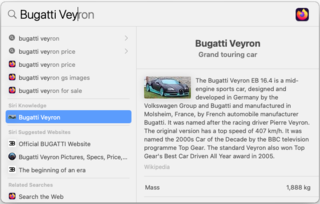
Spotlight is a system-wide desktop search feature of Apple's macOS and iOS operating systems. Spotlight is a selection-based search system, which creates an index of all items and files on the system. It is designed to allow the user to quickly locate a wide variety of items on the computer, including documents, pictures, music, applications, and System Settings. In addition, specific words in documents and in web pages in a web browser's history or bookmarks can be searched. It also allows the user to narrow down searches with creation dates, modification dates, sizes, types and other attributes. Spotlight also offers quick access to definitions from the built-in New Oxford American Dictionary and to calculator functionality. There are also command-line tools to perform functions such as Spotlight searches.
Z39.50 is an international standard client–server, application layer communications protocol for searching and retrieving information from a database over a TCP/IP computer network, developed and maintained by the Library of Congress. It is covered by ANSI/NISO standard Z39.50, and ISO standard 23950.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of relational database management systems. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are based on the stable versions without any add-ons, extensions or external programs.
In computer hypertext, a URI fragment is a string of characters that refers to a resource that is subordinate to another, primary resource. The primary resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), and the fragment identifier points to the subordinate resource.
An OpenURL is similar to a web address, but instead of referring to a physical website, it refers to an article, book, patent, or other resource within a website.
In computing, a virtual folder generally denotes an organizing principle for files that is not dependent on location in a hierarchical directory tree. Instead, it consists of software that coalesces results from a data store, which may be a database or a custom index, and presents them visually in the format in which folder views are presented. A virtual folder can be thought of as a view that lists all files tagged with a certain tag, and thus a simulation of a folder whose dynamic contents can be assembled on the fly, when requested. It is related in concept to several other topics in computer science, with names including saved search, saved query, and filtering.
Federated search retrieves information from a variety of sources via a search application built on top of one or more search engines. A user makes a single query request which is distributed to the search engines, databases or other query engines participating in the federation. The federated search then aggregates the results that are received from the search engines for presentation to the user. Federated search can be used to integrate disparate information resources within a single large organization ("enterprise") or for the entire web.
SPARQL is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description Framework (RDF) format. It was made a standard by the RDF Data Access Working Group (DAWG) of the World Wide Web Consortium, and is recognized as one of the key technologies of the semantic web. On 15 January 2008, SPARQL 1.0 was acknowledged by W3C as an official recommendation, and SPARQL 1.1 in March, 2013.
A spatial database is a general-purpose database that has been enhanced to include spatial data that represents objects defined in a geometric space, along with tools for querying and analyzing such data. Most spatial databases allow the representation of simple geometric objects such as points, lines and polygons. Some spatial databases handle more complex structures such as 3D objects, topological coverages, linear networks, and triangulated irregular networks (TINs). While typical databases have developed to manage various numeric and character types of data, such databases require additional functionality to process spatial data types efficiently, and developers have often added geometry or feature data types. The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) developed the Simple Features specification and sets standards for adding spatial functionality to database systems. The SQL/MM Spatial ISO/IEC standard is a part the SQL/MM multimedia standard and extends the Simple Features standard with data types that support circular interpolations. Almost all current relational and object-relational database management systems now have spatial extensions, and some GIS software vendors have developed their own spatial extensions to database management systems.
Language Integrated Query is a Microsoft .NET Framework component that adds native data querying capabilities to .NET languages, originally released as a major part of .NET Framework 3.5 in 2007.
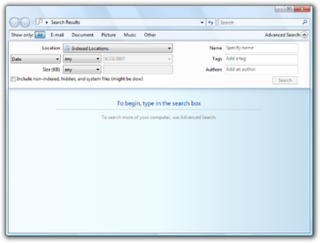
Windows Search is a content index desktop search platform by Microsoft introduced in Windows Vista as a replacement for both the previous Indexing Service of Windows 2000 and the optional MSN Desktop Search for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, designed to facilitate local and remote queries for files and non-file items in compatible applications including Windows Explorer. It was developed after the postponement of WinFS and introduced to Windows constituents originally touted as benefits of that platform.

Visual FoxPro is a Microsoft data-centric procedural programming language with object-oriented programming (OOP) features.
CUBRID ( "cube-rid") is an open-source SQL-based relational database management system (RDBMS) with object extensions developed by CUBRID Corp. for OLTP. The name CUBRID is a combination of the two words cube and bridge, cube standing for a space for data and bridge standing for data bridge.
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (HTTP) but are also used for file transfer (FTP), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications.
References
- 1 2 Lunau, Carrol; Miller, Paul; Moen, William E (June 2000). "The Bath Profile". Archived from the original on 7 January 2001. Retrieved 16 January 2023.
- 1 2 Nicolaides, Fraser (July 2003). "The Bath Profile Four Years On: What's Being Done in the UK?". Ariadne. Archived from the original on 20 September 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2023.
- ↑ "The Bath Profile for SRW, version 2.0". Zing. 6 January 2004. Archived from the original on 22 June 2004. Retrieved 16 January 2023.