Related Research Articles

In classical antiquity, Illyria was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians. Illyrians spoke the Illyrian language, an Indo-European language, which in ancient times perhaps also had speakers in some parts of Southern Italy. The geographical term Illyris was sometimes used to define approximately the area of northern and central Albania down to the Aoös valley, including in most periods much of the lakeland area. In Roman times the terms Illyria / Illyris / Illyricum were extended from the territory that was roughly located in the area of the south-eastern Adriatic coast and its hinterland, to a broader region stretching between the Adriatic Sea and the Danube, and from the upper reaches of the Adriatic down to the Ardiaei. From about mid 1st century BC the term Illyricum was used by the Romans for the province of the Empire that stretched along the eastern Adriatic coast north of the Drin river, south of which the Roman province of Macedonia began.
The Illyrians were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples, who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Greeks.

The Dardani were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society was very complex. The Dardani were the most stable and conservative ethnic element among the peoples of the central Balkans, retaining for several centuries an enduring presence in the region.
Taulantii or Taulantians were an Illyrian people that lived on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria. They dominated at various times much of the plain between the rivers Drin (Drilon) and Vjosa (Aoös). Their central area was the hinterland of Epidamnos-Dyrrhachion, corresponding to present-day Tirana and the region between the valleys of Mat and Shkumbin (Genusus). The Taulantii are among the oldest attested Illyrian peoples, who established a powerful kingdom in southern Illyria. They are among the peoples who most marked Illyrian history, and thus found their place in the numerous works of historians in classical antiquity.
Bato may refer to:
Bato the Daesitiate was a chieftain of the Daesitiates, an Illyrian tribe which fought against the Roman Empire between 6 and 9 AD in a conflict known as Bellum Batonianum.
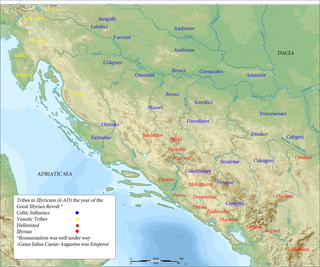
Bato the Breucian or Bato of the Breuci was the chieftain of the Breuci, an Illyrian tribe that fought against the Roman Empire in a war known as Bellum Batonianum. Bato joined his rebel forces with those led by Bato of the Daesitiates. After facing defeat, he surrendered to Tiberius in 8 CE on the bank of the Bosna river. Ultimately, Bato of the Breuci was captured by Bato of Daesitiates and was put to death after a decision was made by an assembly of the Daesitiates.

The Illyrian Kingdom is the name of a country that existed on the Western part of the Balkan Peninsula in ancient times and represented an alliance of Illyrian tribes.
The history of Illyrian warfare of the Illyrians spans from the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC up to the 1st century AD in the region of Illyria and in southern Italy where the Iapygian civilization flourished.

The Illyrian language was an Indo-European language or group of languages spoken by the Illyrians in Southeast Europe during antiquity. The language is unattested with the exception of personal names and placenames. Just enough information can be drawn from these to allow the conclusion that it belonged to the Indo-European language family.
The Dassareti were an Illyrian people that lived in the inlands of southern Illyria, between present-day south-eastern Albania and south-western North Macedonia. Their territory included the entire region between the rivers Asamus and Eordaicus, the plateau of Korça locked by the fortress of Pelion and, towards the north it extended to Lake Lychnidus up to the Black Drin. They were directly in contact with the regions of Orestis and Lynkestis of Upper Macedonia. Their chief city was Lychnidos, located on the edge of the lake of the same name.
Pinnes or Pinnetes was a Pannonian chieftain, who led a rebellion alongside Breucian chieftain Bato until Bato betrayed him and handed him over to the Romans, thus securing the rule over the Breuci.
The Enchelii, the inhabitants of Enchele, were an ancient people that lived around the region of Lake Shkodra and Lake Ohrid, in modern-day Albania and North Macedonia. They are one of the oldest known peoples of the eastern shore of the Adriatic. In ancient sources they sometimes appear as an ethnic group distinct from the Illyrians, but are mostly mentioned as one of the Illyrian tribes.

The Illyrians were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples, who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Greeks.
This article contains information about Illyrian vocabulary. No Illyrian texts survive, so sources for identifying Illyrian words have been identified by Hans Krahe as being of four kinds: inscriptions, glosses of Illyrian words in classical texts, names—including proper names, toponyms and river names—and Illyrian loanwords in other languages. The last category has proven particularly contentious. The names occur in sources that range over more than a millennium, including numismatic evidence, as well as posited original forms of placenames. The Messapian language, which may or may not be related, does have a small attested corpus, but it is not in this page's scope due to the uncertainty about its relationship to Illyrian.
Arduba was a settlement of the Illyrian tribe of the Daesitiates in Illyria. Following the Roman invasion, the settlement was included in the Roman province of Dalmatia. Arduba was located somewhere near the modern city of Zenica in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Most probably the royal city of Vranduk existed in the time of the Illyrians, under the name Arduba.
The Abroi were an Illyrian tribe. They may have been a constituent northern tribe of the larger group of the Taulantii, on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria.

Illyrii proprie dicti or Illyrians proper were a group of ancient illyrian tribes. Ancient Roman writer Pliny the Elder and Pomponius Mela used the term Illyrii proprie dicti to designate a people that was located in the coast of modern Albania and Montenegro.
References
- ↑ Katičić 1995, pp. 127–133.